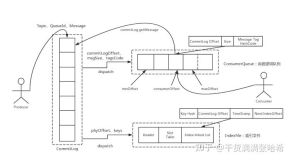
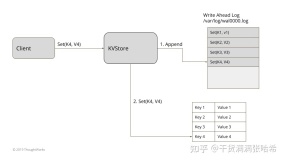
RocketMQ 将消息存储在 Commitlog 文件后,异步更新 ConsumeQueue 还有 Index 文件。这个 ConsumeQueue 还有 Index 文件可以理解为存储状态,CommitLog 在这里扮演的就是 WAL 日志的角色:只有写入到 ConsumeQueue 的消息才会被消费者消费,只有 Index 文件中存在的记录才能被读取定位到。如果消息成功写入 CommitLog 但是异步更新还没执行,RocketMQ 进程挂掉了,这样就存在了不一致。所以在 RocketMQ 启动的时候,会通过如下机制保证 Commitlog 与 ConsumeQueue 还有 Index 的最终一致性.
入口是DefaultMessageStore的load方法:
public boolean load() { boolean result = true; try { //RocketMQ Broker启动时会创建${ROCKET_HOME}/store/abort文件,并添加JVM shutdownhook删除这个文件 //通过这个文件是否存判断是否为正常退出 boolean lastExitOK = !this.isTempFileExist(); log.info("last shutdown {}", lastExitOK ? "normally" : "abnormally"); //加载延迟队列消息,这里先忽略 if (null != scheduleMessageService) { result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load(); } //加载 Commit Log 文件 result = result && this.commitLog.load(); //加载 Consume Queue 文件 result = result && this.loadConsumeQueue(); if (result) { //加载存储检查点 this.storeCheckpoint = new StoreCheckpoint(StorePathConfigHelper.getStoreCheckpoint(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir())); //加载 index,如果不是正常退出,销毁所有索引上次刷盘时间小于索引文件最大消息时间戳的文件 this.indexService.load(lastExitOK); //进行 recover 恢复之前状态 this.recover(lastExitOK); log.info("load over, and the max phy offset = {}", this.getMaxPhyOffset()); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("load exception", e); result = false; } if (!result) { this.allocateMappedFileService.shutdown(); } return result; }
进行恢复是DefaultMessageStore的recover方法:
private void recover(final boolean lastExitOK) { long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue = this.recoverConsumeQueue(); //根据上次是否正常退出,采用不同的恢复方式 if (lastExitOK) { this.commitLog.recoverNormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue); } else { this.commitLog.recoverAbnormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue); } this.recoverTopicQueueTable(); }
当上次正常退出时:
public void recoverNormally(long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue) { boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover(); final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles(); if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) { //只扫描最后三个文件 int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3; if (index < 0) index = 0; MappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer(); long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); long mappedFileOffset = 0; while (true) { //检验存储消息是否有效 DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover); int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize(); //如果有效,添加这个偏移 if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size > 0) { mappedFileOffset += size; } //如果有效,但是大小是0,代表到了文件末尾,切换文件 else if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size == 0) { index++; if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) { // Current branch can not happen log.info("recover last 3 physics file over, last mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName()); break; } else { mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer(); processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); mappedFileOffset = 0; log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName()); } } //只有有无效的消息,就在这里停止,之后会丢弃掉这个消息之后的所有内容 else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) { log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName()); break; } } processOffset += mappedFileOffset; this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset); this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset); //根据有效偏移量,删除这个偏移量以后的所有文件,以及所有文件(正常是只有最后一个有效文件,而不是所有文件)中大于这个偏移量的部分 this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset); //根据 commit log 中的有效偏移量,清理 consume queue if (maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue >= processOffset) { log.warn("maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue({}) >= processOffset({}), truncate dirty logic files", maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue, processOffset); this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset); } } else { //所有commit log都删除了,那么偏移量就从0开始 log.warn("The commitlog files are deleted, and delete the consume queue files"); this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(0); this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(0); this.defaultMessageStore.destroyLogics(); } }
当上次没有正常退出时:
public void recoverAbnormally(long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue) { boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover(); final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles(); if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) { // 从最后一个文件开始,向前寻找第一个正常的可以恢复消息的文件 // 从这个文件开始恢复消息,因为里面的消息有成功写入过 consumer queue 以及 index 的,所以从这里恢复一定能保证最终一致性 // 但是会造成某些已经写入过 consumer queue 的消息再次写入,也就是重复消费。 int index = mappedFiles.size() - 1; MappedFile mappedFile = null; for (; index >= 0; index--) { mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); //寻找第一个有正常消息的文件 if (this.isMappedFileMatchedRecover(mappedFile)) { log.info("recover from this mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName()); break; } } //如果小于0,就恢复所有 commit log,或者代表没有 commit log if (index < 0) { index = 0; mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); } ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer(); long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); long mappedFileOffset = 0; while (true) { //验证消息有效性 DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover); int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize(); //如果消息有效 if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) { if (size > 0) { mappedFileOffset += size; if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isDuplicationEnable()) { //如果允许消息重复转发,则需要判断当前消息是否消息偏移小于已确认的偏移,只有小于的进行重新分发 if (dispatchRequest.getCommitLogOffset() < this.defaultMessageStore.getConfirmOffset()) { //重新分发消息,也就是更新 consume queue 和 index this.defaultMessageStore.doDispatch(dispatchRequest); } } else { //重新分发消息,也就是更新 consume queue 和 index this.defaultMessageStore.doDispatch(dispatchRequest); } } //大小为0代表已经读完,切换下一个文件 else if (size == 0) { index++; if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) { // The current branch under normal circumstances should // not happen log.info("recover physics file over, last mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName()); break; } else { mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer(); processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); mappedFileOffset = 0; log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName()); } } } else { log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " pos=" + byteBuffer.position()); break; } } //更新偏移 processOffset += mappedFileOffset; this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset); this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset); this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset); //清理 if (maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue >= processOffset) { log.warn("maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue({}) >= processOffset({}), truncate dirty logic files", maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue, processOffset); this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset); } } // Commitlog case files are deleted else { log.warn("The commitlog files are deleted, and delete the consume queue files"); this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(0); this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(0); this.defaultMessageStore.destroyLogics(); } }
总结起来就是:
- 首先,根据 abort 文件是否存在判断上次是否正常退出。
- 对于正常退出的:
- 扫描倒数三个文件,记录有效消息的偏移
- 扫描到某个无效消息结束,或者扫描完整个文件
- 设置最新偏移,同时根据这个偏移量清理 commit log 和 consume queue
- 对于没有正常退出的:
- 从最后一个文件开始,向前寻找第一个正常的可以恢复消息的文件
- 从这个文件开始恢复并重发消息,因为里面的消息有成功写入过 consumer queue 以及 index 的,所以从这里恢复一定能保证最终一致性。但是会造成某些已经写入过 consumer queue 的消息再次写入,也就是重复消费。
- 更新偏移,清理
数据库
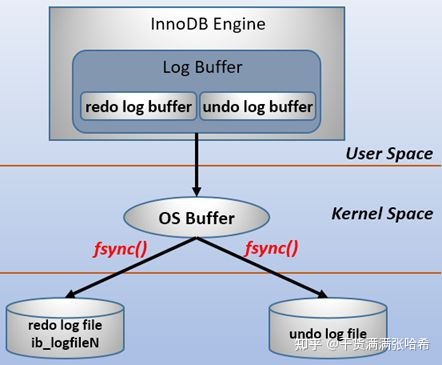
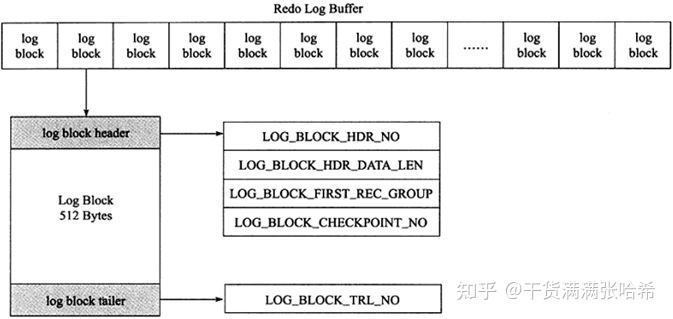
基本上所有的数据库都会有 WAL 类似的设计,例如 MySQL 的 Innodb redo log 等等。
一致性存储
例如 ZK 还有 ETCD 这样的一致性中间件。