💥1 概述
变分模态分解(VMD)是近年来引入的一种自适应数据分析方法,在各个领域引起了广泛的关注。然而,VMD是基于信号模型窄带特性的假设而制定的。为了分析宽带非线性线性调频信号(NCS),我们提出了一种称为变分非线性线性调频模式分解(VNCMD)的替代方法。VNCMD的开发基于这样一个事实,即宽带NCS可以通过使用解调技术转换为窄带信号。因此,我们的分解问题被表述为最优解调问题,通过乘法的交替方向方法(ADMM)有效地求解。我们的方法可以看作是一个时频(TF)滤波器组,它同时提取所有信号模式。提供了一些模拟和真实的数据示例,展示了VNCMD在分析包含接近甚至交叉模式的NCS方面的有效性。
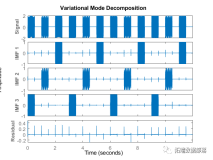
📚2 运行结果
2.1 算例1
2.2 算例2
2.3 算例3
部分代码:
%% initialize [K,N] = size(eIF);%K is the number of the components,N is thenumber of the samples t = (0:N-1)/fs;%time e = ones(N,1); e2 = -2*e; % e2(1) = -1;e2(end) = -1; oper = spdiags([e e2 e], 0:2, N-2, N);% oper = spdiags([e e2 e], -1:1, N, N);%the modified second-order difference matrix opedoub = oper'*oper;% sinm = zeros(K,N);cosm = zeros(K,N);% xm = zeros(K,N);ym = zeros(K,N);%denote the two demodulated quadrature signals iternum = 300; %the maximum allowable iterations IFsetiter = zeros(K,N,iternum+1); IFsetiter(:,:,1) = eIF; %the collection of the obtained IF time series of all the signal modes at each iteration ssetiter = zeros(K,N,iternum+1); %the collection of the obtained signal modes at each iteration lamuda = zeros(1,N);%Lagrangian multiplier for i = 1:K sinm(i,:) = sin(2*pi*(cumtrapz(t,eIF(i,:)))); cosm(i,:) = cos(2*pi*(cumtrapz(t,eIF(i,:)))); Bm = spdiags(sinm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Bdoubm = spdiags((sinm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N);%Bdoubm = Bm'*Bm Am = spdiags(cosm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Adoubm = spdiags((cosm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N);%Adoubm = Am'*Am xm(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Adoubm)\(Am'*s(:)); ym(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Bdoubm)\(Bm'*s(:)); ssetiter(i,:,1) = xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:) + ym(i,:).*sinm(i,:);% end %% iterations iter = 1;% iteration counter sDif = tol + 1;% sum_x = sum(xm.*cosm,1);%cumulative sum sum_y = sum(ym.*sinm,1);%cumulative sum while ( sDif > tol && iter <= iternum ) % betathr = 10^(iter/36-10);%gradually increase the parameter beta during the iterations if betathr>beta betathr = beta; end u = projec(s - sum_x - sum_y - lamuda/alpha,var);%projection operation; u denotes the noise variable; if let var=0, the output u will be zeros. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% update each mode %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% for i = 1:K % lamuda = zeros(1,N);% if one wants to drop the Lagrangian multiplier, just set it to zeros, i.e., delete the first symbol % in this line. %%%%%%%%%%%%% update the two matrices A and B %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Bm = spdiags(sinm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Bdoubm = spdiags((sinm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N); Am = spdiags(cosm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Adoubm = spdiags((cosm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N); %%%%%%%%%%%%% x-update %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% sum_x = sum_x - xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:);% remove the relevant component from the sum xm(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Adoubm)\(Am'* (s - sum_x - sum_y - u - lamuda/alpha)');% interx = xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:);% temp variable sum_x = sum_x + interx;% update the sum %%%%%%%%%%%%% y-update %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% sum_y = sum_y - ym(i,:).*sinm(i,:);% remove the relevant component from the sum ym(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Bdoubm)\(Bm'* (s - sum_x - sum_y - u - lamuda/alpha)'); %%%%%%%%%%%%% update the IFs %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% ybar = Differ(ym(i,:),1/fs); xbar = Differ(xm(i,:),1/fs);%compute the derivative of the functions deltaIF = (xm(i,:).*ybar - ym(i,:).*xbar)./(xm(i,:).^2 + ym(i,:).^2)/2/pi;% obtain the frequency increment by arctangent demodulation deltaIF = (2/betathr*opedoub + speye(N))\deltaIF';% smooth the frequency increment by low pass filtering eIF(i,:) = eIF(i,:) - 0.5*deltaIF';% update the IF %%%%%%%%%%%%% update cos and sin functions %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% sinm(i,:) = sin(2*pi*(cumtrapz(t,eIF(i,:)))); cosm(i,:) = cos(2*pi*(cumtrapz(t,eIF(i,:)))); %%%%%%%%%%%%% update sums %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% sum_x = sum_x - interx + xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:); % sum_y = sum_y + ym(i,:).*sinm(i,:);% ssetiter(i,:,iter+1) = xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:) + ym(i,:).*sinm(i,:);% end IFsetiter(:,:,iter+1) = eIF; %%%%%%%%%%%%% update Lagrangian multiplier %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% lamuda = lamuda + alpha*(u + sum_x + sum_y -s); %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% restart scheme %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% if norm(u + sum_x + sum_y -s)>norm(s) % lamuda = zeros(1,length(t)); for i = 1:K Bm = spdiags(sinm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Bdoubm = spdiags((sinm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N);% Am = spdiags(cosm(i,:)', 0, N, N);Adoubm = spdiags((cosm(i,:).^2)', 0, N, N);% xm(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Adoubm)\(Am'*s(:)); ym(i,:) = (2/alpha*opedoub + Bdoubm)\(Bm'*s(:)); ssetiter(i,:,iter+1) = xm(i,:).*cosm(i,:) + ym(i,:).*sinm(i,:); end sum_x = sum(xm.*cosm,1);% sum_y = sum(ym.*sinm,1);% end %%%%%%%%%%%%% compute the convergence index %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% sDif = 0; for i = 1:K sDif = sDif + (norm(ssetiter(i,:,iter+1) - ssetiter(i,:,iter))/norm(ssetiter(i,:,iter))).^2; end iter = iter + 1; end IFmset = IFsetiter(:,:,1:iter); smset = ssetiter(:,:,1:iter); IA = sqrt(xm.^2 + ym.^2); end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]Chen S, Dong X, Peng Z, et al, Nonlinear Chirp Mode Decomposition: A Variational Method, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017.
[2]Chen S, Dong X, Xing G, et al, Separation of Overlapped Non-Stationary Signals by Ridge Path Regrouping and Intrinsic Chirp Component Decomposition, IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017.
[3]S. Chen, Z. Peng, Y. Yang, et al, Intrinsic chirp component decomposition by using Fourier Series representation, Signal Processing, 2017, 137: 319-327.