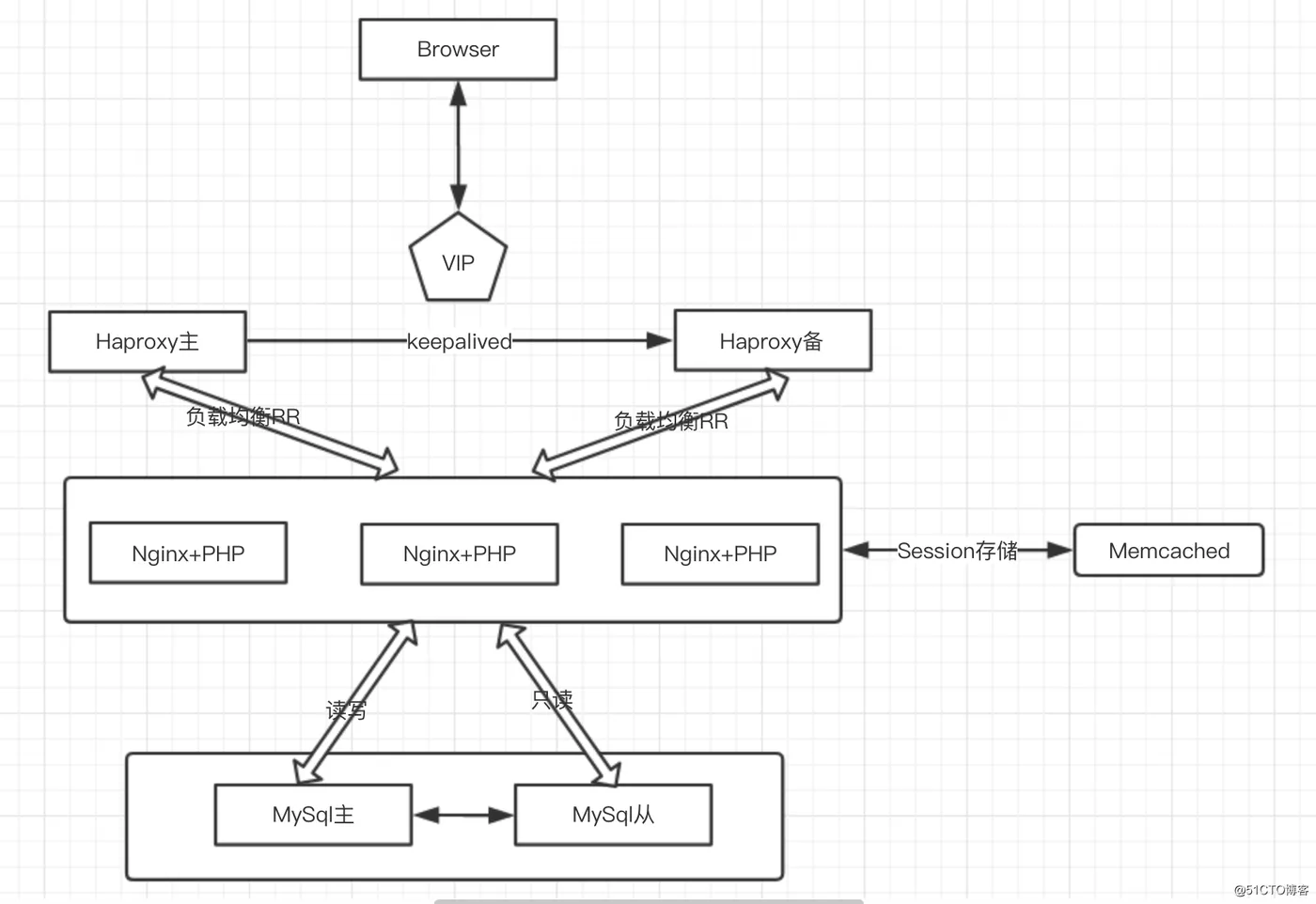
本章主要介绍通过saltstack构建系统高可用架构,以满足业务需求。通过Haproxy实现负载均衡调度后端Nginx+PHP服务器,Keepalived实现系统高可用功能,Memcached存储session会话,后端数据库采用Mysql并且实现主从复制以及读写分离。
一、拓扑图
一、系统架构图
二、saltstack分层管理图
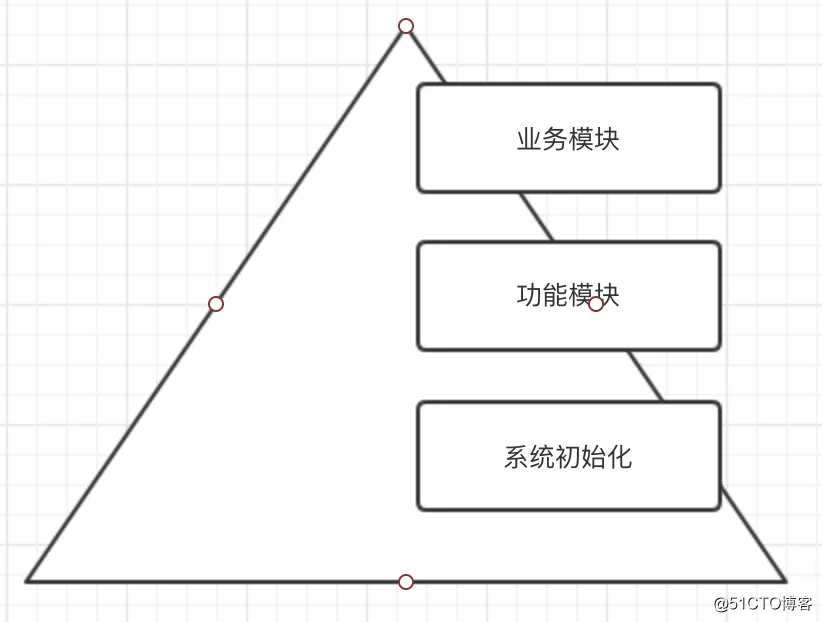
我们通过saltstack实现的整个系统环境可以分为三部分:
系统初始化:用于设定节点状态,如dns、history命令记录、系统内核参数设定等。
功能模块:用于整个系统的功能实现,如Nginx、Mysql、Haproxy、keepalived的安装和脚本文件配置下发等。
业务模块:用于引用一些差异型功能,如hapzory或keeplaived的配置文件下发,每个节点的配置参数是不一样的,我们称之为业务模块。
之所以将功能模块和业务模块分开来做这样的好处在于:
如haproxy的安装以及负载均衡配置的实现之所以分开来做,这样的好处在于随着节点数量不断的增加,差异性不断的扩大。我们安装都引用相同的安装脚本,但是每个节点的参数配置是不相同的,因此我们在业务模块上进行每个节点不同参数的实现。
实验环境:
| IP地址 | Saltstack角色 | 业务角色 | 主机名 | 系统环境 |
| 192.168.39.135 | master | Saltstack-server | centos | CentOS release 6.7 (Final) |
| 192.168.39.200 | minion | Haproxy、keealived | centos-test1 |
CentOS release 6.7 (Final) |
| 192.168.39.201 | minion | Haproxy、keealived | centos-test2 | CentOS release 6.7 (Final) |
| 192.168.39.202 | minion | Nginx+PHP、Mysql |
centos-test3 | CentOS release 6.7 (Final) |
| 192.168.39.203 | minion | Nginx+PHP、Mysql 、Memcached | centos-test4 | CentOS release 6.7 (Final) |
Saltstack的安装、配置、授权等可参考:http://blog.51cto.com/bovin/1984115
二、Salt-Minion端环境配置
一、系统初始化
我们将系统的每个节点都进行一定的系统初始化设定,如dns、history命令记录、系统内核参数设定等。首先,进入salt的base环境,我们所有的系统设定都在此环境下进行设定。
|
1
|
[root@centos files]
# cd /srv/salt/base/
|
创建init目录,用于系统的整个初始化相关设定。
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# mkdir init
|
配置各个节点dns解析:
|
1
|
[root@centos init]
# vim dns.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
/etc/resolv
.conf:
file
.managed:
-
source
: salt:
//init/files/resolv
.conf
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
- template: jinja
- defaults:
DNS_SERVER: 192.168.39.23
|
files下resolv.conf文件内容为:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos init]
# cat files/resolv.conf
# Generated by NetworkManager
nameserver {{ DNS_SERVER }}
|
使各个节点history命令都记录时间:
|
1
|
[root@centos init]
# vim history.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
/etc/profile
:
file
.append:
- text:
-
export
HISTTIMEFORMAT=
"%F %T `whoami`"
|
注:file模块通过append追加方式写入环境变量中
审计sls文件,将每个用户的命令都记录到/var/log/message文件中:
|
1
|
[root@centos init]
# vim audit.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
/etc/bashrc
:
file
.append:
- text:
-
export
PROMPT_COMMAND=
'{ msg=$(history 1 | { read x y; echo $y; }); logger "[euid=$(whoami)]":$(who am i):[`pwd`]"$msg";}'
|
对节点的系统内核参数设定:
|
1
|
[root@centos init]
# vim sysctl.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
vm.swappiness:
sysctl.present:
- value: 0
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range:
sysctl.present:
- value: 10000 65000
fs.
file
-max:
sysctl.present:
- value: 100000
|
引导以上各个功能模块:
|
1
|
[root@centos init]
# vim env_init.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
include:
- init.dns
- init.
history
- init.audit
- init.sysctl
|
注:通过include进行模块引用
编写top file文件:
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls
|
|
1
2
3
|
base:
'*'
:
- init.env_init
|
注:base环境下,init目录查找env_init文件
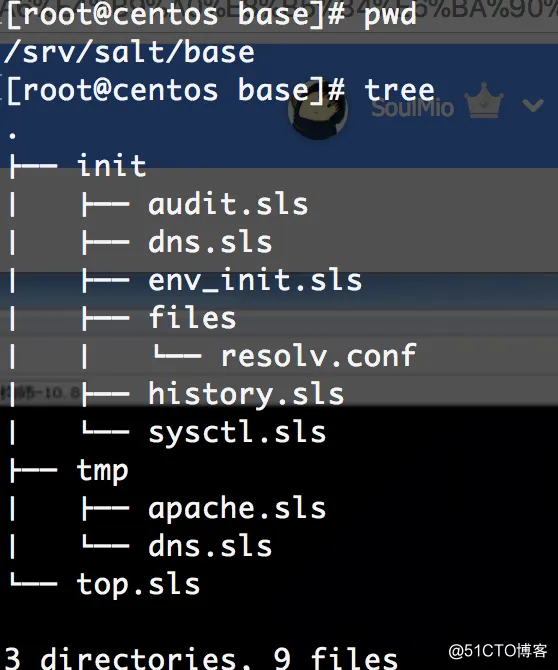
目录文件结构,如下:
在执行时我们可以通过指定参数,模拟执行:
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# salt '*' state.highstate test=True
|
注:test=True模拟执行方式
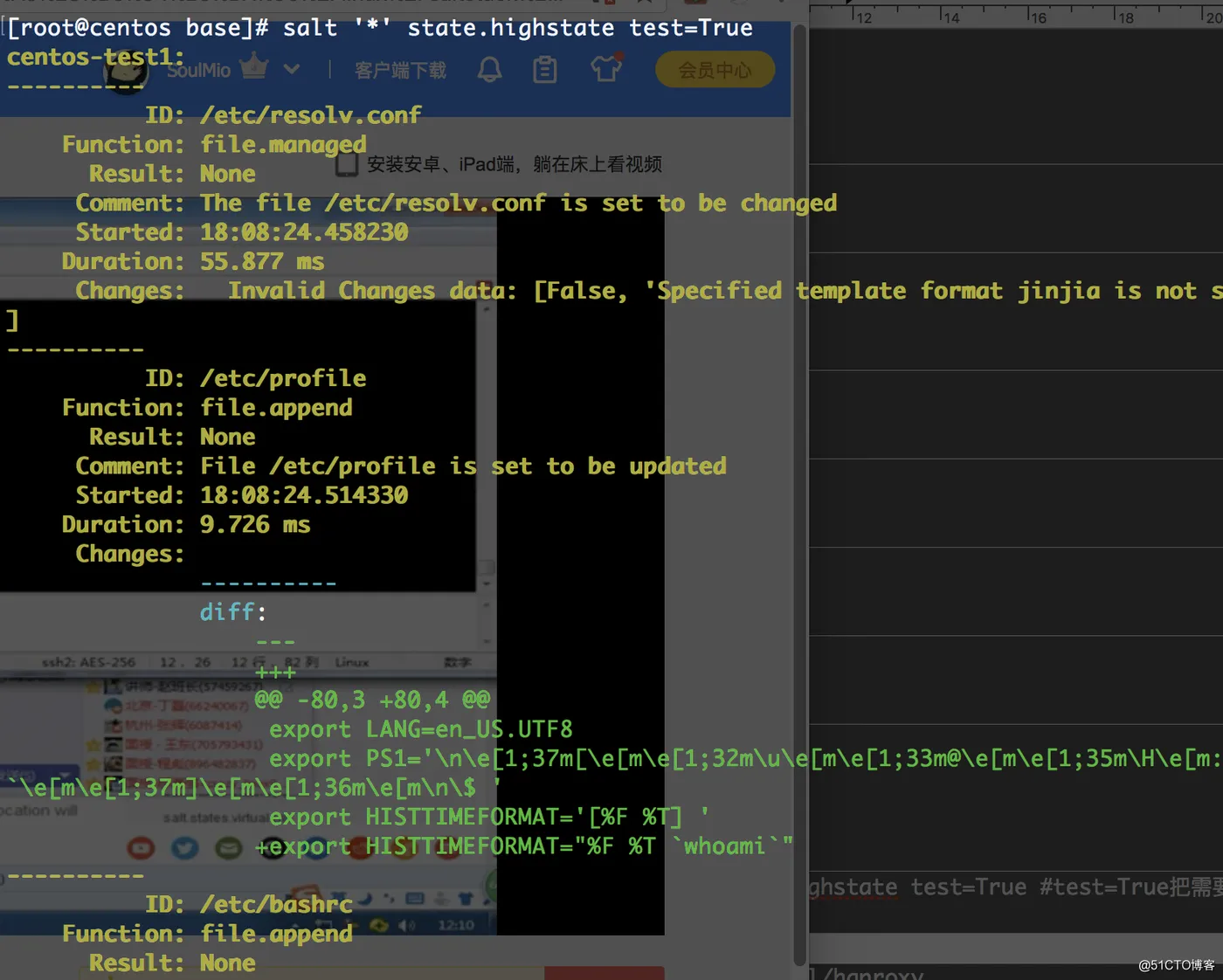
模拟执行完没有报错,我们可以放心去设定节点初始化环境了:
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# salt '*' state.highstate
|
三、前端高可用
根据整个系统架构图,我们可以分为两大部分来完成。前端高可用和后端上线服务,前端高可用主要包括haproxy和keepalived安装及配置。后端线上服务包括nginx、php、memcache、mysql的安装及配置。以下是haproxy和keepalived安装和配置。
一、功能模块之haproxy安装
功能模块分为:前端调度Haproxy,后端Nginx+PHP,数据库Mysql以及会话存储Memcached。以下是saltstack实现功能模块Haproxy的实例安装:
创建Haproxy模块的文件目录:
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/pkg/
|
注:pkg目录用于存放软件安装包
|
1
2
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/haproxy
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/haproxy/files
|
注:haproxy目录用于存放haroxy的安装脚本和文件
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# cd /srv/salt/prod/pkg/
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@centos pkg]
# vim pkg-init.sls
pkg-init:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- gcc
- gcc-c++
- glibc
-
make
- autoconf
- openssl
- openssl-devel
|
注:pkg-init.sls用解决源码安装所需要的相关依赖
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# cd /srv/salt/prod/haproxy
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
[root@centos haproxy]
# vim install.sls
include:
#include haproxy源码包
- pkg.pkg-init
haproxy-
install
:
#安装haproxy 包括两个步骤:管理文件、执行cmd.run
file
.managed:
- name:
/usr/local/src/haproxy-1
.6.2.
tar
.gz
-
source
: salt:
//haproxy/files/haproxy-1
.6.2.
tar
.gz
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name:
cd
/usr/local/src/
&&
tar
-zxf haproxy-1.6.2.
tar
.gz &&
cd
haproxy-1.6.2 &&
make
TARGET=linux26 PREFIX=
/usr/local/haproxy
&&
make
install
PREFIX=
/usr/local/haproxy
- unless:
test
-d
/usr/local/haproxy
#判断haproxy目录是否存在,如果存在不在继续安装
- require:
#执行完cmd.run后,如果执行成功,则继续。否则,不执行以下。
- pkg: pkg-init
-
file
: haproxy-
install
haproxy-init:
#定义haproxy-init,包括:拷贝haproxy启动脚本到相关路径下、添加系统服务
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/init
.d
/haproxy
-
source
: salt:
//haproxy/files/haproxy
.init
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
- require:
- cmd: haproxy-
install
cmd.run:
- name: chkconfig --add haproxy
- unless: chkconfig --list |
grep
haproxy
#如果有chkconfg .. 命令 不在执行name
- require:
-
file
: haproxy-init
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind:
#监听本地ip
sysctl.present:
- value: 1
haproxy-config-
dir
:
#创建haproxy的目录
file
.directory:
- name:
/etc/haproxy
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
|
注:salt文件相关参数介绍:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
功能名称:requisites
功 能:处理状态间关系
常用方法:
require
#依赖某个状态
require_in
#被某个状态依赖
watch
#关注某个状态
watch_in
#被某个状态关注
状态模块:状态间关系
功 能:条件判断,主要用于cmd状态模块
常用方法:
-onlyif:检查的命令,仅当“onlyif”选项指向的命令返回
true
时才执行name定义的命令。
-unless;用于检查的命令,仅当“unless”选项指向的命令返回
false
时才执行name指向的命令。
|
目录结构,如下:
执行安装haproxy:
|
1
|
[root@centos haproxy]
# salt 'centos-test[1-2]' state.sls haproxy.install env=prod
|
注:env=prod 指定prod目录下执行,如果不加此参数会默认从base环境下执行sls文件
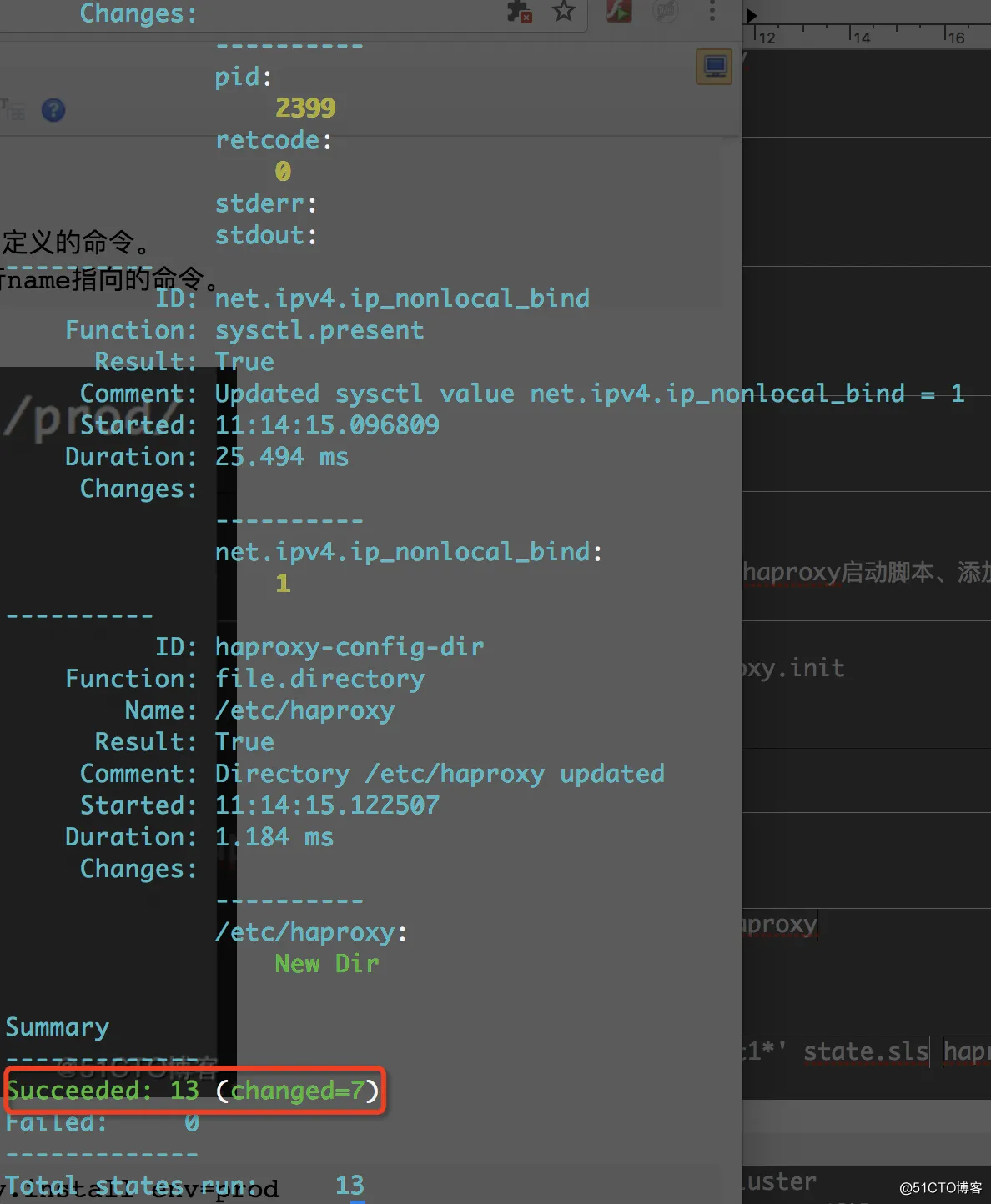
可以看到执行haproxy安装成功了。
二、业务引用之Haproxy负载均衡的实现
Haproxy的安装我们选择源码包进行安装,我们通过文件管理模块进行haproxy的文件配置管理,需要将两个节点配置为负载均衡模式。
创建业务引用相关目录:
业务引用我们都是在cluster目录下进行。
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/cluster #用于存放集群相关文件
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/cluster/files
[root@centos prod]
# cd /srv/salt/prod/cluster/files/ #切换到此目录下创建salt文件
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
[root@centos files]
# vim haproxy-outside.cfg #外网负载均衡配置文件
global
maxconn 100000
chroot
/usr/local/haproxy
uid 99
gid 99
daemon
nbproc 1
pidfile
/usr/local/haproxy/logs/haproxy
.pid
log 127.0.0.1 local3 info
#默认参数设置
defaults
option http-keep-alive
maxconn 100000
mode http
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
#开启Haproxy Status状态监控,增加验证
listen stats
mode http
bind 0.0.0.0:8888
stats
enable
stats uri
/haproxy-status
stats auth haproxy:saltstack
#前端设置
frontend frontend_www_example_com
#bind 10.0.0.11:80
bind 192.168.39.100:80
mode http
option httplog
log global
default_backend backend_www_example_com
#后端设置
backend backend_www_example_com
option forwardfor header X-REAL-IP
option httpchk HEAD / HTTP
/1
.0
#balance source如果想要轮训则改为roundrobin
balance
source
server web-node1 192.168.39.202:8080 check inter 2000 rise 30 fall 15
server web-node2 192.168.39.203:8080 check inter 2000 rise 30 fall 15
|
编写haproxy的salt文件:
salt文件主要涉及到haproxy的安装引用、对配置文件的下发、haproxy的服务启动等功能。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@centos cluster]
# vim haproxy-outside.sls
include:
#include haproxy的安装文件
- haproxy.
install
haproxy-service:
file
.managed:
#将source执行的haproxy配置文件,存放到name指定路径下
- name:
/etc/haproxy/haproxy
.cfg
-
source
: salt:
//cluster/files/haproxy-outside
.cfg
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
service.running:
#启动haproxy服务
- name: haproxy
-
enable
: True
- reload: True
#允许reload服务
- require:
- cmd: haproxy-init
#引用haproxy目录下install文件中的haproxy-init标签
-
watch
:
#通过watch状态监控,如果配置文件发生改变 就reload
-
file
: haproxy-service
#haproxy-servcie标签下的file模块
|
注:此文件依赖于haproxy目录下的install.sls文件。
现在,可以编写top file文件,让其两个haproxy节点能够正常运行服务:
|
1
|
[root@centos cluster]
# cd /srv/salt/base/
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[root@centos base]
# vim top.sls
base:
'*'
:
- init.env_init
prod:
'centos-test1'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
'centos-test2'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
|
编写完top file文件可以,执行高级模式来执行salt文件:
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# salt '*' state.highstate
|
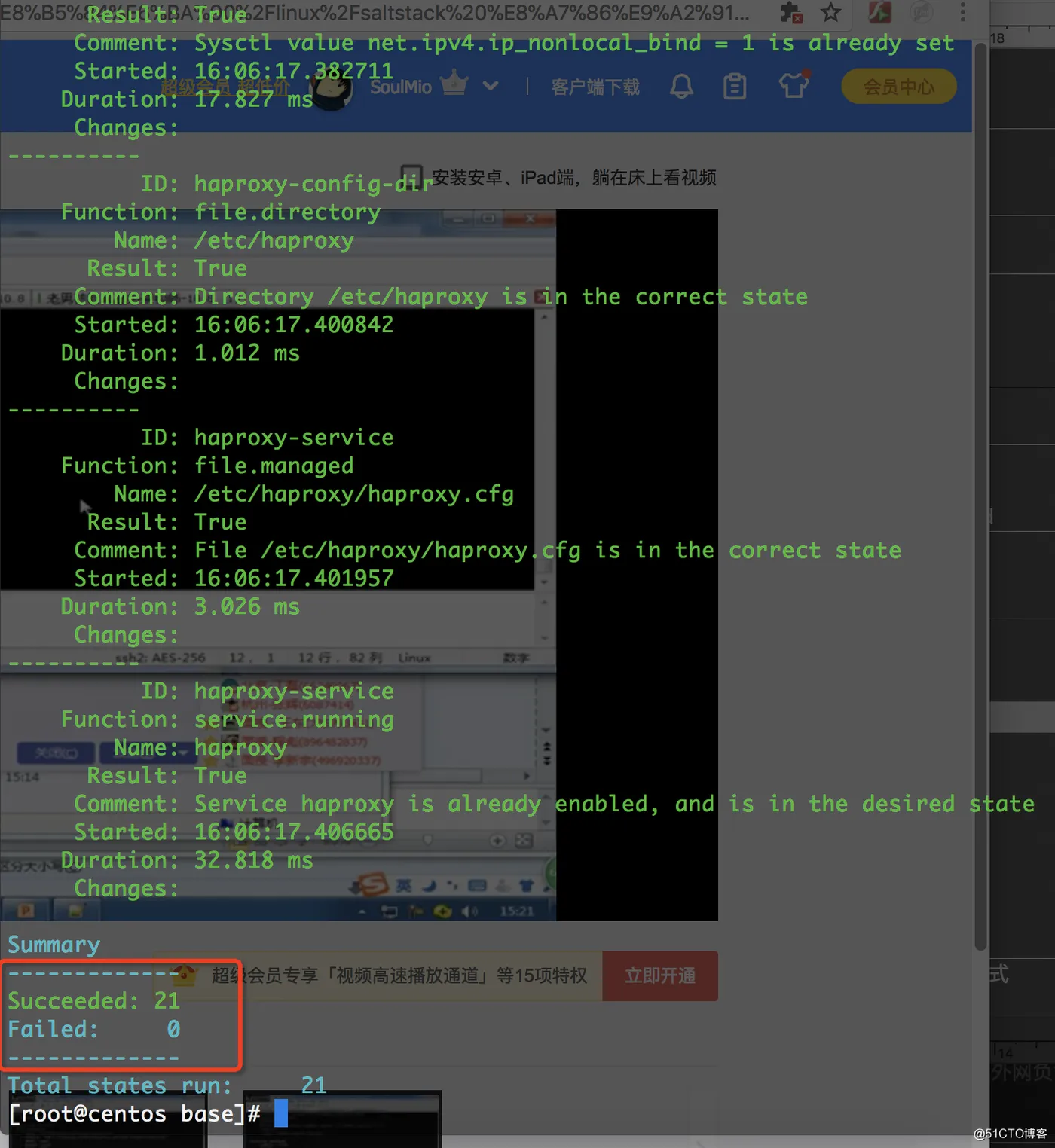
可以看到已经执行成功,成功21项状态。
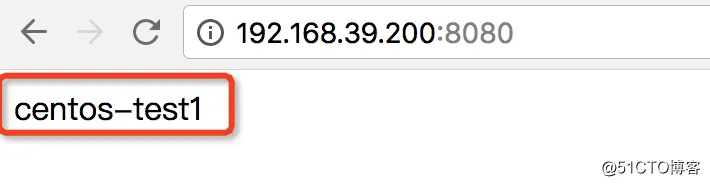
现在,我们可以通过浏览器访问haproxy管理界面:
 在这里由于/var/www/html没有页面信息,健康检查会显示异常,所以需要在两个节点上创建html文件信息。
在这里由于/var/www/html没有页面信息,健康检查会显示异常,所以需要在两个节点上创建html文件信息。
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@centos-test1:
/root
]
# echo ‘centos-test1’ > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@centos-test2:
/root
]
# echo ‘centos-test2’ > /var/www/html/index.html
|
三、功能模块之keepalived的安装
在keepalived安装之前,我们首先需要准备keepalived的安装包、启动脚本以及配置文件等。我们需要将所有的这些东西都放到keepalived/files目录下。
创建keepalived的相关目录:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos etc]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/keepalived
[root@centos etc]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/keepalived/files
|
拷贝keepalived的相关文件:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos etc]
# cp init.d/keepalived.init /srv/salt/prod/keepalived/files/
[root@centos etc]
# cp keepalived/keepalived.conf /srv/salt/prod/keepalived/files/
|
keepalived.init-keepalived的启动脚本
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
#!/bin/sh
#
# Startup script for the Keepalived daemon
#
# processname: keepalived
# pidfile: /var/run/keepalived.pid
# config: /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
# chkconfig: - 21 79
# description: Start and stop Keepalived
# Source function library
.
/etc/rc
.d
/init
.d
/functions
# Source configuration file (we set KEEPALIVED_OPTIONS there)
.
/etc/sysconfig/keepalived
RETVAL=0
prog=
"keepalived"
start() {
echo
-n $
"Starting $prog: "
daemon
/usr/local/keepalived/sbin/keepalived
${KEEPALIVED_OPTIONS}
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -
eq
0 ] &&
touch
/var/lock/subsys/
$prog
}
stop() {
echo
-n $
"Stopping $prog: "
killproc keepalived
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -
eq
0 ] &&
rm
-f
/var/lock/subsys/
$prog
}
reload() {
echo
-n $
"Reloading $prog: "
killproc keepalived -1
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
# See how we were called.
case
"$1"
in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
reload)
reload
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
condrestart)
if
[ -f
/var/lock/subsys/
$prog ];
then
stop
start
fi
;;
status)
status keepalived
RETVAL=$?
;;
*)
echo
"Usage: $0 {start|stop|reload|restart|condrestart|status}"
RETVAL=1
esac
exit
$RETVAL
|
keepalived.conf-keepalived的配置文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
|
! Configuration File
for
keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.200.16
192.168.200.17
192.168.200.18
}
}
virtual_server 192.168.200.100 443 {
delay_loop 6
lb_algo rr
lb_kind NAT
nat_mask 255.255.255.0
persistence_timeout 50
protocol TCP
real_server 192.168.201.100 443 {
weight 1
SSL_GET {
url {
path /
digest ff20ad2481f97b1754ef3e12ecd3a9cc
}
url {
path
/mrtg/
digest 9b3a0c85a887a256d6939da88aabd8cd
}
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
}
virtual_server 10.10.10.2 1358 {
delay_loop 6
lb_algo rr
lb_kind NAT
persistence_timeout 50
protocol TCP
sorry_server 192.168.200.200 1358
real_server 192.168.200.2 1358 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path
/testurl/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl2/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl3/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
real_server 192.168.200.3 1358 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path
/testurl/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334c
}
url {
path
/testurl2/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334c
}
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
}
virtual_server 10.10.10.3 1358 {
delay_loop 3
lb_algo rr
lb_kind NAT
nat_mask 255.255.255.0
persistence_timeout 50
protocol TCP
real_server 192.168.200.4 1358 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path
/testurl/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl2/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl3/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
real_server 192.168.200.5 1358 {
weight 1
HTTP_GET {
url {
path
/testurl/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl2/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
url {
path
/testurl3/test
.jsp
digest 640205b7b0fc66c1ea91c463fac6334d
}
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@centos keepalived]
# cd /usr/local/keepalived/etc/sysconfig/
[root@centos sysconfig]
# ls
keepalived
[root@centos sysconfig]
# cp keepalived /srv/salt/prod/keepalived/files/keepalived.sysconfig
|
现在,我们查看files目录都有哪些东西:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos keepalived]
# ls files/
keepalived-1.2.19.
tar
.gz keepalived.init
keepalived.conf keepalived.sysconfig
|
准备好keepalived的相关文件之后,现在我们可以编写salt文件:
salt文件主要涉及到pkg-init脚本的引用,此脚本主要是解决安装前的依赖;keepalived-install标签用于安装keepalived;keepalived-init标签用于下发启动脚本以及将服务加入到系统启动中;/etc/sysconfg/keepalived标签用于下发配置文件到各个节点上。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
[root@centos keepalived]
# vim install.sls
include:
#引用pkg目录下pkg-init脚本
- pkg.pkg-init
keepalived-
install
:
file
.managed:
#file模块来拷贝keepalived的安装包
- name:
/usr/local/src/keepalived-1
.2.19.
tar
.gz
-
source
: salt:
//keepalived/files/keepalived-1
.2.19.
tar
.gz
- usr: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
#cmd模块的- name函数来执行具体安装命令
- name:
cd
/usr/local/src
&&
tar
-zxf keepalived-1.2.19.
tar
.gz &&
cd
keepalived-1.2.19 && .
/configure
--prefix=
/usr/local/keepalived
--disable-fwmark &&
make
&&
make
install
- unless:
test
-d
/usr/local/keepalived
- require:
#require状态依赖关系
- pkg: pkg-init
-
file
: keepalived-
install
keepalived-init:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/init
.d
/keepalived
-
source
: salt:
//keepalived/files/keepalived
.init
- usr: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name: chkconfig --add keepalived
- unless: chkconfig --list |
grep
keepalived
- require:
-
file
: keepalived-init
/etc/sysconfig/keepalived
:
file
.managed:
-
source
: salt:
//keepalived/files/keepalived
.sysconfig
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
/etc/keepalived
:
file
.directory:
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
|
目录文件结果为:
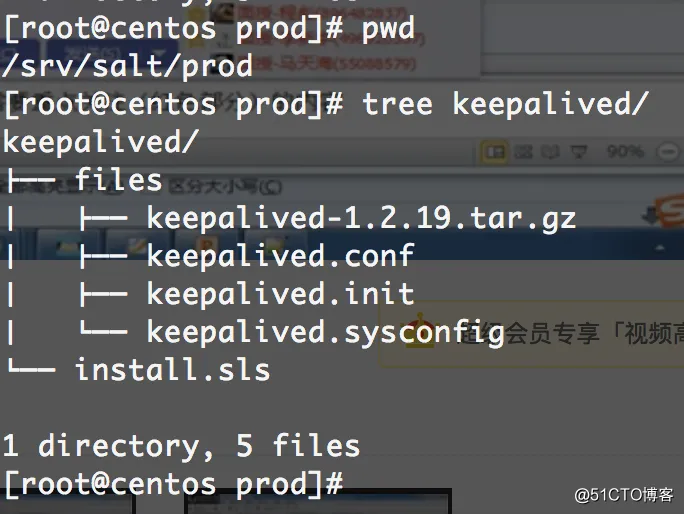
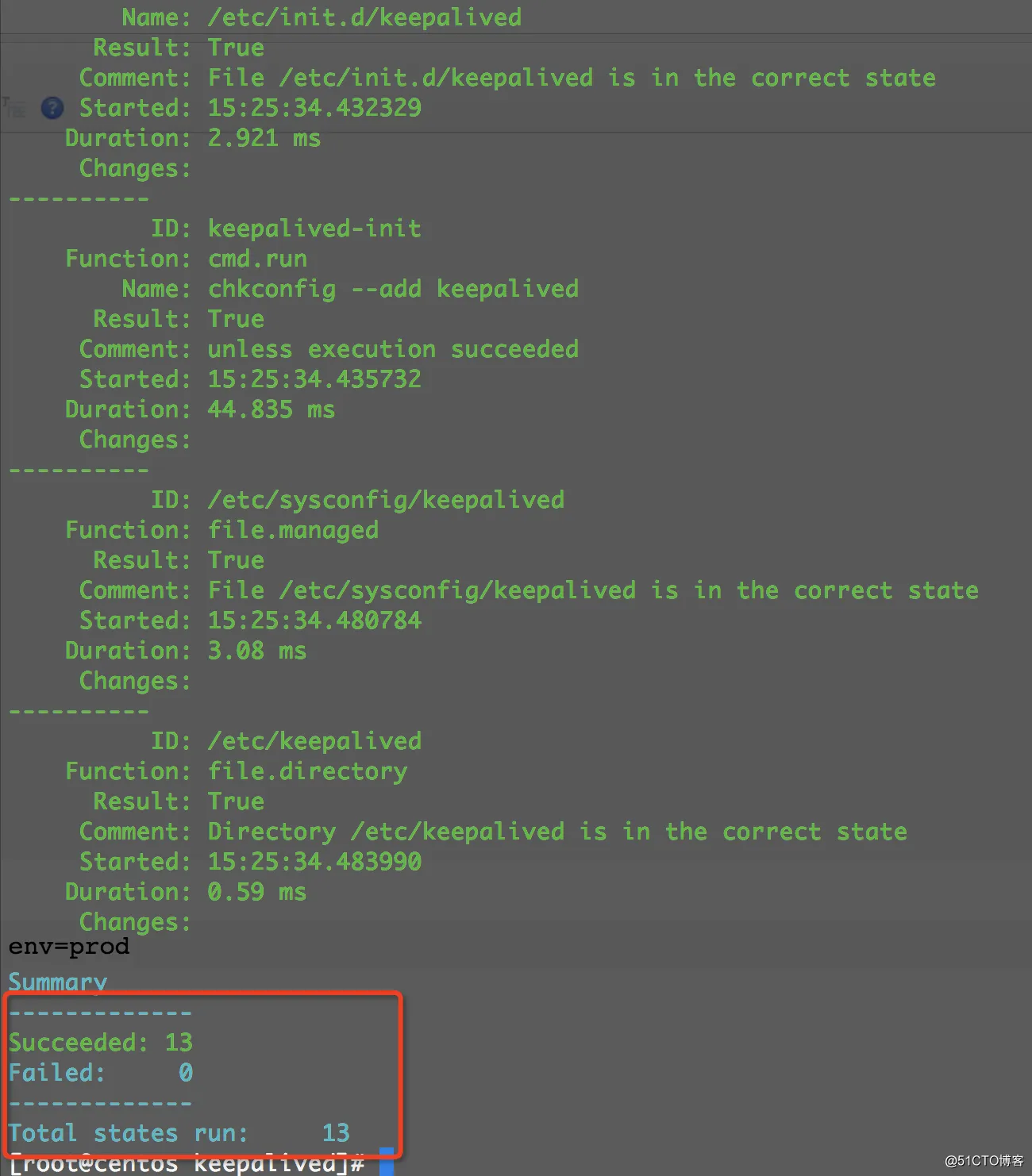
现在,我们开始执行salt文件:
|
1
|
[root@centos keepalived]
# salt 'centos-test[1-2]' state.sls keepalived.install env=prod
|
四、业务引用之keepalived
同haproxy业务引用一样,我们同样在cluster目录下进行。
进入cluster目录:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos keepalived]
# cd ../cluster/
[root@centos cluster]
# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/cluster
|
编写salt文件:
salt文件涉及到keepalived的安装的引用;每个节点的具体参数如何这里主要通过编写jiaja模版来实现每个节点参数的差异性。通过grains的fqdn来判断不同的主机名,实现不同主机不同参数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
[root@centos cluster]
# vim haproxy-outside-keepalived.sls
include:
- keepalived.
install
keepalived-service:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/keepalived/keepalived
.conf
-
source
: salt:
//cluster/files/haproxy-outside-keepalived
.conf
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
- template: jinja
{%
if
grains[
'fqdn'
] ==
'centos-test1'
%}
- ROUTEID: haproxy_ha
- STATEID: MASTER
- PRIORITYID: 150
{%
elif
grains[
'fqdn'
] ==
'centos-test2'
%}
- ROUTEID: haproxy_ha
- STATEID: BACKUP
- PRIORITYID: 100
{% endif %}
service.running:
- name: keepalived
-
enable
: True
-
watch
:
-
file
: keepalived-service
|
keepalived差异性配置文件:
在keepalived安装脚本中,我们为了能够启动keepalived服务,我们在两个节点上都下发相同的keepalived配置文件,这次为了实现每个节点上的keepalived去配置不同的参数,需要下发一份差异性配置文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
[root@centos cluster]
# vim /srv/salt/prod/cluster/files/haproxy-outside-keepalived.conf
! Configuration File
for
keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
saltstack@example.com
}
notification_email_from keepalived@example.com
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id {{ROUTEID}}
# jinja模板变量
}
vrrp_instance haproxy_ha {
state {{STATEID}}
# jinja模板变量
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 36
priority {{PRIORITYID}}
# jinja模板变量
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.39.100
}
}
|
编写top文件:
将业务引用模块keepalived的haprox-outside-keepalived导入。
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@centos base]
# pwd
/srv/salt/base
[root@centos base]
# ls
init tmp
top
.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@centos base]
# vim top.sls
base:
'*'
:
- init.env_init
prod:
'centos-test1'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
'centos-test2'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
|
通过salt高级模式执行:
|
1
|
[root@centos base]
# salt '*' state.highstate
|
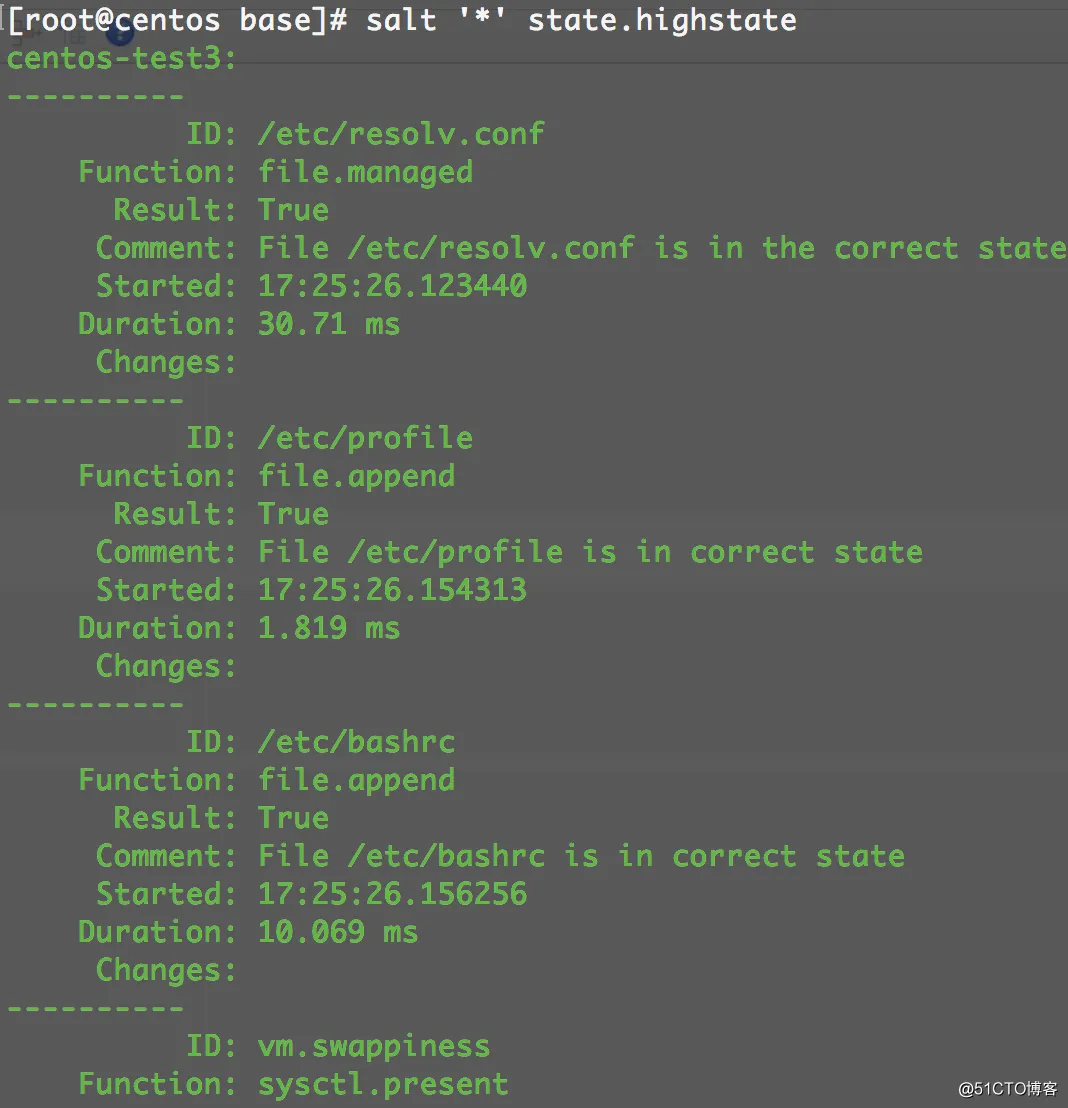
四、后端线上服务
完成前端高可用之后,我们就可以去完成线上服务了。线上服务包括nginx、php、memache、mysql等的安装及配置。
一、功能模块之nginx安装
创建nginx安装目录:
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/nginx/
|
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/nginx/files
|
将nginx安装包和脚本拷贝到files目录下
|
1
|
[root@centos nginx]
# ls files/
|
解决安装nginx依赖关系:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[root@centos prod]
# cat pkg/pkg-nginx.sls
pkg-nginx:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- openssl-devel
- pcre-devel
- zlib-devel
|
编写nginx安装sls文件:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos nginx]
# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/nginx
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
[root@centos nginx]
# vim install.sls
include:
- pkg.pkg-nginx
/usr/local/src
:
file
.directory:
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
nginx-
install
:
file
.managed:
- name:
/usr/local/src/nginx-1
.13.8.
tar
.gz
-
source
: salt:
//nginx/files/nginx-1
.13.8.
tar
.gz
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name:
cd
/usr/local/src/
&&
tar
-zxf nginx-1.13.8.
tar
.gz &&
cd
nginx-1.13.8 && .
/configure
--prefix=
/usr/local/nginx
&&
make
&&
make
install
- unless:
test
-d
/usr/local/nginx
- require:
- pkg: pkg-nginx
-
file
: nginx-
install
nginx-init:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/init
.d
/nginx
-
source
: salt:
//nginx/files/nginx
.init
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name: chkconfig --add nginx
- unless: chkconfig --list |
grep
nginx
- require:
-
file
: nginx-init
/etc/nginx
:
file
.directory:
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
|
目录结果为:
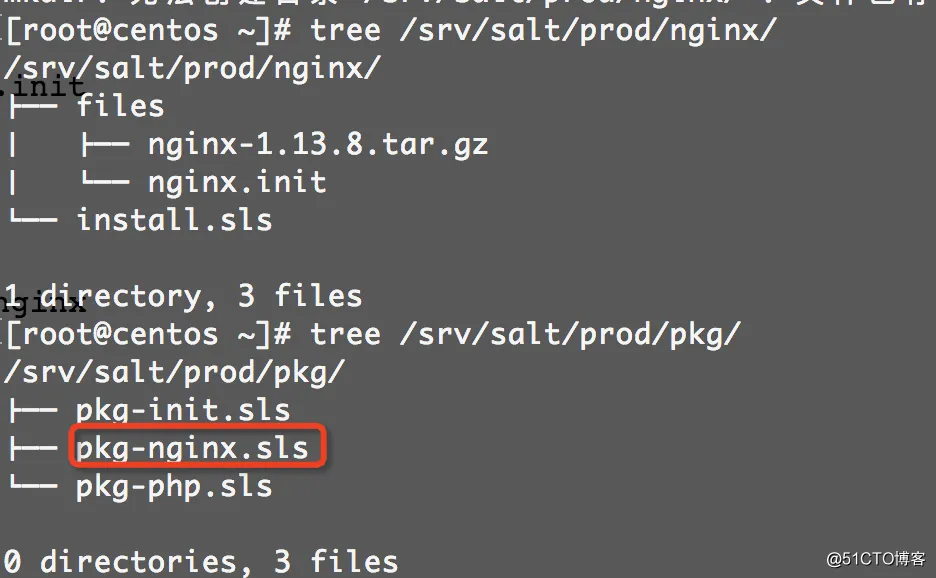
执行安装:
|
1
|
[root@centos prod]
# salt 'centos-test[3-4]' state.sls nginx.install env=prod
|
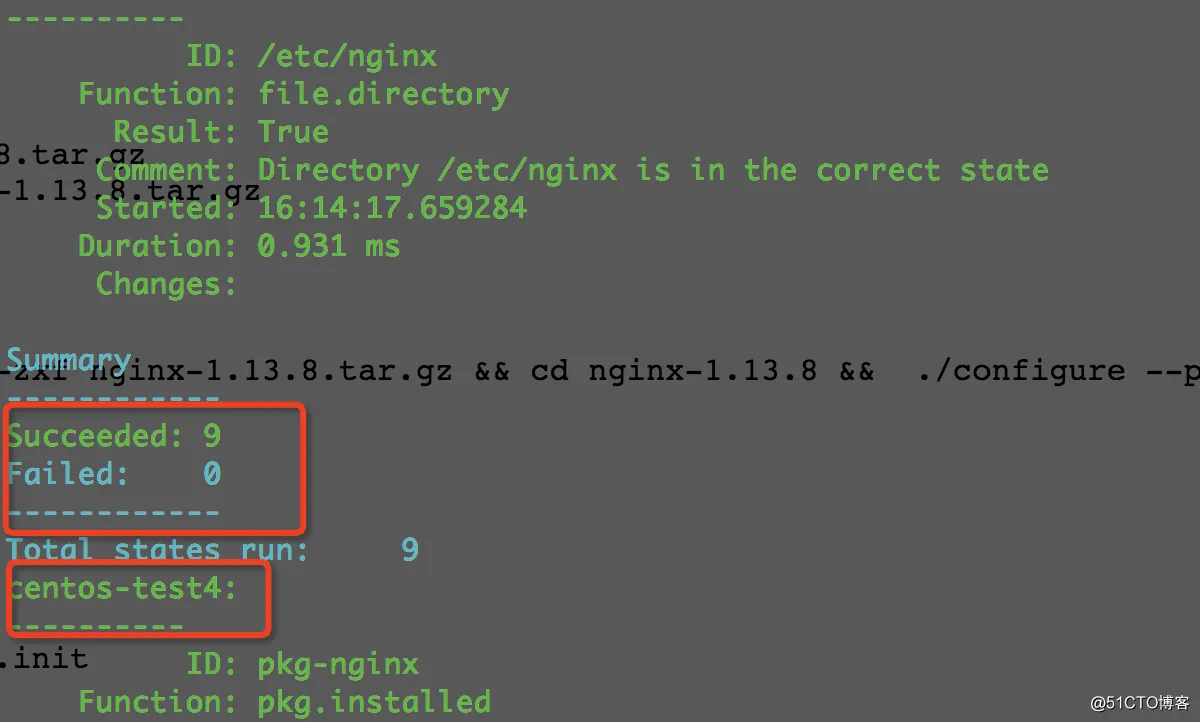
二、业务模块之nginx配置管理
创建app目录用户nginx及php配置文件管理:
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/app/
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/app/files/
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/app/files/nginx/ #用于存放nginx配置文件
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/app/files/php/ #用于存放php配置文件
|
将需要的文件拷贝到files/nginx目录下:
 i
i
编写sls文件进行配置文件管理下发:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos app]
# ls
files nginx.sls php.sls
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@centos app]
# vim nginx.sls
include:
- nginx.
install
{%
for
s
in
[
"fastcgi_params"
,
"mime.types"
,
"nginx.conf"
] %}
nginx-{{s}}:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/nginx/
{{s}}
-
source
: salt:
//app/files/nginx/
{{s}}
- user: root
- group: root
- template: jinja
- mode: 644
service.running:
- name: nginx
-
enable
: True
-
watch
:
-
file
: nginx-nginx.conf
{% endfor %}
|
注:引用jinja模版,将fastcgi_params、mime.types、nginx.conf三个相关文件下发到节点的同一目录下。
执行文件:
|
1
|
[root@centos app]
# salt 'centos-test[3-4]' state.sls app.nginx env=prod
|
|
1
|
三、功能模块之php安装
|
创建php安装目录:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/php
[root@centos ~]
# mkdir /srv/salt/prod/php/files/
|
将安装包拷贝到files目录下:
|
1
2
|
[root@centos prod]
# ls php/files/
php-5.4.40.
tar
.bz2
|
解决php安装的依赖关系:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@centos php]
# cat ../pkg/pkg-php.sls
pkg-php:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- libxml2-devel
|
编写sls文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
[root@centos php]
# vim install.sls
include:
- pkg.pkg-php
php-
install
:
file
.managed:
- name:
/usr/local/src/php-5
.4.40.
tar
.bz2
-
source
: salt:
//php/files/php-5
.4.40.
tar
.bz2
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name:
cd
/usr/local/src/
&&
tar
xf php-5.4.40.
tar
.bz2 &&
cd
php-5.4.40 && .
/configure
--prefix=
/usr/local/php
--
enable
-fpm --with-openssl &&
make
&&
make
install
- unless:
test
-d
/usr/local/php
- require:
- pkg: pkg-php
-
file
: php-
install
|
执行安装:
|
1
|
[root@centos prod]
# salt 'centos-test[3-4]' state.sls php.install env=prod
|
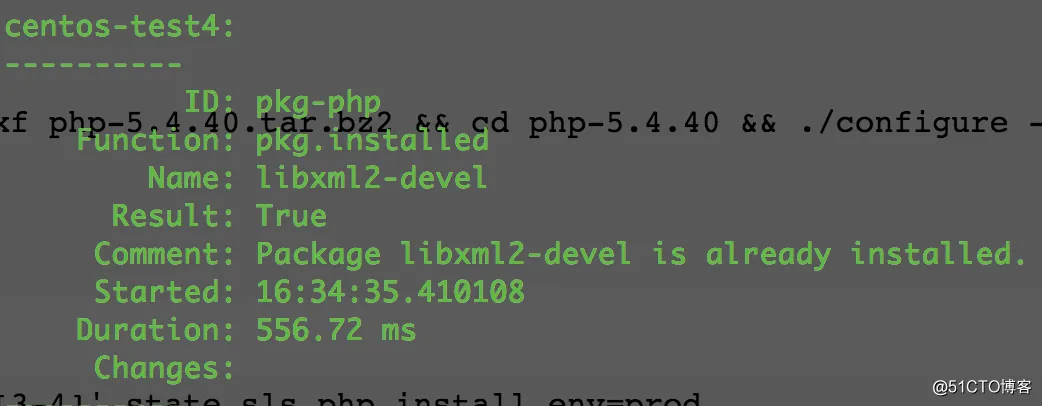
四、业务模块之php配置管理
app目录结构:
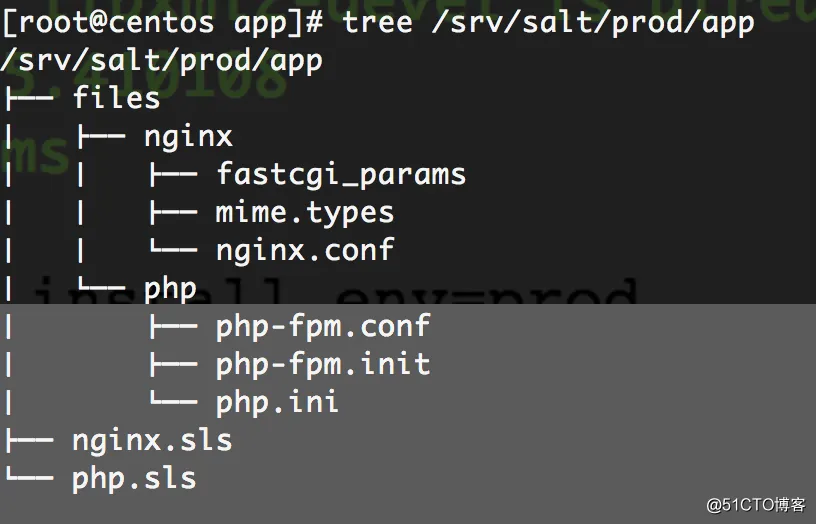
php文件下发脚本内容为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
[root@centos app]
# cat php.sls
include:
- php.
install
php-ini:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/php
.ini
-
source
: salt:
//app/files/php/php
.ini
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
php-fpm-conf:
file
.managed:
- name:
/usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm
.conf
-
source
: salt:
//app/files/php/php-fpm
.conf
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
php-init:
file
.managed:
- name:
/etc/init
.d
/php-fpm
-
source
: salt:
//app/files/php/php-fpm
.init
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name: chkconfig --add php-fpm
- unless: chkconfig --list |
grep
php-fpm
- require:
-
file
: php-init
service.running:
- name: php-fpm
-
enable
: True
-
watch
:
-
file
: php-ini
|
执行配置下发:
|
1
|
[root@centos app]
# salt 'centos-test[3-4]' state.sls app.php env=prod
|
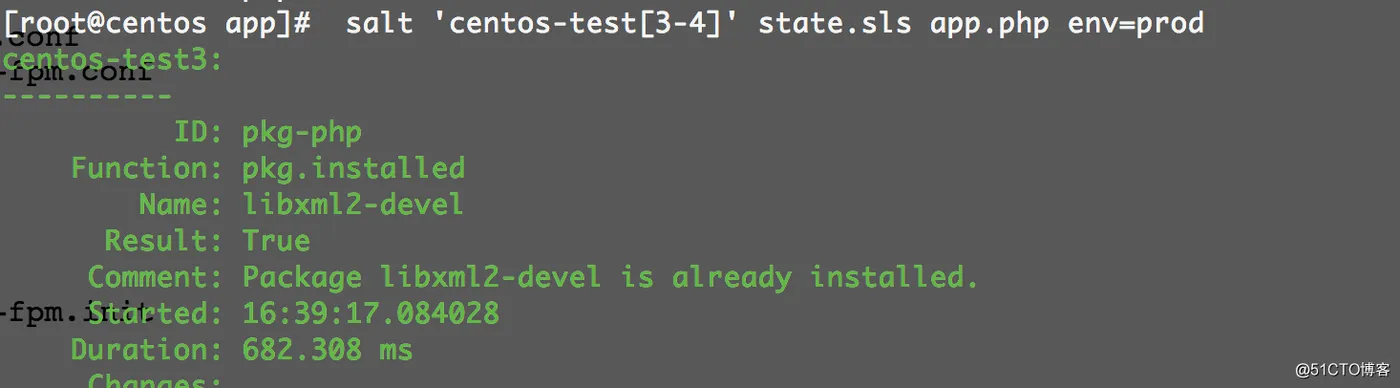
现在,将nginx.sls和php,sls写入top file文件:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@centos app]
# cd /srv/salt/base/
[root@centos base]
# ls
init _modules tmp
top
.sls
|
编写top文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
[root@centos base]
# vim top.sls
base:
'*'
:
- init.env_init
prod:
'centos-test1'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
'centos-test2'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
'centos-test3'
:
- app.nginx
- app.php
'centos-test4'
:
- app.nginx
- app.php
|
五、Memcach安装
memcach通过yum来进行安装,创建memcache目录:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[root@centos base]
# cd /srv/salt/prod/
[root@centos prod]
# ls
app cluster haproxy keepalived nginx php pkg
[root@centos prod]
# mkdir memcache
[root@centos prod]
# ls
app cluster haproxy keepalived memcache nginx php pkg
[root@centos prod]
# cd memcache/
|
编写sls文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
[root@centos memcache]
# vim install.sls
#memcache pkg install
install
-memcached:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- memcached
- php-pecl-memcache
service.running:
- name: memcached
-
enable
: True
#restart-phpfpm:
restart-phpfpm:
cmd.run:
- names:
-
/etc/init
.d
/php-fpm
restart
|
执行安装:
|
1
|
[root@centos memcache]
# salt 'centos-test4' state.sls memcache.install env=prod
|
注:192.168.39.203作为memcache服务器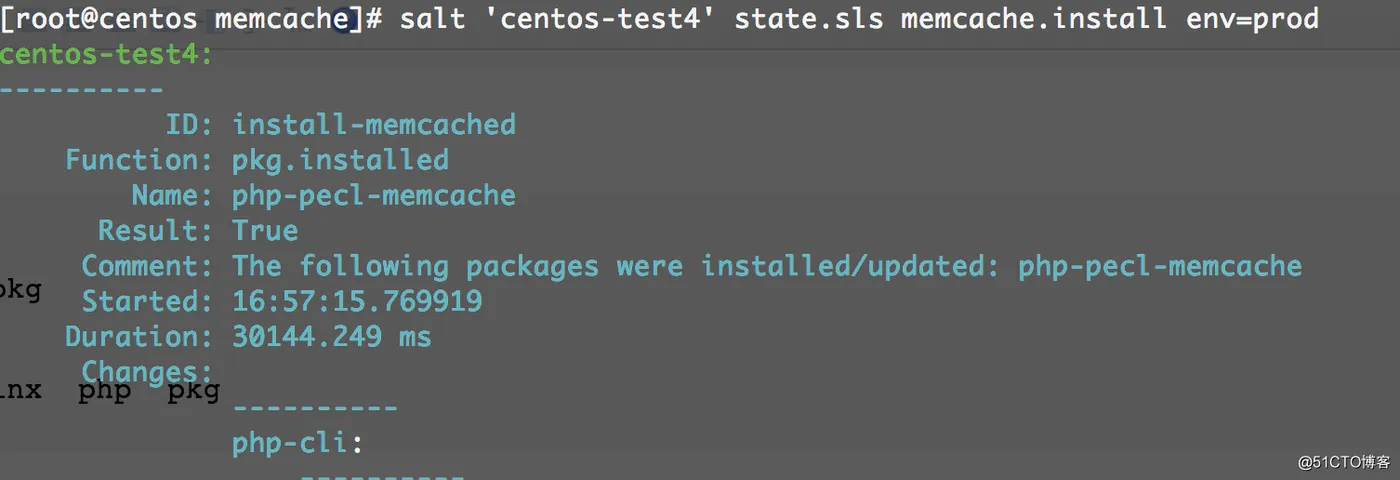
编写top file文件,将memcache安装脚本导入:
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# cd /srv/salt/base/
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@centos base]
# vim top.sls
base:
'*'
:
- init.env_init
prod:
'centos-test1'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
'centos-test2'
:
- cluster.haproxy-outside
- cluster.haproxy-outside-keepalived
'centos-test3'
:
- app.nginx
- app.php
'centos-test4'
:
- app.nginx
- app.php
- memcache.
install
|
高级模式下执行sls:
|
1
|
[root@centos ~]
# salt '*' state.highstate
|
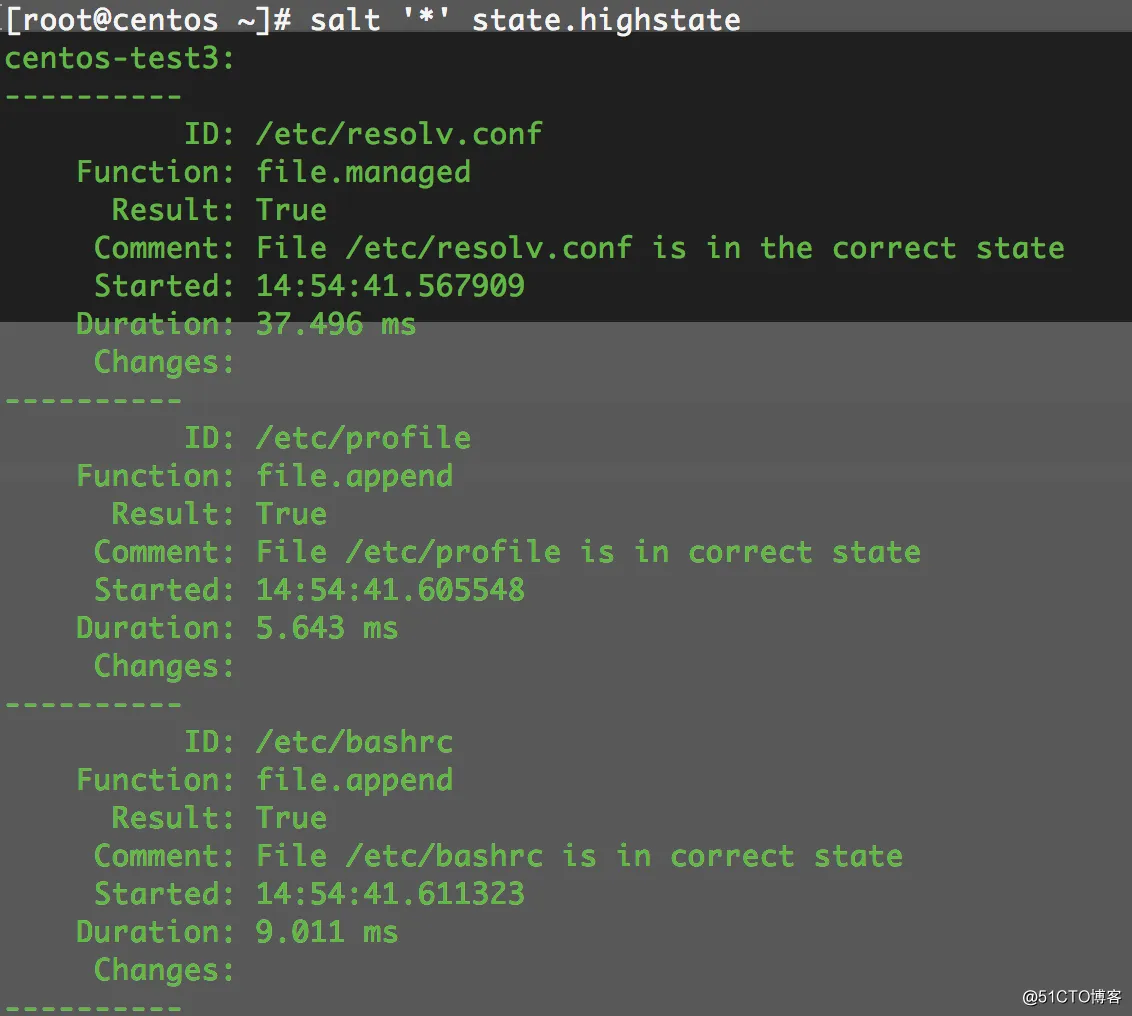
未完待续,,,

