1.思考
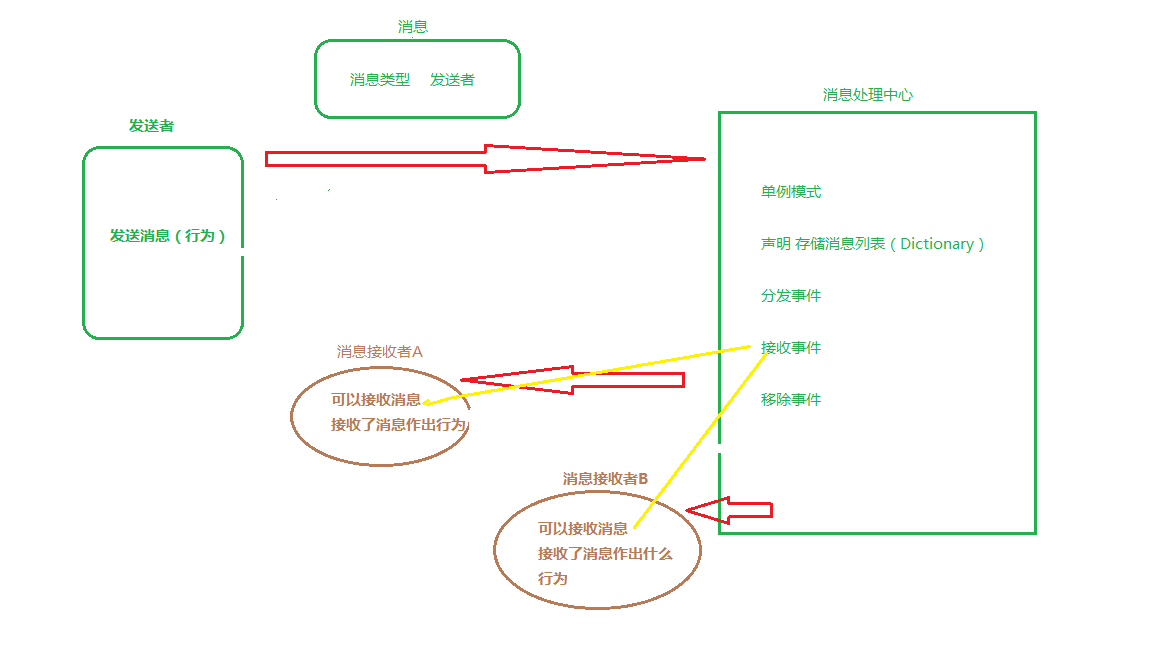
消息发送机制,也可以叫做观察者设计模式(应该是这样的)。
通俗易懂点讲,就是 一个物体发出消息,另外一个,或者几个物体可以同时接收到这一消息并作出各自不同的行为(反馈,处理)。
那么,首先,我们想到,需要什么?
I: 我们需要的是消息(实例),发送者。 消息(实例)+发送者=我们需要的消息,就能够处理任何消息。
II:怎么把这个消息发送出去(消息处理中心)。
III:发送者发送(分发)消息的行为
IV:接收消息。
图解:
2.解析
1)具体消息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
public class Notification
{
/// <summary>
/// 发送者
/// </summary>
public GameObject sender;
/// <summary>
/// 消息内容
/// </summary>
public EventArgs param;
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数 (初始化)
/// </summary>
///<param name="sender">通知发送者
///<param name="param">通知内容
public Notification(GameObject sender, EventArgs param)
{
this.sender = sender;
this.param = param;
}<br>
public Notification()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
///<param name="param">
public Notification(EventArgs param)
{
this.sender = null;
this.param = param;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 传递的消息,这个是消息类中的具体消息种类 类
/// </summary>
public class EventArgsTest : EventArgs
{
public int id;
public string name;
}
|
|
1
|
<span style="color: #008000">Notification是一个稍微抽象一点的消息类,要传递一个消息(类),我前面说到了,肯定是需要知道具体发送者和具体消息类的。</span><br><span style="color: #008000">而具体消息类,就是后面的EventArgsTest,这个是继承于System.EventArgs,该类是自定义类,看到后面,可能会理解为什么这样继承。</span><br><br>
|
2)声明一个消息的委托
|
1
|
public delegate void OnNotification(Notification notific);
|
声明一个委托传递上面所说的消息类的委托,这边通俗一点来讲就是:声明一个可以传递Notification 参数的方法。至于委托的用法这里就不详诉了。
3)消息处理中心

public class NotificationCenter
{ private static NotificationCenter instance = null; public static NotificationCenter Get()
{ if (instance == null)
{
instance = new NotificationCenter(); return instance;
} return instance;
} private Dictionary<uint, NotificationDelegate> eventListeners = new Dictionary<uint, NotificationDelegate>(); public void AddEventListener(uint eventKey, NotificationDelegate listener)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey))
{
NotificationDelegate del = null; //定义方法
eventListeners[eventKey] = del;// 给委托变量赋值 }
eventListeners[eventKey] += listener; //注册接收者的监听 } public void RemoveEventListener(uint eventKey,NotificationDelegate listener)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey)) return;
eventListeners[eventKey] -= listener; if (eventListeners[eventKey] == null)
{
RemoveEventListener(eventKey);
}
} public void RemoveEventListener(uint eventKey)
{
eventListeners.Remove(eventKey);
} /// <summary>
/// 分发事件,不需要知道发送者的情况 /// </summary>
/// <param name="eventKey"></param>
/// <param name="notific"></param>
public void PostDispatchEvent(uint eventKey, Notification notific)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey)) return; // eventListeners[eventKey].Invoke(notific); eventListeners[eventKey](notific);
} /// <summary>
/// 分发事件,需要知道发送者,具体消息的情况 /// </summary>
///<param name="eventKey">事件Key ///<param name="sender">发送者 ///<param name="param">通知内容
public void PostDispatchEvent(uint eventKey, GameObject sender, EventArgs param)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey)) return;
eventListeners[eventKey](new Notification(sender, param));
} public void PostDispatchEvent(uint eventKey)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey)) return;
eventListeners[eventKey](new Notification());
} /// <summary>
/// 分发事件,不需要知道任何,只需要知道发送过来消息了 /// </summary>
///<param name="eventKey">事件Key ///<param name="param">通知内容
public void PostDispatchEvent(uint eventKey, EventArgs param)
{ if (!HasEventListener(eventKey)) return;
eventListeners[eventKey](new Notification(param));
} /// <summary>
/// 是否存在指定事件的监听器 /// </summary>
public bool HasEventListener(uint eventKey)
{ return eventListeners.ContainsKey(eventKey);
}
}

该消息机制的核心,难点也就是在这里了。
首先,既然是消息处理中心,肯定是需要一个存放传递消息(上面那个声明的委托)的容器,于是声明一个
private Dictionary<uint, OnNotification> eventListeners = new Dictionary<uint, OnNotification>();
增加,移除 传递消息(上面那个声明的委托),不就是以下代码,需要注意的是
eventListeners[eventKey] -= listener;//取消接收者的监听 eventListeners.Remove(eventKey);//移除存放在在eventListeners为eventKey的传递消息(上面那个委托)

if (!HasEventListener(eventKey))
{
eventListeners[eventKey] = listener; //注册接收者的监听 } else
{
eventListeners[eventKey] += listener; //注册接收者的监听,这个用法,是委托的一种机制,不理解的自己去百度看看委托咋回事。
}

这样,如何存储消息做完了。
4) 发送者发送(分发)消息的行为

/// <summary>
/// 消息类型,枚举列出,调用时需要强转为uint /// </summary>
public enum ENotificationMsgType // 消息发送的枚举值,应该转为uint型 {
ENull = 0, //Test
ELoadResProgress = 1,
}

以上代码,写枚举,纯是为了提高代码可读性及可维护性,C#中多写枚举,少写那种莫名其妙的 int变量,真心感谢第一家公司对我的影响,保持良好的代码可读性。
EventArgsTest args = new EventArgsTest(); args.id = 3; args.name = "我是Test发送的 name 消息哦"; NotificationCenter.Get().PostDispatchEvent((uint)ENotificationMsgType.ENull, args); // NotificationCenter.Get().PostDispatchEvent((uint)ENotificationMsgType.ENull); //我就是通知,不发送具体啥消息,也是可以的哦
这边需要理解的是 PostDispatchEvent,这个方法,这边我 写了三重重载,因为发送消息分三种情况,如注释那样
{
只需要通知发送,不需要知道发送的具体消息类型,也不需要发送者。
只需要发送具体消息类型,不需要发送者。
需要发送具体消息类型,需要发送者。
}
5)接收消息

void Awake()
{
NotificationCenter.Get().AddEventListener((uint)ENotificationMsgType.ENull, UpdateTest);
} void OnDestroy()
{
NotificationCenter.Get().RemoveEventListener((uint)ENotificationMsgType.ENull, UpdateTest);
} void UpdateTest(Notification e)
{
EventArgsTest args = e.param as EventArgsTest; if (args != null)
{ string strName = args.name; int strId = args.id;
}
}

可能你会奇怪,注册事件和移除事件为什么这样写。这是一种标准写法。
写初始(Start),结束(OnDestroy),使得每个消息拥有一个自己的生命周期。
作为一个一直只做手游的程序员,消息发送机制真的是对于每一个游戏项目是非常基础重要的功能。
本文转自 sshpp 51CTO博客,原文链接:http://blog.51cto.com/12902932/1924093,如需转载请自行联系原作者

