I am the trainer of one standard course “Programming Language Concept” within SAP and there is a set of concept Covariance and Contravariance, which has only built-in support by a subset of programming language like Java. For those ABAPers who don’t have chance to touch this concept in their daily work, I have built a small example to simulate how the concept works in ABAP as well for ease of understanding. The example explained in this example is just a prototype purely for training and education purpose.
Covariance and Contravariance in computer science
Both concept are closely related to inheritance in Object-Oriented world.
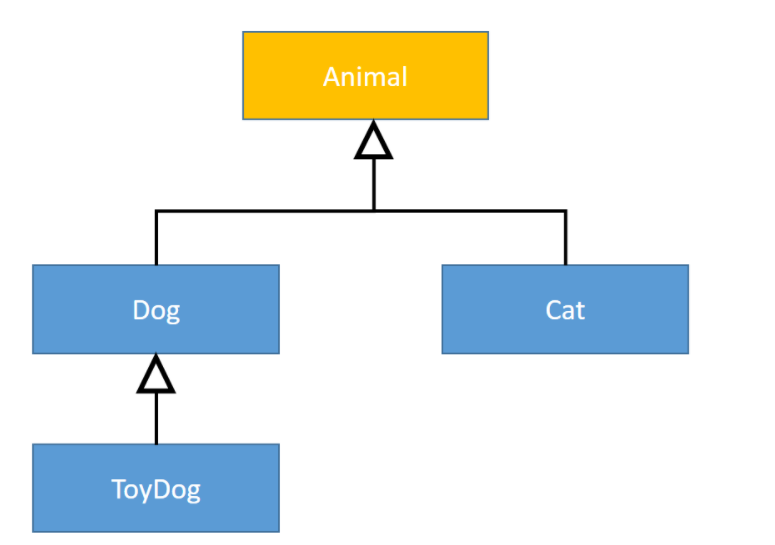
In this blog I use the following classes with hierarchical inheritance relationship.
It is very straight-forward that both Dog and Cat are a kind of sub class of Animal, and ToyDog is a sub class of Dog.
However, how about the relationship between Animal container and Dog container? In order to describe the sub-typing relationship among more complex types ( in my example above, complex types mean Animal container and Dog container ) built via component type ( in my example component types refers to class Animal and Dog ).
You can find the definition of concept Covariance and Contravariance in Wikipedia.
Covariance
the complex type preserves the inheritance ordering of component type, which orders types from more specific to more generic. For example, we already have prerequisite that Dog is a sub class of Animal, and if Dog container is also a sub class of Animal container, we now say the subtyping relationship between Dog container and Animal container fulfills the Covariance contract.
Contravariance
Reverses this ordering.
In this blog, I will only focus on Covariance, since Contravariance works the same way as Covariance except that the inheritance relationship of complex types is reverted.
Covariance in Java
See this example below. In line 126, in signature of method forABAPer,
List<? extends Dog> declares a List container which must adhere to Covariance contract. ABAPers can analogize the symbol “?” to the generic type in ABAP such as ANY, ANY TABLE etc, which acts as a place holder and variable with concrete data type must be filled as parameter when the method is consumed.
List<? extends Dog> in method signature means the method can only accept a list container which fulfills Covariance contract, that is, the actual type of ? must be Dog itself, or any other sub class of Dog.
Due to Covariance contract, the Dog container created in line 113 and Toy Dog container in line 117 pass the syntax check, it is ok to call both via method forABAPer. For cat container in line 121, since Cat is not a sub class of Dog, syntax error is raised accordingly.
Contravariance contract, on the other hand, is defined via
“<? super T>“, where T is a generic COMPONENT type of super class, and ? is the concrete type you must specify when you call the method.
Covariance and Contravariance is widely used in JDK implementation and many Java framework like Spring.
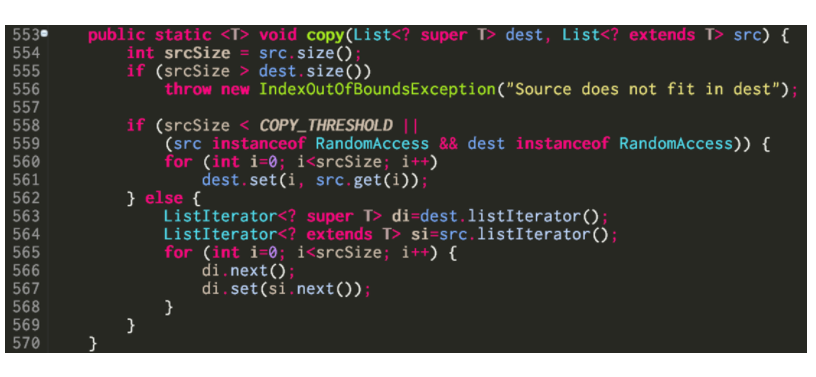
See one example below about the implementation of utility method java.util.Collections.copy, which does a shadow copy of each element from source container to destination container.
Another guideline of Covariance and Contractvariance is the so called PECS https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wildcard_(Java) which is much more sophisticated and is out of scope of this blog.
How to simulate Covariance in ABAP
In ABAP since we don’t have real container type with Object-Oriented behavior, we have to simulate Covariance with internal table plus interface instead.
(1) declare a tag interface
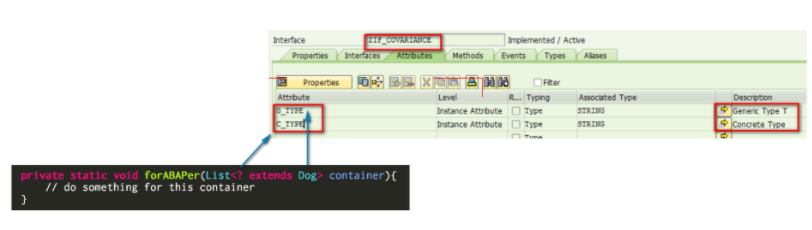
I declare a tag interface ZIF_COVARIANCE without any method defined there, but only with two attribute G_TYPE and C_TYPE.
Here G_TYPE simulates generic type of list container and C_TYPE simulates concrete type “?” in Java, which must be filled by a real data type when method is called.
(2) build a Animal container with Covariance contract
In this container class, I assign the tag interface ZIF_COVARIANCE to it, meaning that this container is now under the Covariance syntax check.
The generic type G_TYPE is now determined in the design time, ZCL_DOG.
This means in compiler time, only Covariance compliant code can pass syntax check:
When you instantiate a new instance of this animal container, the concrete class type you use must be either ZCL_DOG itself, or any sub class of ZCL_DOG.
When you try to add a new animal to this animal container, the data type of the element to be inserted must be either ZCL_DOG itself, or any sub class of ZCL_DOG.
(3) implement a custom Covariance syntax check
In this animal container class, I use an internal table with type ZCL_ANIMAL to store the inserted animal reference.
types TY_REF type ref to ZCL_ANIMAL .
data: DATA type STANDARD TABLE OF ty_ref .
As a result, by default the following code will pass the syntax check, since ZCL_CAT is also a sub class of ZCL_ANIMAL, so the instance of it could be successfully inserted to internal table with TYPE REF TO ZCL_ANIMAL, although this is a violation of Covariance.
There are two places in the following code which do not obey Covariance:
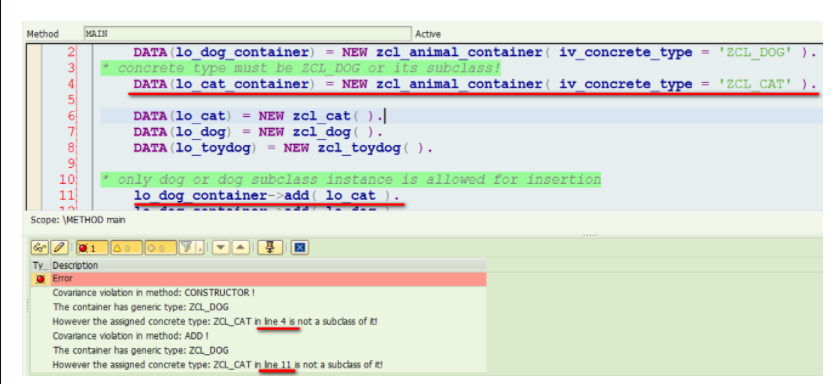
In line 4, since the animal container has already marked generic type as ZCL_DOG, the concrete data type must be either ZCL_DOG itself, or any sub class of ZCL_DOG. ZCL_CAT is not allowed.
In line 11, it is not allowed to insert a cat to a dog container.
The expected behavior is: once you click Ctrl+F2 to trigger syntax check, all Covariance violation are found and listed, see example below:How to implement Covariance Syntax check in class builder
The main logic of Covariance check is done in method ZCL_ABAP_COVARIANCE_TOOL~COVARIANCE_SYNTAX_CHECK, which only consists of 45 lines:
METHOD covariance_syntax_check.
DATA: lv_include TYPE progname,
lv_main TYPE progname,
lv_index TYPE int4 VALUE 1.
FIELD-SYMBOLS:<method> LIKE LINE OF mt_result.
initialize( ).
ms_working_method = is_method_def.
fill_method_source( ).
lv_include = cl_oo_classname_service=>get_method_include( is_method_def ).
lv_main = cl_oo_classname_service=>get_classpool_name( is_method_def-clsname ).
DATA(lo_compiler) = NEW cl_abap_compiler( p_name = lv_main p_include = lv_include ).
lo_compiler->get_all( IMPORTING p_result = mt_result ).
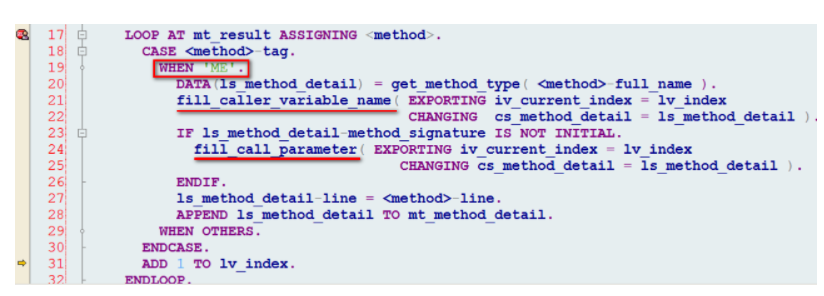
LOOP AT mt_result ASSIGNING <method>.
CASE <method>-tag.
WHEN 'ME'.
DATA(ls_method_detail) = get_method_type( <method>-full_name ).
fill_caller_variable_name( EXPORTING iv_current_index = lv_index
CHANGING cs_method_detail = ls_method_detail ).
IF ls_method_detail-method_signature IS NOT INITIAL.
fill_call_parameter( EXPORTING iv_current_index = lv_index
CHANGING cs_method_detail = ls_method_detail ).
ENDIF.
ls_method_detail-line = <method>-line.
APPEND ls_method_detail TO mt_method_detail.
WHEN OTHERS.
ENDCASE.
ADD 1 TO lv_index.
ENDLOOP.
DELETE mt_method_detail WHERE caller_variable_name IS INITIAL.
LOOP AT mt_method_detail ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<result>).
CHECK is_covariance_check_needed( <result>-caller_variable_name ) = abap_true.
CASE <result>-method_type.
WHEN cs_method_type-constructor.
check_ctor_covariance( <result> ).
WHEN cs_method_type-instance.
check_instance_covariance( <result> ).
ENDCASE.
ENDLOOP.
RT_ERROR_MESSAGE = MT_ERROR_MESSAGE.
ENDMETHOD.(1) perform syntax analysis on instance method and constructor method
With help of CL_ABAP_COMPILER, I can get a list of all methods call and used variable within the method being checked. The used information returned by CL_ABAP_COMPILER has the following format.
As the Covariance check only makes sense on method call,
so in my Covariance syntax analysis, I will only handle the entry for method call ( marked with tag “ME” in CL_ABAP_COMPILER returning result ).
After the loop in line 17 is finished, I have successfully regularized the result from CL_ABAP_COMPILER with raw format to my customized data format as below:
The internal table mt_method_detail has line type defined by myself, TY_METHOD_DETAIL.
Take the first row in above screenshot for example
Method_type 1 means it is a constructor call.
CALLER_VARIABLE_NAME lo_dog_container means this variable is instantiated via keyword NEW.
METHOD_CLS_NAME ZCL_ANIMAL_CONTAINER means the variable lo_dog_container is initialized by NEW with type ZCL_ANIMAL_CONTAINER.
CALL_PARAMETER_NAME ZCL_DOG means the string literal “ZCL_DOG” is passed into constructor as a parameter.
Take record with index 6 in above screenshot for illustration
Method_type 2 means it is an instance method call.
CALLER_VARIABLE_NAME lo_dog_container means it is this variable which performs the current instance method.
METHOD_CLS_NAME ZCL_ANIMAL_CONTAINER means the instance variable lo_dog_container has class type ZCL_ANIMAL_CONTAINER.
METHOD_NAME ADD means the instance method being called has name “ADD”.
CALL_PARAMETER_NAME LO_CAT means the instance lo_cat is passed into instance method ADD.
(2) perform the real Covariance check based on regularized method call information generated in previous step
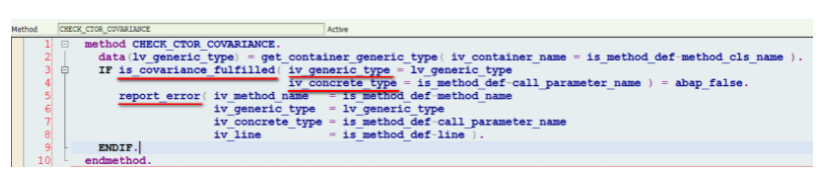
Since now the essential information for Covariance check, the generic type and concrete type are already available, it is ready to perform check.
(2.1) Covariance relevance check
I just loop every record and first check whether the current method call is relevant for Covariance check. I am using the assumption that a method call should only be checked against Covariance when the class of the instance which performs the call has been assigned with tag interface ZIF_COVARIANCE.
(2.2) Covariance check implementation by evaluate the relationship between generic type and concrete type
The evaluation is done in method below: if generic type and concrete type does not fulfill Covariance, syntax error is reported.
How to play around with this prototype by yourself
(1) Follow my blog Implement Custom Syntax Check in SAP GUI to setup necessary configuration create a new custom syntax check handler class ZCL_WB_CLEDITOR( source code could be found from my github mentioned above ).
(2) Create a class with any name and a new method with following source code:
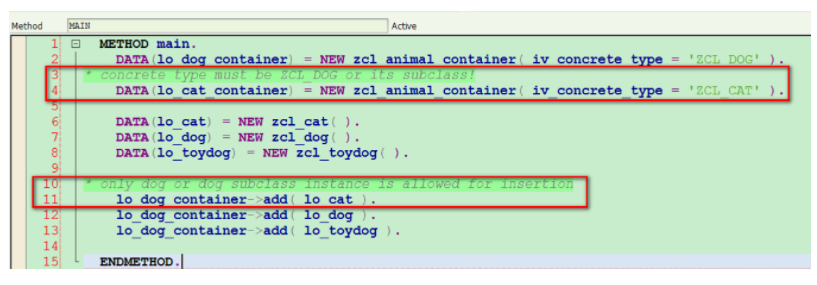
METHOD main.
DATA(lo_dog_container) = NEW zcl_animal_container( iv_concrete_type = 'ZCL_DOG' ).
* concrete type must be ZCL_DOG or its subclass!
DATA(lo_cat_container) = NEW zcl_animal_container( iv_concrete_type = 'ZCL_CAT' ).
DATA(lo_cat) = NEW zcl_cat( ).
DATA(lo_dog) = NEW zcl_dog( ).
DATA(lo_toydog) = NEW zcl_toydog( ).
* only dog or dog subclass instance is allowed for insertion
lo_dog_container->add( lo_cat ).
lo_dog_container->add( lo_dog ).
lo_dog_container->add( lo_toydog ).
ENDMETHOD.(3) In Class builder under Form-based mode, press Ctrl+F2 and you should see two error messages for Covariance violation:
Further reading
I have written a series of blogs which compare the language feature among ABAP, JavaScript and Java. You can find a list of them below:
Lazy Loading, Singleton and Bridge design pattern in JavaScript and in ABAP
Functional programming – Simulate Curry in ABAP
Functional Programming – Try Reduce in JavaScript and in ABAP
Simulate Mockito in ABAP
A simulation of Java Spring dependency injection annotation @Inject in ABAP
Singleton bypass – ABAP and Java
Weak reference in ABAP and Java
Fibonacci Sequence in ES5, ES6 and ABAP
Java byte code and ABAP Load
How to write a correct program rejected by compiler: Exception handling in Java and in ABAP
An small example to learn Garbage collection in Java and in ABAP
String Template in ABAP, ES6, Angular and React
Try to access static private attribute via ABAP RTTI and Java Reflection
Local class in ABAP, Java and JavaScript
Integer in ABAP, Java and JavaScript
Covariance in Java and simulation in ABAP
Various Proxy Design Pattern implementation variants in Java and ABAP
Implement CGLIB in ABAP