终于把MyBatis学完了 下一个Spring 希望早日学完 好想拥有自己的网站呀
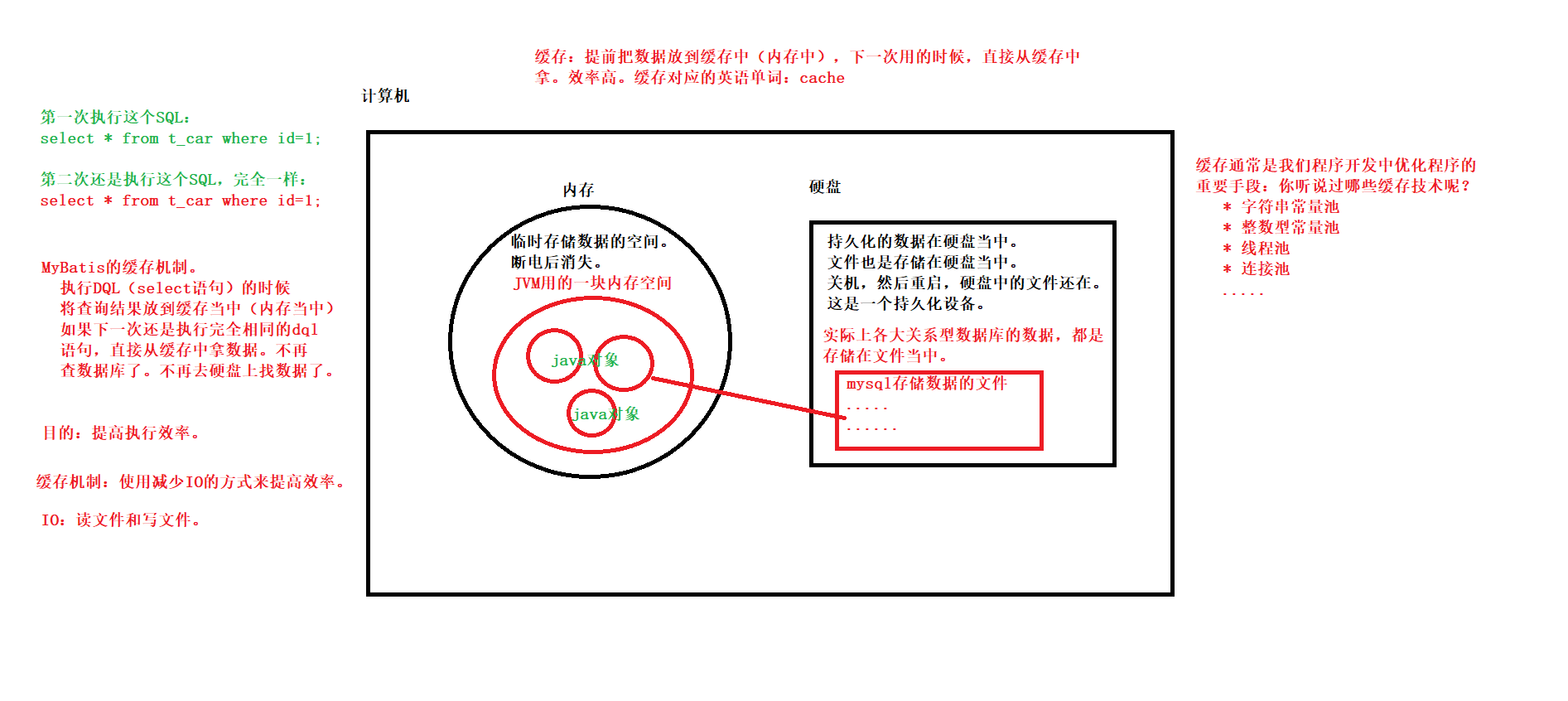
JDBC的缺点
1.SQL语句写死在java程序中,如果需要修改SQL语句,就要改java代码,违背OCP原则
。OCP原则:软件实体(包括类、模块、功能等)应该对扩展开放,但是对修改关闭
2.JDBC代码繁琐且重复
比如获取值、创建对象、给对象的属性赋值
MyBatis
一、基础概念
- 本质上就是对JDBC的封装,完成CRUD的操作
- 属于持久层框架
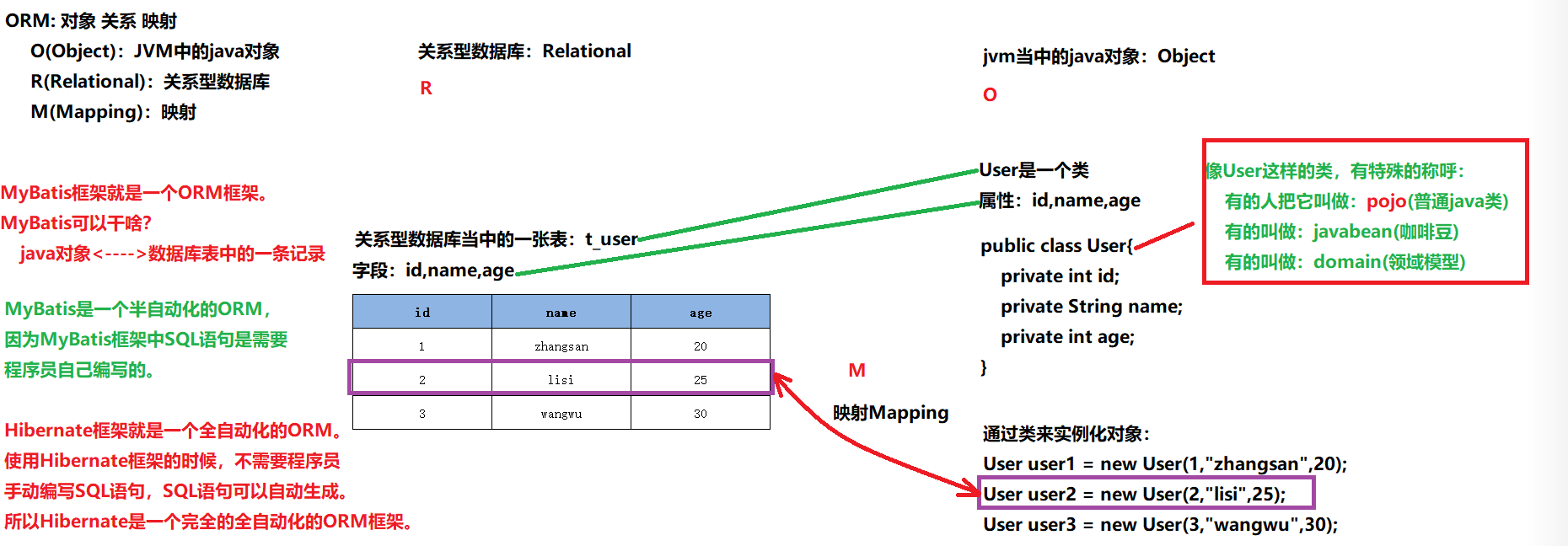
- ORM
。Object:JVM中的java对象
。Relational:关系型数据库
。Mapping:映射,将java虚拟机中的java对象映射到数据库表中一行记录,或是将数据库表中一行记录映射成Java虚拟机中的一个Java对象
。MyBatis是一个半自动化的ORM框架,因为SQL语句是需要自己编写
。Hibernate是一个全自动化的ORM框架
- MyBatis框架特点
。支持定制化SQL、存储过程、基本映射以及高级映射->Hibernate虽然全自动化,但是SQL语句可能不是最优的
。避免了几乎所有的JDBC代码中手动设置参数以及获取结果集
。支持XML开发,也支持注解式开发。
- 为了保证sql语句的灵活,所以mybatis大部分是采用XML方式开发。
。将接口和Java的POJOs(Plain Ordinary Java Object,简单普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录
。体积小好学:两个jar包,两个XML 配置文件
。完全做到sq|解耦合
。提供了基本映射标签
。提供了高级映射标签
。提供了XML标签,支持动态SQL的编写
二、开发第一个mybatis程序
开发我的第一个MyBatis程序
1.resources目录:
- 放在这个目录当中的,一般都是资源文件,配置文件。
- 直接放到resources目录下的资源,等同于放到了类的根路径下。
2.开发步骤
- 第一步:打包方式jar
- 第二步:引入依赖
https://www.mvnrepository.com/ 寻找相关依赖
。mybatis依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.10</version> </dependency>
。mysql驱动依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.30</version> </dependency>
- 第三步:编写mybatis核心配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
。这个文件名不是必须叫做mybatis-config.xml,可以用其他的名字。
。这个文件存放的位置也不是固定的,可以随意,但一般情况下,会放到类的根路径下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"/> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!-- 执行XxxMapper.xml文件的路径--> <!-- resource属性会自动从根目录下开始查找--> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
。报错添加jdbc.properties至rescources
并在configuration下面
- 第四步:编写XxxxMapper.xml文件
。在这个配置文件当中编写SQL语句。
。这个文件名也不是固定的,放的位置也不是固定,我们这里给它起个名字,叫做:CarMapper.xml
把它暂时放到类的根路径下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="ddda"> <insert id="insertCar"> insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,'1003','丰田',30.0,'2003-9-10','燃油车') </insert> </mapper>
- 第五步:在mybatis-config.xml文件中指定XxxxMapper.xml文件的路径:
<mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/>
注意:resource属性会自动从类的根路径下开始查找资源。
- 第六步:编写MyBatis程序。(使用mybatis的类库,编写mybatis程序,连接数据库,做增删改查就行了。)
。在MyBatis当中,负责执行SQL语句的那个对象叫做什么呢?
- SqlSession
SqlSession是专门用来执行SQL语句的,是一个Java程序和数据库之间的一次会话。
- 要想获取SqlSession对象,需要先获取SqlSessionFactory对象,通过SqlSessionFactory工厂来生产SqlSession对象。
- 怎么获取SqlSessionFactory对象呢?
- 需要首先获取SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象。
通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象的build方法,来获取一个SqlSessionFactory对象。
。mybatis的核心对象包括:
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- SqlSessionFactory
- SqlSession
。SqlSessionFactoryBuilder --> SqlSessionFactory --> SqlSession
package com.st.mybatis.test; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -MyBatisIntroductionTest * @Pcakage: com.st.mybatis.test.MyBatisIntroductionTest * @Date: 2022年10月28日 19:26 * @Description: */ public class MyBatisIntroductionTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); // 输入流指向核心配置文件 InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");// Resources.getResourceAsStream默认从类的根路径下开始查找资源 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); int count = sqlSession.insert("insertCar");// 执行sql语句 System.out.println("插入了几条记录:" + count); sqlSession.commit();// 手动提交 底层调用了conn.commit() } }
3.从 XML 中构建 SqlSessionFactory
- 通过官方的这句话,你能想到什么呢?
。第一:在MyBatis中一定是有一个很重要的对象,这个对象是:对象。
。第二:SqlSessionFactory对象的创建需要XML。
- XML是什么?
它一定是一个配置文件。
4.mybatis中有两个主要的配置文件:
- mybatis-config.xml,这是核心配置文件,主要配置连接数据库的信息等。(一个)
- XxxxMapper.xml,这个文件是专门用来编写SQL语句的配置文件。(一个表一个)
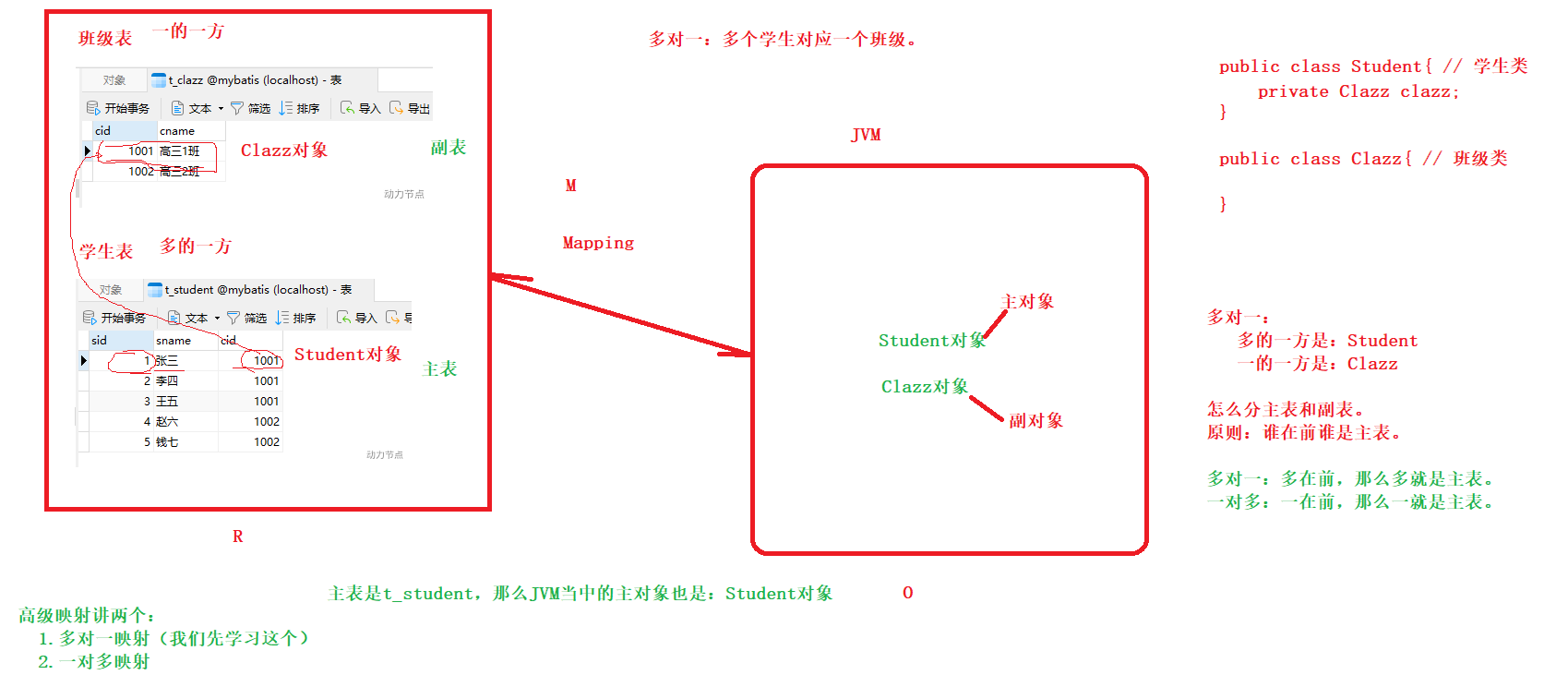
。t_user表,一般会对应一个UserMapper.xml
。t_student表,一般会对应一个StudentMapper.xml
5.关于第一个程序的小细节
- mybatis中sql语句的结尾";"可以省略。
- Resources.getResourceAsStream
。小技巧:以后凡是遇到resource这个单词,大部分情况下,这种加载资源的方式就是从类的根路径下开始加载。(开始查找)
。优点:采用这种方式,从类路径当中加载资源,项目的移植性很强。项目从windows移植到linux,代码不需要修改,因为这个资源文件一直都在类路径当中。
- 输入流
。InputStream is = new FileInputStream(“d:\mybatis-config.xml”);
- 采用这种方式也可以。
- 缺点:可移植性太差,程序不够健壮。可能会移植到其他的操作系统当中。导致以上路径无效,还需要修改java代码中的路径。这样违背了OCP原则。
。InputStream is = **ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().**getResourceAsStream(“mybatis-config.xml”);
- ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() 获取系统的类加载器。
系统类加载器有一个方法叫做:getResourceAsStream,它就是从类路径当中加载资源的。
- 通过源代码分析发现:
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(“mybatis-config.xml”);
底层的源代码其实就是:
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(“mybatis-config.xml”);
- mybatis核心配置文件的名字,不一定是:mybatis-config.xml。可以是其它名字。
mybatis核心配置文件存放的路径,也不一定是在类的根路径下。可以放到其它位置。但为了项目的移植性,健壮性,最好将这个配置文件放到类路径下面。
- CarMapper.xml文件的名字是固定的吗?CarMapper.xml文件的路径是固定的吗?
都不是固定的。
resource属性:这种方式是从类路径当中加载资源。
url属性:这种方式是从绝对路径当中加载资源。
6.关于mybatis的事务管理机制。(深度剖析)
- 在mybatis-config.xml文件中,可以通过以下的配置进行mybatis的事务管理
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
- type属性的值包括两个,不区分大小写
。JDBC(jdbc)
JDBC事务管理器
。MANAGED(managed)
MANAGED事务管理器:
- mybatis 提供了 Transaction接口,该接口有两个实现类
。JdbcTransaction
。ManagedTransaction
- JDBC事务管理器:
。mybatis框架自己管理事务,自己采用原生的JDBC代码去管理事务:
- conn.setAutoCommit(false);
开启事务。
- …业务处理…
- conn.commit();
手动 提交事务
。使用JDBC事务管理器的话,底层创建的事务管理器对象:JdbcTransaction对象。
。如果你编写的代码是下面的代码:
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);// 表示没有开启事务。 因为这种方式压根不会执行:conn.setAutoCommit(false); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();// 底层调用conn.setAutoCommit(false);
MANAGED事务管理器:
。mybatis不再负责事务的管理了。事务管理交给其它容器来负责。例如:spring。
。对于我们当前的单纯的只有mybatis的情况下,如果配置为:MANAGED
那么事务这块是没人管的。没有人管理事务表示事务压根没有开启。
没有人管理事务就是没有事务。
- JDBC中的事务:
如果你没有在JDBC代码中执行:conn.setAutoCommit(false);的话,默认的autoCommit是true。
- 在JDBC事务中,没有执行conn.setAutoCommit(false);那么autoCommit就是true。
如果autoCommit是true,就表示没有开启事务。只要执行任意一条DML语句就提交一次。
- 重点:
只要你的autoCommit是true(自动提交),就表示没有开启事务。
只有你的autoCommit是false的时候,就表示开启了事务。
7.完整版MyBatis程序
package com.st.mybatis.test; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -MyBatisCompleteTest * @Pcakage: com.st.mybatis.test.MyBatisCompleteTest * @Date: 2022年10月29日 13:21 * @Description: 完整版的MyBatis程序 */ public class MyBatisCompleteTest { public static void main(String[] args) { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 执行SQL语句,处理相关业务 int count = sqlSession.insert("insertCar"); System.out.println(count); // 执行到治理,没有发生任何异常,提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { // 回滚事务 if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.rollback(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { // 关闭会话(释放资源) if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } } }
8.junit单元测试
- 单元测试(测试方法):用的是junit, junit是一个专门测试的框架(工具)。
。junit测试的内容: 测试的是类中的方法, 每一个方法都是独立测试的。
。方法是测试的基本单位(单元)。
- 单元测试中有两个重要的概念
。实际值:被测试的业务方法的真正执行结果
。期望值:执行这个业务方法之后,你期望的执行结果
- 在pom中加入相应的依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
- maven项目中的src/test/java目录下,创建测试程序。
。推荐的创建类和方法的提示:
1.测试类的名称 是Test + 你要测试的类名
例如你要测试HelloMaven , 创建测试类 TestHelloMaven
2.测试的方法名称 是:Test + 方法名称
- 方法是public的,必须的
- 方法没有返回值, 必须的
- 方法名称是自定义的,推荐是Test + 方法名称
- 在方法的上面加入 @Test
package com.st.junit.service; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -MathService * @Pcakage: com.st.junit.service.MathService * @Date: 2022年10月29日 13:56 * @Description: */ public class MathService { public int sum(int a, int b){ return a+b; } public int sub(int a, int b){ return a-b; } }
public class MathServiceTest { @Test public void testSum(){ MathService mathService = new MathService(); int actual = mathService.sum(1,2); int expected = 3; // 加断言进行测试 Assert.assertEquals(expected,actual); } @Test public void testSub(){ MathService mathService = new MathService(); int actual = mathService.sub(1,2); int expected = -1; // 加断言进行测试 Assert.assertEquals(expected,actual); } }
9.mybatis集成日志组件[调试起来更加方便]
- mybatis常见的集成的日志组件有哪些呢?
SLF4J(沙拉风):沙拉风是一个日志标准
。logback,它实现了沙拉风规范。
。LOG4J
。LOG4J2
。STDOUT_LOGGING
…
注意:log4j log4j2 logback都是同一个作者开发的。
- STDOUT_LOGGING是标准日志,mybatis已经实现了这种标准日志。mybatis框架本身已经实现了这种标准。只要开启即可。
。怎么开启呢?在mybatis-config.xml文件中在configuration使用settings标签进行配置开启。
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> </settings>
。这个标签在编写的时候要注意,它应该出现在environments标签之前。
- 注意顺序。当然,不需要记忆这个顺序。
因为有dtd文件进行约束呢。我们只要参考dtd约束即可。
。这种可以看到一些信息,比如:连接对象什么时候创建,什么时候关闭,sql语句是怎样的。
但是没有详细的日期,线程名字,等。如果你想使用更加丰富的配置,可以集成第三方的log组件。
- 集成logback日志框架。
logback日志框架实现了SLF4J标准。(沙拉风:日志门面。日志标准。)
1.第一步:引入logback的依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.2.11</version> </dependency>
2.第二步:引入logback所必须的xml配置文件。
。这个配置文件的名字必须叫做:logback.xml或者logback-test.xml,不能是其它的名字。
。这个配置文件必须放到类的根路径下。
。主要配置日志输出相关的级别以及日志具体的格式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration debug="false"> <!-- 控制台输出 --> <appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder"> <!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符--> <pattern>[%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <!--mybatis log configure--> <logger name="com.apache.ibatis" level="TRACE"/> <logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/> <logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/> <logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/> <!-- 日志输出级别,logback日志级别包括五个:TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR --> <root level="DEBUG"> <appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/> <appender-ref ref="FILE"/> </root> </configuration>
三、使用mybatis完成CRUD
1.什么是CRUD
- C: Create增
- R: Retrieve查(检索)
- U: Update改
- D: Delete删
2.insert
- 最原始的insert代码
<insert id="insertCar"> insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,'1003','丰田霸道',30.0,'2000-10-11','燃油车'); </insert>
。这样写的问题是?
- 值是写死到配置文件中的。
- 这个在实际开发中不存在,在实际开发中一定是前端的form表单提交过来数据,然后将值传给sql语句。
- JDBC的代码是怎么写的?
String sql = "insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,?,?,?,?,?)"; ps.setString(1, xxx); ps.setString(2, yyy); ....
- 在JDBC当中占位符采用的是?,在mybatis当中是什么呢?
。和?等效的写法是:#{}
。在mybatis当中不能使用?占位符,必须使用 #{} 来代替JDBC当中的 ?
。#{} 和 JDBC当中的 ? 是等效的。
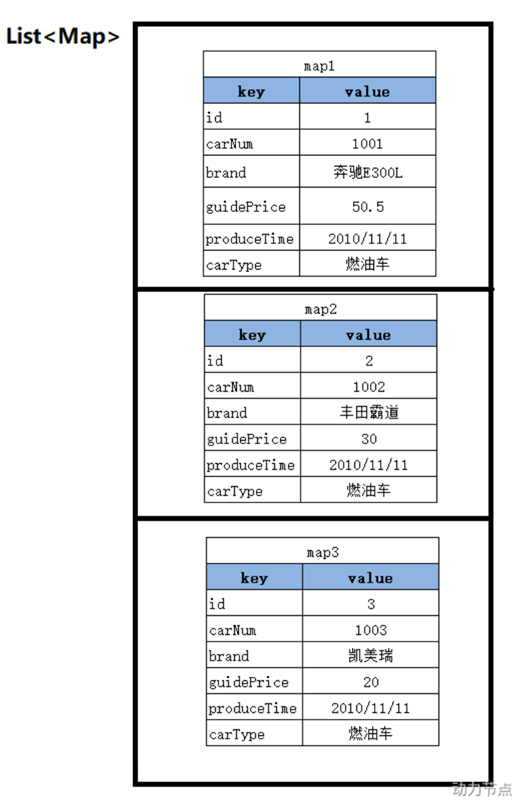
- java程序中使用Map可以给SQL语句的占位符传值:
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("k1", "1111"); map.put("k2", "比亚迪汉"); map.put("k3", 10.0); map.put("k4", "2020-11-11"); map.put("k5", "电车");
- MyBatis的insert代码
insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType});
。注意:#{}这里写什么?写map集合的key,如果key不存在,获取的是null
。一般map集合的key起名的时候要见名知意。
。测试代码
public class CarMapperTest { @Test public void testInsertCar(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // 前段传过来的数据 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("carNum", "1111"); map.put("brand", "比亚迪汉2"); map.put("guidePrice", 10.0); map.put("produceTime", "2020-11-11"); map.put("carType", "电车"); sqlSession.insert("insertCar",map); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } }
- java程序中使用POJO类给SQL语句的占位符传值:
Car car = new Car(null, “3333”, “比亚迪秦”, 30.0, “2020-11-11”, “新能源”);
。注意:占位符#{},大括号里面写:pojo类的属性名
insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
。如果把SQL语句写成这个德行:
insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,#{xyz},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
- 出现了什么问题呢?
There is no getter for property named ‘xyz’ in ‘class com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car’
mybatis去找:Car类中的getXyz()方法去了。没找到。报错了。
- 怎么解决的?
可以在Car类中提供一个getXyz()方法。这样问题就解决了。
- 通过这个测试,得出一个结论:如果使用POJO对象传递值的话,#{}这个大括号中到底写什么?
写的是get方法的方法名去掉get,然后将剩下的单词首字母小写,然后放进去。
- 例如:getUsername() --> #{username}
- 例如:getEmail() --> #{email}
- 也就是说mybatis在底层给?传值的时候,先要获取值,怎么获取的?
调用了pojo对象的get方法。例如:car.getCarNum(),car.getCarType(),car.getBrand()
。测试代码
@Test public void testInsertCarByPojo(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // 封装数据 Car car= new Car(null,"333","比亚迪秦",30.0,"2020-10-20","新能源"); sqlSession.insert("insertCar",car); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
3.delete
- 需求:根据id删除数据
将id=59的数据删除。
- 实现:
int count = sqlSession.delete("deleteById", 59);
<delete id="deleteById"> delete from t_car where id = #{fdsfd} </delete>
注意:如果占位符只有一个,那么#{}的大括号里可以随意。但是最好见名知意。
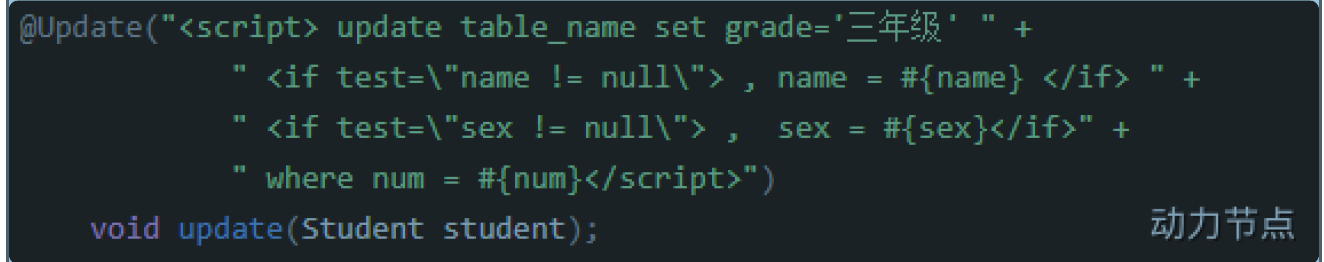
4.update
- 需求:根据id修改某条记录。
- 实现:
<update id="updateById"> update t_car set car_num=#{carNum}, brand=#{brand}, guide_price=#{guidePrice}, produce_time=#{produceTime}, car_type=#{carType} where id = #{id} </update>
Car car = new Car(4L, "9999", "凯美瑞", 30.3, "1999-11-10", "燃油车"); int count = sqlSession.update("updateById", car);
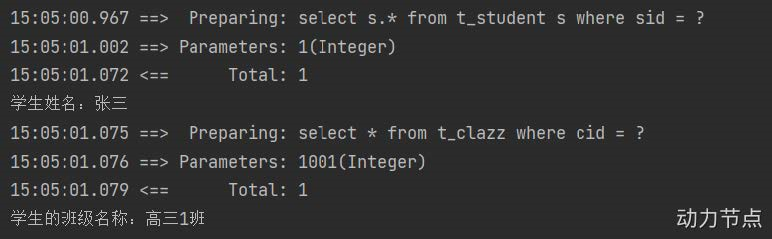
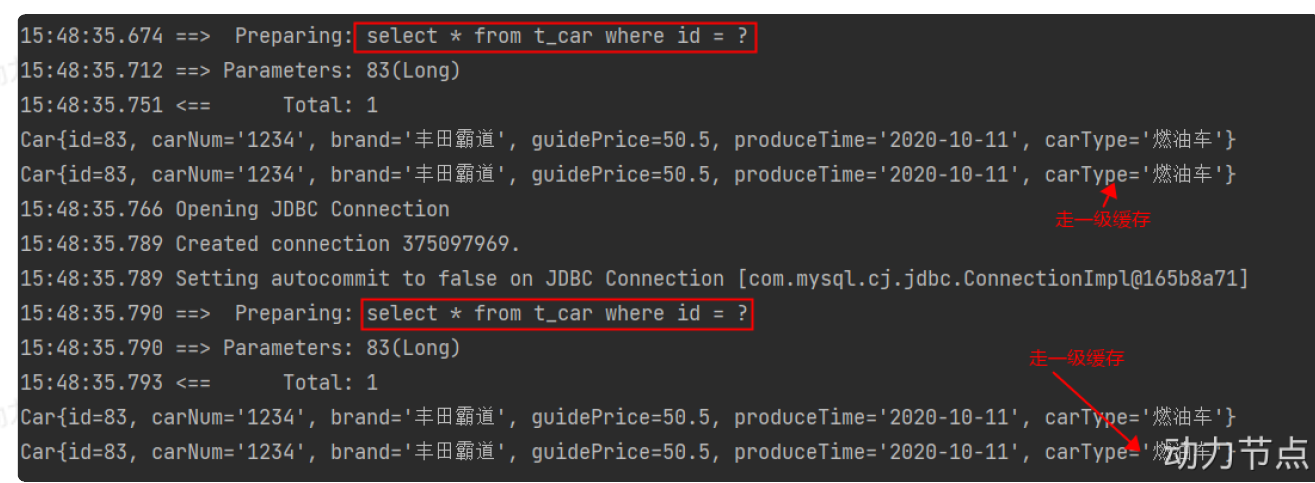
5.select(查一个)
根据主键查询的话,返回的结果一定是一个。
- 需求:根据id查询。
- 实现
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.st.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select * from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
Object car = sqlSession.selectOne("selectById", 1);
- 需要特别注意的是:
。select标签中resultType属性,这个属性用来告诉mybatis,查询结果集封装成什么类型的java对象。
。resultType通常写的是:全限定类名。
- 输出结果有点不对劲:
Car{id=1, carNum=‘null’, brand=‘宝马520’, guidePrice=null, produceTime=‘null’, carType=‘null’}
。id和brand属性有值,其他属性为null。
- carNum以及其他的这几个属性没有赋上值的原因是什么?
select * from t_car where id = 1 执行结果: +----+---------+-----------+-------------+--------------+----------+ | id | car_num | brand | guide_price | produce_time | car_type | +----+---------+-----------+-------------+--------------+----------+ | 1 | 1001 | 宝马520Li | 10.00 | 2020-10-11 | 燃油车 | +----+---------+-----------+-------------+--------------+----------+
。car_num、guide_price、produce_time、car_type这是查询结果的列名。
这些列名和Car类中的属性名对不上。
Car类的属性名:carNum、guidePrice、produceTime、carType
。那这个问题怎么解决呢?
select语句查询的时候,查询结果集的列名使用as关键字起别名的。
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id,car_num as carNum,brand,guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where id = #{id} </select> 起别名之后: +----+--------+-----------+------------+-------------+---------+ | id | carNum | brand | guidePrice | produceTime | carType | +----+--------+-----------+------------+-------------+---------+ | 1 | 1001 | 宝马520Li | 10.00 | 2020-10-11 | 燃油车 | +----+--------+-----------+------------+-------------+---------+
6.select(查所有的)
- 实现
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id,car_num as carNum,brand,guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car </select>
List<Object> cars = sqlSession.selectList("selectAll");
- 注意:resultType还是指定要封装的结果集的类型。不是指定List类型,是指定List集合中元素的类型。
selectList方法:mybatis通过这个方法就可以得知你需要一个List集合。它会自动给你返回一个List集合。
7.namespace
- 在sql mapper.xml文件当中有一个namespace,这个属性是用来指定命名空间的。用来防止id重复。
- 怎么用?
在xml文件中:
<mapper namespace="car"> <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id,car_num as carNum,brand,guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type from t_car </select> </mapper>
在java程序中的写法:
List<Object> cars = sqlSession.selectList("car.selectAll");
- 实际上,本质上,mybatis中的sqlId的完整写法: namespace.id
四、MyBatis核心配置文件
第一行表明xml文件根标签的内容,一个xml只有一个根,以及采用的dtd约束
configuration配置
properites 属性
- java.util.Properties类。是一个Map集合。key和value都是String类型
- 在properties标签中可以配置很多属性
<!--<properties>--> <!--这是其中的一个属性--> <!--<property name="属性名" value="属性值"/>--> <property name="jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/st"/> <property name="jdbc.username" value="root"/> <property name="jdbc.password" value="root"/> <!--</properties>-->
- 使用
<environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"> <property name="..." value="..."/> </transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
- 使用属性配置文件
<!--resource,一定是从类路径下开始查找资源--> <!--<properties resource="jdbc.properties" />--> <!--从绝对路径当中加载资源。绝对路径怎么写?file:///路径--> <properties url="file:///d:/jdbc.properties" />
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.jdbc.jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/st jdbc.jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123
environments 环境配置
- 一个configuration中可以包含多个环境
- 一个环境对应一个数据库
- 一个环境对应一个SqlSessionFactory对象
- 如何配置环境?
<environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"> <property name="..." value="..."/> </transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
。default
默认使用的环境 ID(比如:default=“development”)。
。id
每个 environment 元素定义的环境 ID(比如:id=“development”)。
。transactionManager
事务管理器的配置(比如:type=“JDBC”)。
。dataSource
数据源的配置,使用哪个数据库连接池(比如:type=“POOLED”)
- 根据环境id创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"),"tiki"); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // sql语句 sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close();
datasource
- 为程序提供Connection对象 [但凡是给程序提供Connection对象的,都叫做数据源]
- 数据源实际上是一套规范,JDK中有这套规范(接口):javax.sql.DataSource
- 数据库连接池实现了该接口,所以就是数据源
- 常见的数据源组件【数据库连接池】
1.阿里巴巴的德鲁伊连接处:druid
2.c3p0
3.dbcp
- type属性用来指定数据源的类型,就是指定具体使用什么方式来获取Connection对象
type=“[UNPOOLED|POOLED|JNDI]”
1.UNPOOLED:不使用数据库连接池技术。每一次请求过来之后,都是创建新的Connection对象。
2.POOLED:使用mybatis自己实现的数据库连接池。
3.JNDI:集成其它第三方的数据库连接池。
。JNDI是一套规范。
。谁实现了这套规范呢?大部分的web容器都实现了JNDI规范:
例如:Tomcat、Jetty、WebLogic、WebSphere,这些服务器(容器)都实现了JNDI规范。
。JNDI是:java命名目录接口。Tomcat服务器实现了这个规范。
- 连接池的优点
。效率高
。连接对象的创建数量可控
- UNPOOLED参数配置
。driver – 这是 JDBC 驱动的 Java 类全限定名(并不是 JDBC 驱动中可能包含的数据源类)。
。url – 这是数据库的 JDBC URL 地址。
。username – 登录数据库的用户名。
。password – 登录数据库的密码。
。defaultTransactionIsolationLevel – 默认的连接事务隔离级别。
。defaultNetworkTimeout – 等待数据库操作完成的默认网络超时时间(单位:毫秒)。查看 java.sql.Connection#setNetworkTimeout() 的 API 文档以获取更多信息
- 除了以上参数外,POOLED池中常见参数配置有:
。poolMaximumActiveConnections:连接池当中最多的正在使用的连接对象的数量上限。
最多有多少个连接可以活动。默认值10
。poolTimeToWait:如果获取连接花费了相当长的时间,连接池会每隔2秒打印日志,并且尝试获取连接对象
。poolMaximumCheckoutTime:在被强制返回之前,池中连接被检出(checked out)时间
默认值:20000 毫秒(即 20 秒)
。poolMaximumIdleConnections:最多的空闲数量
<dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> <!--提醒:正常使用连接池的话,池中有很多参数是需要设置的。设置好参数,可以让连接池发挥的更好。事半功倍的效果。--> <!--具体连接池当中的参数如何配置呢?需要反复的根据当前业务情况进行测试。--> <!--poolMaximumActiveConnections:连接池当中最多的正在使用的连接对象的数量上限。最多有多少个连接可以活动。默认值10--> <property name="poolMaximumActiveConnections" value="10"/> <!--每隔2秒打印日志,并且尝试获取连接对象--> <property name="poolTimeToWait" value="2000"/> <!--强行让某个连接空闲,超时时间的设置--> <property name="poolMaximumCheckoutTime" value="10000"/> <!--最多的空闲数量--> <property name="poolMaximumIdleConnections" value="5"/> </dataSource>
mapper
指定SQL映射文件的路径
<mappers> <!-- 执行XxxMapper.xml文件的路径--> <!-- resource属性会自动从根目录下开始查找--> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> </mappers>
五、手写MyBatis框架【无基础先跳过】
5.1 dom4j解析XML文件
第一步:编写pom.xml 引入dom4j依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.st</groupId> <artifactId>parse-xml-by-dom4j</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <!--依赖--> <dependencies> <!--dom4j的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.dom4j</groupId> <artifactId>dom4j</artifactId> <version>2.1.3</version> </dependency> <!--jaxen依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>jaxen</groupId> <artifactId>jaxen</artifactId> <version>1.2.0</version> </dependency> <!--junit依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> </properties> </project>
第二步:编写mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <environments default="mybatisDB"> <environment id="stDB"> <transactionManager type="MANAGED"/> <dataSource type="UNPOOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/st"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> <environment id="mybatisDB"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
第三步:使用dom4j解析核心配置文件文件
@Test public void testParseMyBatisConfigXML() throws Exception{ // 创建SAXReader对象 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); // 获取输入流 InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); // 读XML文件,返回document对象。document对象是文档对象,代表了整个XML文件。 Document document = reader.read(is); // 获取文档当中的根标签 //Element rootElt = document.getRootElement(); //String rootEltName = rootElt.getName(); //System.out.println("根节点的名字:" + rootEltName); //获取default默认的环境id // xpath是做标签路径匹配的。能够让我们快速定位XML文件中的元素。 // 以下的xpath代表了:从根下开始找configuration标签,然后找configuration标签下的子标签environments String xpath = "/configuration/environments"; Element environments = (Element) document.selectSingleNode(xpath); // Element是Node类的子类,方法更多,使用更便捷。 // 获取属性的值 String defaultEnvironmentId = environments.attributeValue("default"); //System.out.println("默认环境的id:" + defaultEnvironmentId); // 获取具体的环境environment xpath = "/configuration/environments/environment[@id='"+defaultEnvironmentId+"']"; //System.out.println(xpath); Element environment = (Element) document.selectSingleNode(xpath); // 获取environment节点下的transactionManager节点(Element的element()方法用来获取孩子节点) Element transactionManager = environment.element("transactionManager"); String transactionType = transactionManager.attributeValue("type"); System.out.println("事务管理器的类型:" + transactionType); // 获取dataSource节点 Element dataSource = environment.element("dataSource"); String dataSourceType = dataSource.attributeValue("type"); System.out.println("数据源的类型:" + dataSourceType); // 获取dataSource节点下的所有子节点 List<Element> propertyElts = dataSource.elements(); // 遍历 propertyElts.forEach(propertyElt -> { String name = propertyElt.attributeValue("name"); String value = propertyElt.attributeValue("value"); System.out.println(name + "=" + value); }); // 获取所有的mapper标签 // 不想从根下开始获取,你想从任意位置开始,获取所有的某个标签,xpath该这样写 xpath = "//mapper"; List<Node> mappers = document.selectNodes(xpath); // 遍历 mappers.forEach(mapper -> { Element mapperElt = (Element) mapper; String resource = mapperElt.attributeValue("resource"); System.out.println(resource); }); }
第四步:编写配置文件Carmapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="car"> <insert id="insertCar"> insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType}) </insert> <select id="selectById" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id,car_num as carNum,brand,guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
第五步:解析CarMapper.xml
@Test public void testParseSqlMapperXML() throws Exception{ SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("CarMapper.xml"); Document document = reader.read(is); // 获取namespace String xpath = "/mapper"; Element mapper = (Element) document.selectSingleNode(xpath); String namespace = mapper.attributeValue("namespace"); System.out.println(namespace); // 获取mapper节点下所有的子节点 List<Element> elements = mapper.elements(); // 遍历 elements.forEach(element -> { // 获取sqlId String id = element.attributeValue("id"); System.out.println(id); // 获取resultType String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType"); // 没有这个属性的话,会自动返回"null" System.out.println(resultType); // 获取标签中的sql语句(表示获取标签中的文本内容,而且去除前后空白) String sql = element.getTextTrim(); System.out.println(sql); // insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType}) // insert into t_car values(null,?,?,?,?,?) // mybaits封装了jdbc。早晚要执行带有?的sql语句。 // 转换 String newSql = sql.replaceAll("#\\{[0-9A-Za-z_$]*}", "?"); System.out.println(newSql); }); }
5.2 GodBatis
手写框架之前,如果没有思路,可以先参考一下mybatis的客户端程序,通过客户端程序来逆推需要的类,参考代码:
package com.st.mybatis.test; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -MyBatisCompleteTest * @Pcakage: com.st.mybatis.test.MyBatisCompleteTest * @Date: 2022年10月29日 13:21 * @Description: 完整版的MyBatis程序 */ public class MyBatisCompleteTest { public static void main(String[] args) { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 执行SQL语句,处理相关业务 int count = sqlSession.insert("insertCar"); System.out.println(count); // 执行到治理,没有发生任何异常,提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { // 回滚事务 if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.rollback(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { // 关闭会话(释放资源) if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } } }
第一步:IDEA中创建模块
- 模块:godbatis(创建普通的Java Maven模块,打包方式jar),引入相关依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.god.ibatis</groupId> <artifactId>godbatis</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <!--依赖--> <dependencies> <!--dom4j依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.dom4j</groupId> <artifactId>dom4j</artifactId> <version>2.1.3</version> </dependency> <!--jaxen依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>jaxen</groupId> <artifactId>jaxen</artifactId> <version>1.2.0</version> </dependency> <!--junit依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--mysql驱动依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.30</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> </properties> </project>
第二步:资源工具类,方便获取指向配置文件的输入流
- 这个工具类专门完成“类路径”中资源的加载。
- 工具类的构造方法都是建议私有化的。
。因为工具类中的方法都是静态的,不需要创建对象就能调用。
。为了避免new对象,所有构造方法私有化。
- 代码
package org.god.ibatis.utils; import java.io.InputStream; /** * godbatis框架提供的一个工具类。 * 这个工具类专门完成“类路径”中资源的加载。 * @author 动力节点 * @since 1.0 * @version 1.0 */ public class Resources { /** * 工具类的构造方法都是建议私有化的。 * 因为工具类中的方法都是静态的,不需要创建对象就能调用。 * 为了避免new对象,所有构造方法私有化。 * 这只是一种编程习惯。 */ private Resources(){} /** * 从类路径当中加载资源。 * @param resource 放在类路径当中的资源文件。 * @return 指向资源文件的一个输入流。 */ public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource){ return ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(resource); } }
第三步:定义SqISessionFactoryBuilder类
- SqISessionFactoryBuilder:SqlSessionFactory构建器对象。
通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法来解析godbatis-config.xml文件,然后创建SqlSessionFactory对象。
第四步:分析SqlSessionFactory类中有哪些属性
- SqISessionFactoryBuilder.build方法返回一个SqlSessionFactory类对象,那么这个对象应该具有哪些属性呢?
。根据核心配置文件,SqlSessionFactory类中至少有以下属性
- 事务管理器属性:可以灵活切换->接口
- 数据源属性:分析可得SqlSessionFactory类中可以不设置数据源
事务管理器对象中需要数据源对象获取连接对象Connection,因此可以通过事务管理器对象获取数据源对象
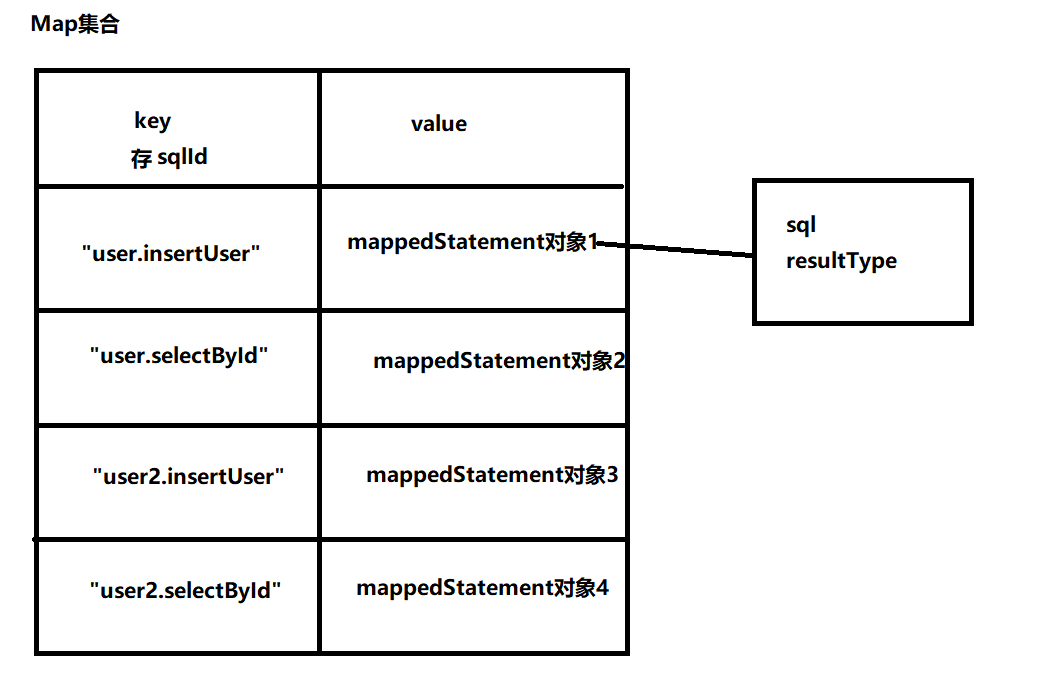
- 一个大的Map集合:存储所有mapper映射文件的sql语句,key为sqlId,value为封装好的SQL标签信息对象MappedStatement
Transaction接口
- Transaction事务管理器接口:提供管理事务方法
。所有的事务管理器都应该遵循该规范。
。JDBC事务管理器,MANAGED事务管理器都应该实现这个接口
- 代码
package org.god.ibatis.core; import java.sql.Connection; /** * 事务管理器接口。 * 所有的事务管理器都应该遵循该规范。 * JDBC事务管理器,MANAGED事务管理器都应该实现这个接口。 * Transaction事务管理器:提供管理事务方法。 * @author 动力节点 * @version 1.0 * @since 1.0 */ public interface Transaction { /** * 提交事务 */ void commit(); /** * 回滚事务 */ void rollback(); /** * 关闭事务 */ void close(); /** * 真正的开启数据库连接。 */ void openConnection(); /** * 获取数据库连接对象的。 */ Connection getConnection(); }
MappedStatement POJO类
- 根据sql标签,定义SQL标签信息对象MappedStatement[简单的]
。一个MappedStatement对象对应一个SQL标签
。一个SQL标签中的所有信息封装到MappedStatement对象当中
。面向对象编程思想
- 属性
。private String sql;
sql语句
。private String resultType;
要封装的结果集类型。有的时候resultType是null。
- 比如:insert delete update语句的时候resultType是null。
- 只有当sql语句是select语句的时候resultType才有值。
package org.god.ibatis.core; /** * 普通的java类。POJO,封装了一个SQL标签。 * 一个MappedStatement对象对应一个SQL标签。 * 一个SQL标签中的所有信息封装到MappedStatement对象当中。 * 面向对象编程思想。 * @author 动力节点 * @version 1.0 * @since 1.0 */ public class MappedStatement { /** * sql语句 */ private String sql; /** * 要封装的结果集类型。有的时候resultType是null。 * 比如:insert delete update语句的时候resultType是null。 * 只有当sql语句是select语句的时候resultType才有值。 */ private String resultType; @Override public String toString() { return "MappedStatement{" + "sql='" + sql + '\'' + ", resultType='" + resultType + '\'' + '}'; } public String getSql() { return sql; } public void setSql(String sql) { this.sql = sql; } public String getResultType() { return resultType; } public void setResultType(String resultType) { this.resultType = resultType; } public MappedStatement(String sql, String resultType) { this.sql = sql; this.resultType = resultType; } public MappedStatement() { } }
第五步:定义JdbcTransaction
GodBatis只对JdbcTransaction进行实现
- 思路
。控制事务的时候需要通过连接对象Connecton进行事务的提交、回滚以及关闭
。那么Connection对象从哪里来?—>通过属性数据源获得Connection对象
因此SqlSessionFactory类中可以不设置数据源属性:通过事务管理器对象获取数据源对象
。commit、rollback、close方法中需使用一个Connection对象,因此需要添加属性connection,通过openConnection方法对空的connection进行赋值,真正开启数据库连接
- 属性
。private DataSource dataSource;
。private boolean autoCommit;
。private Connection connection;
- 方法
。public void commit()
。public void rollback()
。public void close()
。public void openConnection()
。public Connection getConnection()
- 通过数据源对事务管理器进行完善代码
package org.god.ibatis.core; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * JDBC事务管理器(godbatis框架目前只对JdbcTransaction进行实现。) * @author 动力节点 * @version 1.0 * @since 1.0 */ public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction{ /** * 数据源属性 * 经典的设计:面向接口编程。 */ private DataSource dataSource; /** * 自动提交标志 * true表示自动提交 * false表示不采用自动提交 */ private boolean autoCommit; /** * 连接对象 */ private Connection connection; @Override public Connection getConnection() { return connection; } /** * 创建事务管理器对象 * @param dataSource * @param autoCommit */ public JdbcTransaction(DataSource dataSource, boolean autoCommit) { this.dataSource = dataSource; this.autoCommit = autoCommit; } @Override public void commit() { try { connection.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void rollback() { try { connection.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void close() { try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void openConnection(){ if (connection == null) { try { connection = dataSource.getConnection(); // 开启事务 connection.setAutoCommit(autoCommit); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
第六步︰事务管理器中需要数据源,定义UnpooledDataSource
- 数据源用于获取connection对象
- 数据源种类有:POOLED UNPOOLED JNDI
。因此也需要设计一个接口
。好消息:所有数据源都要实现JDK的规范:javax.sql.DataSource
。因此不需要自己设计接口
- UnPooledDataSource实现类
。不使用连接池,每一次都新建Connection对象。
。属性
- url
- username
- password
package org.god.ibatis.core; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException; import java.util.logging.Logger; /** * 数据源的实现类:UNPOOLED (重点实现这种方式。) * 不使用连接池,每一次都新建Connection对象。 * @author 动力节点 * @version 1.0 * @since 1.0 */ public class UnPooledDataSource implements javax.sql.DataSource{ private String url; private String username; private String password; /** * 创建一个数据源对象。 * @param driver * @param url * @param username * @param password */ public UnPooledDataSource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) { try { // 直接注册驱动 Class.forName(driver); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } this.url = url; this.username = username; this.password = password; } @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); return connection; } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return null; } @Override public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException { return null; } @Override public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException { } @Override public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException { } @Override public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException { return 0; } @Override public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException { return null; } @Override public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { return null; } @Override public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { return false; } }
第七步:SqISessionFactoryBuilder获取数据源对象和事务管理器对象
- 思路
。使用dom4j解析核心配置文件,获取事务管理器Transaction、数据源Datasource、SQL映射文件的标签元素,并根据其属性值获取相应的对象
/** * 获取事务管理器 * @param transactionElt 事务管理器标签元素 * @param dataSource 数据源对象 * @return */ private Transaction getTransaction(Element transactionElt, DataSource dataSource) { Transaction transaction = null; String type = transactionElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase(); if (Const.JDBC_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) { transaction = new JdbcTransaction(dataSource, false); // 默认是开启事务的,将来需要手动提交的。 } if (Const.MANAGED_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) { transaction = new ManagedTransaction(); } return transaction; } /** * 获取数据源对象 * @param dataSourceElt 数据源标签元素 * @return */ private DataSource getDataSource(Element dataSourceElt) { Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); // 获取所有的property List<Element> propertyElts = dataSourceElt.elements("property"); propertyElts.forEach(propertyElt -> { String name = propertyElt.attributeValue("name"); String value = propertyElt.attributeValue("value"); map.put(name, value); }); DataSource dataSource = null; String type = dataSourceElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();// 去空格并转化为大写 if (Const.UN_POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new UnPooledDataSource(map.get("driver"), map.get("url"), map.get("username"), map.get("password")); } if (Const.POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new PooledDataSource(); } if (Const.JNDI_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new JNDIDataSource(); } return dataSource; } }
第八步:SqISessionFactoryBuilder获取存储SQL的Map集合
/** * 解析所有的SqlMapper.xml文件,然后构建Map集合。 * @param sqlMapperXMLPathList * @return */ private Map<String, MappedStatement> getMappedStatements(List<String> sqlMapperXMLPathList) { Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new HashMap<>(); sqlMapperXMLPathList.forEach(sqlMapperXMLPath -> { try { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(Resources.getResourceAsStream(sqlMapperXMLPath)); Element mapper = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("mapper");// 根mapper String namespace = mapper.attributeValue("namespace");// 防止id重复 List<Element> elements = mapper.elements(); elements.forEach(element -> { String id = element.attributeValue("id"); // 这里进行了namespace和id的拼接,生成最终的sqlId String sqlId = namespace + "." + id; String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType"); String sql = element.getTextTrim();//除去前后空白 MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement(sql, resultType); mappedStatements.put(sqlId, mappedStatement); }); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); return mappedStatements; }
第九步:完善SqISessionFactoryBuilder中的buld方法
- 技巧:将常量定义在Const类中
- 主要方法
。public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream in);
解析godbatis-config.xml文件,来构建SqlSessionFactory对象。
。private Map<String, MappedStatement> getMappedStatements(List sqlMapperXMLPathList);
解析所有的SqlMapper.xml文件,然后构建Map集合。
。private Transaction getTransaction(Element transactionElt, DataSource dataSource)
获取事务管理器
。private DataSource getDataSource(Element dataSourceElt)
获取数据源对象
- 代码
package org.god.ibatis.core; import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.DocumentException; import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.Node; import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; import org.god.ibatis.utils.Resources; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * SqlSessionFactory构建器对象。 * 通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法来解析 * godbatis-config.xml文件,然后创建SqlSessionFactory对象。 * @author 动力节点 * @version 1.0 * @since 1.0 */ public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder { /** * 无参数构造方法。 */ public SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(){} /** * 解析godbatis-config.xml文件,来构建SqlSessionFactory对象。 * @param in 指向godbatis-config.xml文件的一个输入流。 * @return SqlSessionFactory对象。 */ public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream in){ SqlSessionFactory factory = null; try { // 解析godbatis-config.xml文件 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(in); Element environments = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("/configuration/environments"); String defaultId = environments.attributeValue("default"); Element environment = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("/configuration/environments/environment[@id='" + defaultId + "']"); Element transactionElt = environment.element("transactionManager"); Element dataSourceElt = environment.element("dataSource"); List<String> sqlMapperXMLPathList = new ArrayList<>(); List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//mapper"); // //获取整个配置文件中所有的mapper标签 nodes.forEach(node -> { Element mapper = (Element) node; String resource = mapper.attributeValue("resource"); sqlMapperXMLPathList.add(resource); }); // 获取数据源对象 DataSource dataSource = getDataSource(dataSourceElt); // 获取事务管理器 Transaction transaction = getTransaction(transactionElt,dataSource); // 获取mappedStatements Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = getMappedStatements(sqlMapperXMLPathList); // 解析完成之后,构建SqlSessionFactory对象。 factory = new SqlSessionFactory(transaction, mappedStatements); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return factory; } /** * 解析所有的SqlMapper.xml文件,然后构建Map集合。 * @param sqlMapperXMLPathList * @return */ private Map<String, MappedStatement> getMappedStatements(List<String> sqlMapperXMLPathList) { Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new HashMap<>(); sqlMapperXMLPathList.forEach(sqlMapperXMLPath -> { try { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(Resources.getResourceAsStream(sqlMapperXMLPath)); Element mapper = (Element) document.selectSingleNode("mapper");// 根mapper String namespace = mapper.attributeValue("namespace");// 防止id重复 List<Element> elements = mapper.elements(); elements.forEach(element -> { String id = element.attributeValue("id"); // 这里进行了namespace和id的拼接,生成最终的sqlId String sqlId = namespace + "." + id; String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType"); String sql = element.getTextTrim();//除去前后空白 MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement(sql, resultType); mappedStatements.put(sqlId, mappedStatement); }); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); return mappedStatements; } /** * 获取事务管理器 * @param transactionElt 事务管理器标签元素 * @param dataSource 数据源对象 * @return */ private Transaction getTransaction(Element transactionElt, DataSource dataSource) { Transaction transaction = null; String type = transactionElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase(); if (Const.JDBC_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) { transaction = new JdbcTransaction(dataSource, false); // 默认是开启事务的,将来需要手动提交的。 } if (Const.MANAGED_TRANSACTION.equals(type)) { transaction = new ManagedTransaction(); } return transaction; } /** * 获取数据源对象 * @param dataSourceElt 数据源标签元素 * @return */ private DataSource getDataSource(Element dataSourceElt) { Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); // 获取所有的property List<Element> propertyElts = dataSourceElt.elements("property"); propertyElts.forEach(propertyElt -> { String name = propertyElt.attributeValue("name"); String value = propertyElt.attributeValue("value"); map.put(name, value); }); DataSource dataSource = null; String type = dataSourceElt.attributeValue("type").trim().toUpperCase();// 去空格并转化为大写 if (Const.UN_POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new UnPooledDataSource(map.get("driver"), map.get("url"), map.get("username"), map.get("password")); } if (Const.POOLED_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new PooledDataSource(); } if (Const.JNDI_DATASOURCE.equals(type)) { dataSource = new JNDIDataSource(); } return dataSource; } }
第十步:在SqISessionFactory中添加openSession方法
- openSession方法:获取Sql会话对象
/** * 获取Sql会话对象。 * @return */ public SqlSession openSession(){ // 开启会话的前提是开启连接。(连接打开了) transaction.openConnection(); // 创建SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = new SqlSession(this);// 将SqlSessionFactory传入 return sqlSession; }
- SqlSession私有变量 构造方法
private SqlSessionFactory factory; public SqlSession(SqlSessionFactory factory) { this.factory = factory; }
第十一步:编写SqlSession类中commit rollback close方法
- 代码
/** * 提交事务 */ public void commit(){ factory.getTransaction().commit(); } /** * 回滚事务 */ public void rollback(){ factory.getTransaction().rollback(); } /** * 关闭事务 */ public void close(){ factory.getTransaction().close(); }
第十二步:编写SqlSession类中的insert方法
- 思路:将原sql转换为jdbc中的sql,并动态给占位符赋值
。属性名怎么获得?通过#的位置获得属性名⌈ \lceil⌈#后不能有空格⌋ \rfloor⌋
。属性值怎么获得?通过调用get属性名()方法获得属性值
。获得属性类型->set类型(index,属性值)
- 代码
/** * 执行insert语句,向数据库表当中插入记录。 * @param sqlId sql语句的id * @param pojo 插入的数据。 * @return */ public int insert(String sqlId, Object pojo){ int count = 0; try { // JDBC代码,执行insert语句,完成插入操作。 Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection(); // insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age}) String godbatisSql = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId).getSql(); // insert into t_user(id,name,age) values(?,?,?) String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?"); PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 给?占位符传值 // 难度是什么: // 第一:你不知道有多少个? // 第二:你不知道该将pojo对象中的哪个属性赋值给哪个 ? // ps.String(第几个问号, 传什么值); // 这里都是setString,所以数据库表中的字段类型要求都是varchar才行。这是godbatis比较失败的地方。 int fromIndex = 0; int index = 1; while(true){ int jingIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("#", fromIndex); if (jingIndex < 0) { break; } int youKuoHaoIndex = godbatisSql.indexOf("}", fromIndex); String propertyName = godbatisSql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim(); fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1; // 有属性名id,怎么获取id的属性值呢?调用getId()方法 String getMethodName = "get" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1); Method getMethod = pojo.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(getMethodName); Object propertyValue = getMethod.invoke(pojo); ps.setString(index, propertyValue.toString()); index++; } // 执行SQL语句 count = ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return count; }
第十三步:编写SqISession类中的selectOne方法
- 思路
。假设只有一个参数,那么直接传值即可
。怎么封装结果集?
- 通过mappedStatement获取结果类型
- 然后通过Class.forName获取Class
- 调用无参数构造方法创建对象
- 给obj的属性赋值:将查询结果的字段名作为属性名,拼接set方法进行赋值
- rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1); 下标从1开始
- 代码
/** * 执行查询语句,返回一个对象。该方法只适合返回一条记录的sql语句。 * @param sqlId * @param param * @return */ public Object selectOne(String sqlId, Object param){ Object obj = null; try { Connection connection = factory.getTransaction().getConnection(); MappedStatement mappedStatement = factory.getMappedStatements().get(sqlId); // 这是那个DQL查询语句 // select * from t_user where id = #{id} String godbatisSql = mappedStatement.getSql(); String sql = godbatisSql.replaceAll("#\\{[a-zA-Z0-9_$]*}", "?"); PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 给占位符传值 ps.setString(1, param.toString()); // 查询返回结果集 ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); // 要封装的结果类型。 String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType(); // org.god.ibatis.pojo.User // 从结果集中取数据,封装java对象 if (rs.next()) { // 获取resultType的Class Class<?> resultTypeClass = Class.forName(resultType); // 调用无参数构造方法创建对象 obj = resultTypeClass.newInstance(); // Object obj = new User(); // 给User类的id,name,age属性赋值 // 给obj对象的哪个属性赋哪个值。 /* mysql> select * from t_user where id = '1111'; +------+----------+------+ | id | name | age | +------+----------+------+ | 1111 | zhangsan | 20 | +------+----------+------+ 解决问题的关键:将查询结果的列名作为属性名。 列名是id,那么属性名就是:id 列名是name,那么属性名就是:name */ ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { String propertyName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1); // 拼接方法名 String setMethodName = "set" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1); // 获取set方法 Method setMethod = resultTypeClass.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, String.class); // 调用set方法给对象obj属性赋值 setMethod.invoke(obj, rs.getString(propertyName)); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } // 局部测试 public static void main(String[] args) { String sql = "insert into t_user values(#{id},#{name},#{age})"; int fromIndex = 0; int index = 1; while(true){ int jingIndex = sql.indexOf("#", fromIndex); if (jingIndex < 0) { break; } System.out.println(index); index++; int youKuoHaoIndex = sql.indexOf("}", fromIndex); String propertyName = sql.substring(jingIndex + 2, youKuoHaoIndex).trim(); System.out.println(propertyName); fromIndex = youKuoHaoIndex + 1; } }
5.3 GodBatis使用Maven打包
- 双击install,在本地仓库中查看是否有jar包生成
5.4 总结MyBatis框架的重要实现原理
- 为什么insert语句中 #{} 里填写的必须是属性名?
。通过属性名给占位符赋值
- 为什么select语句查询结果列名要属性名一致?
。将查询结果的字段名作为属性名,拼接set方法进行赋值
六、在WEB中应用MyBatis(使用MVC架构模式)
6.1 需求描述
完成银行账户转账的功能
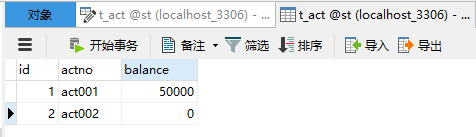
6.2 数据库表的设计和准备数据
6.3 实现步骤
第一步 :环境搭建
1.创建maven web项目
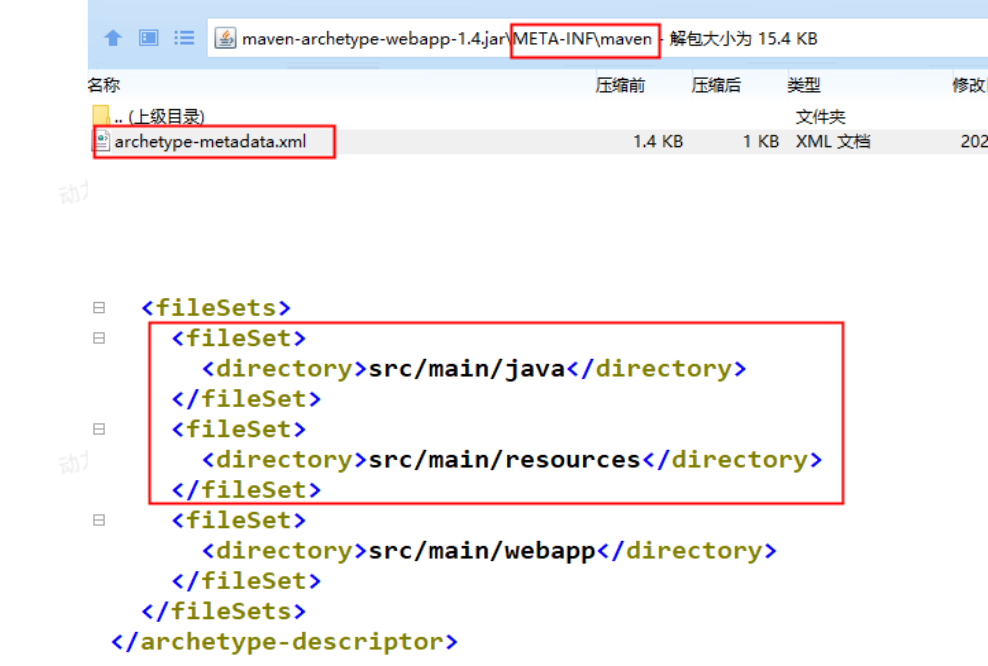
2.默认创建的maven web应用没有java和sesources目录
。手动加
。修改maven-archetype-webapp-1.4.jar中的配置文件
3.配置tomcat
4.修改web.xml文件为高版本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd" version="5.0" metadata-complete="true"> </web-app>
5.确定pom.xml文件中的打包方式是war包
6.pom.xml 引入相关依赖
。编译器版本修改为17
。引入的依赖包括:mybatis,mysql,logback,servlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.st</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis004-web</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>mybatis-004-web Maven Webapp</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.10</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.30</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.2.11</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>mybatis004-web</finalName> <pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) --> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </plugin> <!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.0.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.0</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.22.1</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.8.2</version> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project>
7.引入相关配置文件,放入resources目录
。mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"/> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!-- 执行XxxMapper.xml文件的路径--> <!-- resource属性会自动从根目录下开始查找--> <mapper resource="AccountMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
。AccountMapper.xml
。logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration debug="false"> <!-- 控制台输出 --> <appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder"> <!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符--> <pattern>[%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <!--mybatis log configure--> <logger name="com.apache.ibatis" level="TRACE"/> <logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/> <logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/> <logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/> <!-- 日志输出级别,logback日志级别包括五个:TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR --> <root level="DEBUG"> <appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/> <appender-ref ref="FILE"/> </root> </configuration>
。jdbc.properties
第二步:前段页面index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>银行账户转账</title> </head> <body> <form action="/bank/transfer" method="post"> 转出账户:<input type="text" name="fromActno"><br> 转入账户:<input type="text" name="toActno"><br> 转账金额:<input type="text" name="money"><br> <input type="submit" value="转账"> </form> </body> </html>
第三步:根据mvc架构模式创建包
- com.st.bank.pojo
- com.st.bank.service
- com.st.bank.service.impl
- com.st.bank.dao->使用mybatis框架使 dao常被命名为dao
- com.st.bank.dao.impl
- com.st.bank.web.controller
- com.st.bank.utils
- com.st.bank.exception
第四步:定义pojo类
Account
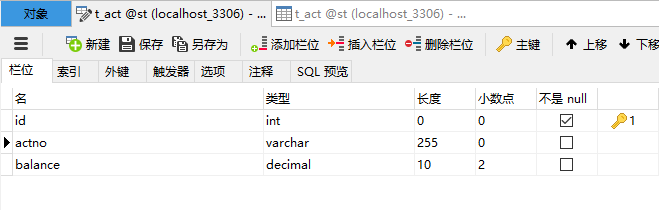
package com.st.bank.pojo; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -Account * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.pojo.Account * @Date: 2022年11月12日 20:18 * @Description:银行账户类 */ public class Account { private Long id; private String actno; private Double balance; public Account() { } public Account(Long id, String actno, Double balance) { this.id = id; this.actno = actno; this.balance = balance; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getActno() { return actno; } public void setActno(String actno) { this.actno = actno; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", actno='" + actno + '\'' + ", balance=" + balance + '}'; } }
第五步:编写AccountDao接口以及AccountDanImp实现类
- 分析dao中至少需要提供几个方法,才能完成转账
。转账前需要查询余额是否充足:selectByActno
。转账时要更新账户:update
- AccountDao接口
package com.st.bank.dao; import com.st.bank.pojo.Account; /** * 账户的DAO对象,负责t_act表中数据的CRUD */ public interface AccountDao { int updateAccount(Account account); Account selectByActno(String actno); }
- AccountDanImp实现类
package com.st.bank.dao.impl; import com.st.bank.dao.AccountDao; import com.st.bank.pojo.Account; import com.st.bank.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -AccountDaoImpl * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl * @Date: 2022年11月15日 16:12 * @Description: */ public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Override public int updateAccount(Account account) { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); int count = sqlSession.update("account.updateAccount",account); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); return count; } @Override public Account selectByActno(String actno) { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); Account account = (Account) sqlSession.selectOne("account.selectByActno", actno); sqlSession.close(); return account; } }
第六步:编写SQL映射文件
- 根据Dao接口编写sql语句
。selectByActno
。update
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="account"> <select id="selectByActno" resultType="com.st.bank.pojo.Account"> select * from t_act where actno = #{actno}; </select> <update id="updateAccount" > update t_act set balance = #{balance} where actno = #{actno}; </update> </mapper>
第七步:编写AccountService接口以及AccountServiceImpl实现类
- AccountService接口
package com.st.bank.service; import com.st.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException; import com.st.bank.exceptions.TransferException; /** * 账户业务类 */ public interface AccountService { /** 账户转账业务 * @param fromActno 转出账户 * @param toActno 转入账户 * @param money 转账金额 */ void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException; }
- AccountServiceImpl实现类
package com.st.bank.service.impl; import com.st.bank.dao.AccountDao; import com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl; import com.st.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException; import com.st.bank.exceptions.TransferException; import com.st.bank.pojo.Account; import com.st.bank.service.AccountService; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -AccountServiceImpl * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl * @Date: 2022年11月15日 16:03 * @Description: */ public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); @Override public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException { // 1. 判断转出账户的余额是否充足(select) Account fromAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno); if (fromAccount.getBalance() < money){ // 2. 如果转出账户余额不足,提示用户exception throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足"); } // 3. 如果转出账户余额充足,更新转出账户余额(update) fromAccount.setBalance(fromAccount.getBalance() - money); int count = accountDao.updateAccount(fromAccount); // 4. 更新转入账户余额(update) Account toAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno); toAccount.setBalance(toAccount.getBalance() + money); count += accountDao.updateAccount(toAccount); if (count != 2) { throw new TransferException("转账失败"); } } }
- MoneyNotEnoughException异常
package com.st.bank.exceptions; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -MoneyNotEnoughException * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException * @Date: 2022年11月15日 20:52 * @Description: */ public class MoneyNotEnoughException extends Exception{ public MoneyNotEnoughException() {} public MoneyNotEnoughException(String message) { super(message); } }
- TransferException异常
package com.st.bank.exceptions; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -TransferException * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.exceptions.TransferException * @Date: 2022年11月15日 21:03 * @Description:转账异常 */ public class TransferException extends Exception{ public TransferException() {} public TransferException(String message) { super(message); } }
第八步:编写AccountController
package com.st.bank.web; import com.st.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException; import com.st.bank.exceptions.TransferException; import com.st.bank.service.AccountService; import com.st.bank.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -AccountServlet * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.web.AccountServlet * @Date: 2022年11月15日 15:55 * @Description: */ @WebServlet("/transfer") public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet { // 为了让变量在其他方法也能使用 private AccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl(); @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 1.获取表单数据 String fromActno = request.getParameter("fromActno"); String toActno = request.getParameter("toActno"); double money = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter("money")); try { // 2.调用service的转账方法完成转账(调业务层) accountService.transfer(fromActno, toActno, money); // 3.调用视图层进行结果展示 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/success.html"); } catch (MoneyNotEnoughException e) { response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error1.html"); } catch (TransferException e) { response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error2.html"); } } }
6.4 MyBatis对象作用域以及事务管理器
6.4.1 MyBatis核心对象的作用域
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- 这个类可以被实例化、使用和丢弃,一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了。
- 因此 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 实例的最佳作用域是方法作用域(也就是局部方法变量)。
- 你可以重用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 来创建多个 SqlSessionFactory 实例,但最好还是不要一直保留着它,以保证所有的 XML 解析资源可以被释放给更重要的事情。
SqlSessionFactory
- SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例。
- 使用 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳实践是在应用运行期间不要重复创建多次,多次重建 SqlSessionFactory 被视为一种代码“坏习惯”。
- 因此 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳作用域是应用作用域application。 有很多方法可以做到,最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。
SqlSession
- 每个线程都应该有它自己的 SqlSession 实例。
- SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求request或方法作用域。
。绝对不能将 SqlSession 实例的引用放在一个类的静态域,甚至一个类的实例变量也不行。
。也绝不能将 SqlSession 实例的引用放在任何类型的托管作用域中,比如 Servlet 框架中的 HttpSession。
- 如果你现在正在使用一种 Web 框架,考虑将 SqlSession 放在一个和 HTTP 请求相似的作用域中。 换句话说,每次收到 HTTP 请求,就可以打开一个 SqlSession,返回一个响应后,就关闭它。 这个关闭操作很重要,为了确保每次都能执行关闭操作,你应该把这个关闭操作放到 finally 块中。
6.4.2 事务问题
- 在之前的转账业务中,更新了两个账户,我们需要保证它们的同时成功或同时失败,这个时候就需要使用事务机制,在transfer方法开始执行时开启事务,直到两个更新都成功之后,再提交事务
- 当出现异常时,两个账户的更新一个失败一个成功就出现了事务问题
。原因:service和dao中使用的SqlSession对象不是同一个
6.4.3 简单的ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal:实际上是一下Map集合
package com.powernode.threadlocal; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * 自定义一个ThreadLocal类 */ public class MyThreadLocal<T> { /** * 所有需要和当前线程绑定的数据要放到这个容器当中 */ private Map<Thread, T> map = new HashMap<>(); /** * 向ThreadLocal中绑定数据 */ public void set(T obj){ map.put(Thread.currentThread(), obj); } /** * 从ThreadLocal中获取数据 * @return */ public T get(){ return map.get(Thread.currentThread()); } /** * 移除ThreadLocal当中的数据 */ public void remove(){ map.remove(Thread.currentThread()); } }
6.4.4 事务的解决方法【重要】
- 为了保证service和dao中使用的SqlSession对象是同一个,可以将SqlSession对象存放到 ThreadLocal当中【保证一个线程对应一个SqlSession】
。修改SqlSessionUtil工具类:将SqlSession对象存放到 ThreadLocal当中,并添加close函数
package com.st.bank.utils; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -SqlSessionUtil * @Pcakage: com.st.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil * @Date: 2022年10月29日 14:53 * @Description:MyBatis工具类 */ public class SqlSessionUtil { private SqlSessionUtil(){};// 工具类的构方法私有化,防止new对象 private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; // 类加载时执行 // SqlSessionUtil工具类在进行第一次加载的时候,解析mybatis-config.xml文件,创建SqlSessionFactory对象 static { try { sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private static ThreadLocal<SqlSession> local = new ThreadLocal<>(); /** * @return 返回一个SqlSession对象 */ public static SqlSession openSession(){ SqlSession sqlSession = local.get(); if (sqlSession == null){ sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 将sqlSession对象绑定到当前线程 local.set(sqlSession); } return sqlSession; } /** 关闭SqlSession对象(从当前线程中溢出SqlSession对象) * @param sqlSession */ public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){ if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); local.remove(); } } }
。修改dao中的方法:AccountDaoImpl中所有方法中的提交commit和关闭close代码全部删除
package com.st.bank.dao.impl; import com.st.bank.dao.AccountDao; import com.st.bank.pojo.Account; import com.st.bank.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -AccountDaoImpl * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl * @Date: 2022年11月15日 16:12 * @Description: */ public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Override public int updateAccount(Account account) { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); int count = sqlSession.update("account.updateAccount",account); return count; } @Override public Account selectByActno(String actno) { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); Account account = (Account) sqlSession.selectOne("account.selectByActno", actno); return account; } }
。修改service中的代码:添加事务控制代码(提交事务 关闭事务)
package com.st.bank.service.impl; import com.st.bank.dao.AccountDao; import com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl; import com.st.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException; import com.st.bank.exceptions.TransferException; import com.st.bank.pojo.Account; import com.st.bank.service.AccountService; import com.st.bank.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -AccountServiceImpl * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl * @Date: 2022年11月15日 16:03 * @Description: */ public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); @Override public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException { // 添加事务控制代码 SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // 1. 判断转出账户的余额是否充足(select) Account fromAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno); if (fromAccount.getBalance() < money){ // 2. 如果转出账户余额不足,提示用户exception throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足"); } // 3. 如果转出账户余额充足,更新转出账户余额(update) fromAccount.setBalance(fromAccount.getBalance() - money); int count = accountDao.updateAccount(fromAccount); // 模拟异常 // String s = null; // s.toString(); // 4. 更新转入账户余额(update) Account toAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno); toAccount.setBalance(toAccount.getBalance() + money); count += accountDao.updateAccount(toAccount); if (count != 2) { throw new TransferException("转账失败"); } // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 关闭事务 sqlSession.close(); } }
七、使用javassist生成类
7.1 Javassist的使用
- 引入Javassist依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.javassist</groupId> <artifactId>javassist</artifactId> <version>3.29.1-GA</version> </dependency>
- 生成第一个类
@Test public void testGenerateFirstClass() throws Exception{ // 获取类池,这个类池就是用来给我生成class的 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); // 制造类(需要告诉javassist,类名是啥) CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"); // 制造方法 String methodCode = "public void insert(){System.out.println(123);}"; CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode, ctClass); // 将方法添加到类中 ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod); // 在内存中生成class ctClass.toClass(); // 类加载到JVM当中,返回AccountDaoImpl类的字节码 Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"); // 创建对象 Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); // 获取AccountDaoImpl中的insert方法 Method insertMethod = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("insert"); // 调用方法insert insertMethod.invoke(obj); }
未解决
7.2 使用Javassist生成DaoImpl类
- AccountDao接口
package com.st.bank.dao; /** * 账户的DAO对象,负责t_act表中数据的CRUD */ public interface AccountDao { void delete(); int insert(String actno); int update(String actno, Double balance); String selectByActno(String actno); }
- 使用Javassist生成AccountDaoImpl类
@Test public void testGenerateAccountDaoImpl() throws Exception{ // 获取类池 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); // 制造类 CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.st.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"); // 制造接口 CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.st.bank.dao.AccountDao"); // 实现接口 ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface); // 实现接口中所有的方法 // 获取接口中所有的方法 Method[] methods = AccountDao.class.getDeclaredMethods(); Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> { // method是接口中的抽象方法 // 把method抽象方法给实现了。 try { // public void delete(){} // public int update(String actno, Double balance){} StringBuilder methodCode = new StringBuilder(); methodCode.append("public "); // 追加修饰符列表 methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName()); // 追加返回值类型 methodCode.append(" "); methodCode.append(method.getName()); //追加方法名 methodCode.append("("); // 拼接参数 String actno, Double balance Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) { Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i]; methodCode.append(parameterType.getName()); methodCode.append(" "); methodCode.append("arg" + i); if(i != parameterTypes.length - 1){ methodCode.append(","); } } methodCode.append("){System.out.println(11111); "); // 动态的添加return语句 String returnTypeSimpleName = method.getReturnType().getSimpleName(); if ("void".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)) { }else if("int".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)){ methodCode.append("return 1;"); }else if("String".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)){ methodCode.append("return \"hello\";"); } methodCode.append("}"); System.out.println(methodCode); CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(), ctClass); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 在内存中生成class,并且加载到JVM当中 Class<?> clazz = ctClass.toClass(); // 创建对象 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) clazz.newInstance(); // 调用方法 accountDao.insert("aaaaa"); accountDao.delete(); accountDao.update("aaaa", 1000.0); accountDao.selectByActno("aaaa"); }
7.3 GenerateDaoProxy工具类P62-63
创建GenerateDaoProxy工具类,根据Dao接口,自动生成实现类的字节码文件
凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy的,SQLMapper.xml映射文件中namespace必须是dao接口的全名,id必须是dao接口中的方法名。
package com.st.bank.utils; import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.ClassPool; import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtClass; import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtMethod; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author: TIKI * @Project: mybatis -GenerateDaoProxy * @Pcakage: com.st.bank.utils.GenerateDaoProxy * @Date: 2022年11月17日 20:24 * @Description:工具类 可以动态的生成DAO的实现类(可以动态生成DAO的代理类) */ public class GenerateDaoProxy { /** * 生成dao接口实现类,并且将实现类的对象创建出来并返回。 * @param daoInterface dao接口 * @return dao接口实现类的实例化对象。 */ public static Object generate(SqlSession sqlSession, Class daoInterface){ // 类池 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); // 制造类(com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao --> com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDaoProxy) CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(daoInterface.getName() + "Proxy"); // 实际本质上就是在内存中动态生成一个代理类。 // 制造接口 CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface(daoInterface.getName()); // 实现接口 ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface); // 实现接口中所有的方法 Method[] methods = daoInterface.getDeclaredMethods(); Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> { // method是接口中的抽象方法 // 将method这个抽象方法进行实现 try { // Account selectByActno(String actno); // public Account selectByActno(String actno){ 代码; } StringBuilder methodCode = new StringBuilder(); methodCode.append("public "); methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName()); methodCode.append(" "); methodCode.append(method.getName()); methodCode.append("("); // 需要方法的形式参数列表 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) { Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i]; methodCode.append(parameterType.getName()); methodCode.append(" "); methodCode.append("arg" + i); if(i != parameterTypes.length - 1){ methodCode.append(","); } } methodCode.append(")"); methodCode.append("{"); // 需要方法体当中的代码 // 包名需要完整包名 methodCode.append("org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession sqlSession = com.st.bank.utils.SqlSessionUtil.openSession();"); // 需要知道是什么类型的sql语句 // sql语句的id是框架使用者提供的,具有多变性。对于我框架的开发人员来说。我不知道。 // 既然我框架开发者不知道sqlId,怎么办呢?mybatis框架的开发者于是就出台了一个规定: // 凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy机制的。sqlId都不能随便写。namespace必须是dao接口的全限定名称。id必须是dao接口中方法名。 String sqlId = daoInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName(); // 获取sql语句的类型 SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(sqlId).getSqlCommandType(); if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.INSERT) { } if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.DELETE) { } if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.UPDATE) { // 与先前的代码相对应 arg0 methodCode.append("return sqlSession.update(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);"); } if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) { String returnType = method.getReturnType().getName(); methodCode.append("return ("+returnType+")sqlSession.selectOne(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);"); } methodCode.append("}"); CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(), ctClass); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 创建对象 Object obj = null; try { Class<?> clazz = ctClass.toClass(); obj = clazz.newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } }
八、MyBatis中接口代理机制及使用
- 一般使用mybatis的话,一般不叫做XXXDao,叫做XXXMapper
- 使用代理机制实现xxxMapper接口的实现类
SQLMapper.xml映射文件中namespace必须是dao接口的全名,id必须是dao接口中的方法名。!!!!
// private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); // 使用GenerateDaoProxy实现AccountDao // private AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) GenerateDaoProxy.generate(SqlSessionUtil.openSession(),AccountDao.class); // 使用mybatis的代理类生成dao接口的实现类:在内存中生成dao接口的代理类,然后创建代理类的实例 // 注意:SQLMapper.xml映射文件中namespace必须是dao接口的全名,id必须是dao接口中的方法名。!!!! private AccountDao accountDao = SqlSessionUtil.openSession().getMapper(AccountDao.class);
九、MyBatis小技巧
9.1 #{}和${}
区别
- #{}:先编译sql语句,再给占位符?传值,底层是PreparedStatement实现。
。可以防止sql注入,比较常用。
- ${}:先进行sql语句拼接,然后再编译sql语句,底层是Statement实现。
。存在sql注入现象。只有在需要进行sql语句关键字拼接的情况下才会用到。
- 优先使用#{},避免sql注入的风险
- sql注入现象:sql语句的原意被扭曲
。在数据交互中,前端的数据传入到后台处理时,没有做严格的判断,导致其传入的“数据”拼接到SQL语句中后,被当作SQL语句的一部分执行。 从而导致数据库受损(被脱库、被删除、甚至整个服务器权限陷)。【百度百科】
。用户输入的信息中含有sql语句的关键字,并且这些关键字参与sql语句的编译过程,导致sql语句的原意被扭曲,进而导致sql注入
#{}的执行结果: [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = ? [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters: 新能源(String) [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - <== Total: 2
${}的执行结果: [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = 新能源 [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters: org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException: ### Error querying database. Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column '新能源' in 'where clause' ### The error may exist in CarMapper.xml ### The error may involve defaultParameterMap ### The error occurred while setting parameters ### SQL: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = 新能源 ### Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column '新能源' in 'where clause'
什么情况下必须使用${}
拼接关键字
- ${}如果需要把SQL语句的关键字放到SQL语句中,只能使用${},因为#{}是以值的形式**‘值’**放到SQL语句当中的。
- 需求:通过向sql语句中注入asc或desc关键字,来完成数据的升序或降序排列。
#{}的执行结果: Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time ? Parameters: asc(String) select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time 'asc'
${}的执行结果: Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time asc Parameters:
拼接表名
- 向SQL语句当中拼接表名,就需要使用${}
- 现实业务当中,可能会存在分表存储数据的情况。因为一张表存的话,数据量太大。查询效率比较低。
可以将这些数据有规律的分表存储,这样在查询的时候效率就比较高。因为扫描的数据量变少了。
- 日志表:专门存储日志信息的。如果t_log只有一张表,这张表中每一天都会产生很多log,慢慢的,这个表中数据会很多。
。怎么解决问题?
可以每天生成一个新表。每张表以当天日期作为名称,例如:
t_log_20220901
t_log_20220902
…
。你想知道某一天的日志信息怎么办?
假设今天是20220901,那么直接查:t_log_20220901的表即可。
- 使用#{}会是这样:select * from t_log_‘20220901’
- 使用${}会是这样:select * from t_log_20220901
批量删除
- 批量删除:一次性删除多条记录
- sql语句写法
。delete from t_user where id= 1 or id= 2 or id= 3;
。delete from t_user where id in (1, 2, 3);
- delete from t_car where id in (${ids});
模糊查询
- 需求:查询奔驰系列的汽⻋。【只要品牌brand中含有奔驰两个字的都查询出来。】
- sql语句写法
select * from t_car where brand like '%奔驰%'; select * from t_car where brand like '%比亚迪%';
- 第一种方案:
select * from t_car where brand like ‘%${brand}%’
。进行sql拼接
- 第二种方案:concat函数,这个是mysql数据库当中的一个函数,专门进行字符串拼接
select * from t_car where brand like concat(‘%’,#{brand},‘%’)
- 第三种方案:比较鸡肋了。可以不算。
select * from t_car where brand like concat(‘%’,‘${brand}’,‘%’)
- 第四种方案:
select * from t_car where brand like “%”#{brand}“%”
9.2 typeAliases
resultType属性用来指定查询结果集的封装类型,这个名字太⻓,可以起别名吗?可以。
在mybatis-config.xml文件中使用typeAliases标签来起别名,包括两种方式:
- 第一种方式:typeAlias
。type:指定给哪个类型起别名
。alias:指定别名
- 注意:别名不区分大小写
- 省略alias后,别名就是类的简名
- 第二种方式:package
将这个包下的所有的类全部自动起别名,别名就是简类名,不区分大小写
<typeAliases> <!--别名自己指定的--> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="aaa"/> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" alias="bbb"/> <!--采用默认的别名机制--> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"/> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log"/> <!--包下所有的类自动起别名。使用简名作为别名。--> <package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/> </typeAliases>
- namespace不能使用别名机制,只能使用全限定接口名称
9.3 mappers
mybatis-config.xml文件中的mappers标签。
mapper标签的作用是指定SqlMapper.xml文件的路径
SQL映射文件的配置方式包括四种:
- resource:从类的根路径下开始查找资源。
。要求SQL映射文件必须放在resources目录下或其子目录下
- url:从指定的全限定资源路径中 加载
- class:使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名,必须带有包名的。
。SQL映射文件和mapper接口放在同一个目录下
。SQL映射文件的名字也必须和mapper接口名一致
思考:mapper标签的作用是指定SqlMapper.xml文件的路径,指定接口名有什么用呢?
如果你class指定是:com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper
那么mybatis框架会自动去com/powernode/mybatis/mapper目录下查找CarMapper.xml文件。
注意:也就是说:如果你采用这种方式,那么你必须保证CarMapper.xml文件和CarMapper接口必须在同一个目录下。并且名字一致。
CarMapper接口-> CarMapper.xml
LogMapper接口-> LogMapper.xml
提醒!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
在IDEA的resources目录下新建多重目录的话,必须是这样创建:
com/powernode/mybatis/mapper
不能这样:
com.powernode.mybatis.mapper
- package:将包内的映射器接⼝实现全部注册为映射器
要求同上
。SQL映射文件和mapper接口放在同一个目录下
。SQL映射文件的名字也必须和mapper接口名一致
<mappers> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> 要求类的根路径下必须有:CarMapper.xml <mapper url="file:///d:/CarMapper.xml"/> 要求在d:/下有CarMapper.xml文件 <mapper class="全限定接口名,带有包名"/> <package name="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper"/> </mappers>
9.4 idea配置文件模板
在File->Settings->Editor->File and Code Templates中添加模板
- MyBatis核心配置文件 mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <properties resource="" /> <typeAliases> <package name=""/> </typeAliases> <environments default="stDB"> <environment id="stDB"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <package name=""/> </mappers> </configuration>
- MyBatisSQL映射文件 XXXMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace=""> </mapper>
9.5 插入数据时获取自动生成的主键
- 前提:主键是⾃动生成的。
- 业务背景:插入一条新的记录之后,⾃动生成了主键,⽽这个主键需要在其他表中使用时。
。比如:一个用户有多个⻆⾊。
- 代码
<!-- useGeneratedKeys="true" 使用自动生成的主键值。 keyProperty="id" 指定主键值赋值给对象的哪个属性。这个就表示将主键值赋值给Car对象的id属性。 --> <insert id="insertCarUseGeneratedKeys" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType}) </insert>
@Test public void testInsertCarUseGeneratedKeys(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = new Car(null,"9991", "凯美瑞", 30.0, "2020-11-11", "燃油车"); mapper.insertCarUseGeneratedKeys(car); System.out.println(car); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
十、MyBatis参数处理
Mapper接口中参数的问题
10.1 单个简单类型参数
- 简单类型包括
。byte short int long float double char
。Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Character
。String
。java.util.Date
。java.sql.Date
- 简单类型对于mybatis来说都是可以自动类型识别的:
也就是说对于mybatis来说,它是可以自动推断出ps.setXxxx()方法的。ps.setString()还是 ps.setInt()。
- 完整代码
。其中sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,以及select标签中的parameterType属性,都是用来帮助 mybatis进行类型确定的。【可以省略】
。parameterType属性:告诉mybatis框架,这个方法的参数类型是什么的
mybatis框架由自动推断机制[获取实际方法调用的参数类型],所以大部分情况下parameterType属性都是可以省略不写的
SQL语句最终是这样的:
select * from t_student where id = ?
JDBC代码是一定要给?传值的。
怎么传值?ps.setXxx(第几个问号, 传什么值);
ps.setLong(1, 1L); ps.setString(1, “zhangsan”); ps.setDate(1, new Date()); ps.setInt(1, 100); …
mybatis底层到底调用setXxx的哪个方法,取决于parameterType属性的值。
<select id="selectById" resultType="Student" parameterType="long"> select * from t_student where id = #{id} </select> <!--加上Type mybatis不需要做自动类型推断--> <select id="selectByName" resultType="student"> select * from t_student where name = #{name, javaType=String, jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select>
- 如果参数只有一个的话,#{}里面的内容就随便写了。对于${}来说,注意加单引号。
10.2 Map参数
- 这种方式是⼿动封装Map集合,将每个条件以key和value的形式存放到集合中。然后在使用的时候通过# {map集合的key}来取值。
- 代码
<!--<insert id="insertStudentByMap" parameterType="map">--> <insert id="insertStudentByMap"> insert into t_student(id,name,age,sex,birth,height) values(null,#{姓名},#{年龄},#{性别},#{生日},#{身高}) </insert>
@Test public void testInsertStudentByMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("姓名", "赵六"); map.put("年龄", 20); map.put("身高", 1.81); map.put("性别", '男'); map.put("生日", new Date()); mapper.insertStudentByMap(map); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
10.3 pojo实体类参数
- #{}里面写的是属性名字。这个属性名其本质上是:set/get方法名去掉set/get之后 的名字。
- 代码
<!--<insert id="insertStudentByPOJO" parameterType="student">--> <insert id="insertStudentByPOJO"> insert into t_student(id,name,age,sex,birth,height) values(null,#{name},#{age},#{sex},#{birth},#{height}) </insert>
@Test public void testInsertStudentByPOJO(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); // POJO对象 Student student = new Student(); student.setName("张飞"); student.setAge(50); student.setSex('女'); student.setBirth(new Date()); student.setHeight(10.0); mapper.insertStudentByPOJO(student); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
10.4 多参数
- 需求:使用多个参数一起进行查询
- 实现原理:实际上在mybatis底层会创建一个map集合,以arg0或者param1为key,以方法上的参数为 value
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("arg0", name); map.put("arg1", sex); map.put("param1", name); map.put("param2", sex); // 所以可以这样取值:#{arg0} #{arg1} #{param1} #{param2} // 其本质就是#{map集合的key}
- 代码
<!-- 注意:低版本的mybatis中,使用的是:#{0}和#{1},以及#{2}... 高版本的mybatis中,使用的是: #{arg0} #{arg1} #{arg2} #{arg3} #{arg4} #{param1} #{param2} #{param3} #{param4} --> <select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="Student"> <!--select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{arg1}--> <!--select * from t_student where name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}--> select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{param2} </select>
@Test public void testSelectByNameAndSex(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex("张三", '男'); students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); sqlSession.close(); }
10.5 @Param注解(命名参数)
- 使用 @Param注解即可自定义map集合的key,可以增强可读性。
。@Param(“这⾥填写的其实就是map集合的key”)
。使用了@Param注解之后,arg0和arg1失效了
。使用了@Param注解之后,param1和param2还可以用
- 代码
StudentMapper接⼝
/** * 根据name和age查询 * value可以省略不写 * @param name * @param age * @return */ List<Student> selectByNameAndAge(@Param(value="name") String name, @Param("age") int age);
<select id="selectByNameAndSex2" resultType="Student"> <!--使用了@Param注解之后,arg0和arg1失效了--> <!--select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{arg1}--> <!--使用了@Param注解之后,param1和param2还可以用--> <!--select * from t_student where name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}--> select * from t_student where name = #{name} and sex = #{sex} </select>
@Test public void testSelectByNameAndSex2(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // mapper实际上指向了代理对象 StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); // mapper是代理对象 // selectByNameAndSex2是代理方法 List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex2("张三", '男'); students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student)); sqlSession.close(); }
10.6 @Param源码分析
- 代理模式
。代理对象 中介公司
。代理方法 找房子
。目标对象 我
。目标方法 找房子
- 源码分析
10.7 数组、集合
十一、MyBatis查询语句返回结果专题
- select标签的returnType属性,用来指定返回结果的类型
。mybatis为常见的Java类型内建的别名
- select标签的resultMap属性,用来指定使用哪个结果映射。resultMap后面的值是resultMap的id
11.1 返回pojo类 Car
查询结果是一条的话,返回一个pojo对象
查询结果是一条的话可以使用List集合接收吗?当然可以。
- 接口
/** * 根据id查询Car信息 * @param id * @return */ Car selectById(Long id);
- mapper.xml
<!--声明一个SQL片段--> <sql id="carColumnNameSql"> id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType </sql> <select id="selectById" resultType="car"> select <!--将声明的sql片段包含进来。--> <include refid="carColumnNameSql"/> from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = mapper.selectById(158L); System.out.println(car); sqlSession.close(); }
11.2 返回List<Car>
当查询的记录条数是多条的时候,必须使用集合接收。
如果使用单个实体类接收会出现异常TooManyResultsException。
- mapper接口
/** * 获取所有的Car * @return */ List<Car> selectAll();
- mapper.xml
返回car
<select id="selectAll" resultType="car"> select <include refid="carColumnNameSql"/> from t_car </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAll(); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
11.3 返回Map
当返回的数据,没有合适的实体类对应的话,可以采用Map集合接收。字段名做key,字段值做value。
查询如果可以保证只有一条数据,则返回一个Map集合即可。
- 接口
/** * 根据id获取汽车信息。将汽车信息放到Map集合中。 * +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+ * | id | car_num | brand | guide_price | produce_time | car_type | * +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+ * | 158 | 1111 | 比亚迪汉 | 3.00 | 2000-10-10 | 新能源 | * +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+ * * Map<String, Object> * k v * ----------------------- * "id" 158 * "car_num" 1111 * "brand" 比亚迪汉 * .... * * @param id * @return */ Map<String, Object> selectByIdRetMap(Long id);
- xml
<select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map"> select * from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByIdRetMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Map<String, Object> car = mapper.selectByIdRetMap(158L); System.out.println(car); sqlSession.close(); }
11.4 返回List<Map>
查询结果条数⼤于等于1条数据,则可以返回一个存储Map集合的List集合。List<Map>等同于List<Car>
- mapper接口
@Test public void testSelectAllRetListMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Map<String, Object>> maps = mapper.selectAllRetListMap(); maps.forEach(map -> System.out.println(map)); sqlSession.close(); }
- mapper.xml
map
<!--这个resultType不是list,是map--> <select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map"> select * from t_car </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectAllRetListMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Map<String, Object>> maps = mapper.selectAllRetListMap(); maps.forEach(map -> System.out.println(map)); sqlSession.close(); }
11.5 返回Map<String,Map>
返回一个大的Map集合:拿Car的id做key,以后取出对应的Map集合时更方便。
- mapper接口
/** * 查询所有的Car,返回一个大Map集合。 * Map集合的key是每条记录的主键值。 * Map集合的value是每条记录。 * { * 160={car_num=3333, id=160, guide_price=32.00, produce_time=2000-10-10, brand=奔驰E300L, car_type=新能源}, * 161={car_num=4444, id=161, guide_price=32.00, produce_time=2000-10-10, brand=奔驰C200, car_type=新能源}, * 162={car_num=9999, id=162, guide_price=30.00, produce_time=2020-10-11, brand=帕萨特, car_type=燃油车}, * 163={car_num=9991, id=163, guide_price=30.00, produce_time=2020-11-11, brand=凯美瑞, car_type=燃油车}, * 158={car_num=1111, id=158, guide_price=3.00, produce_time=2000-10-10, brand=比亚迪汉, car_type=新能源}, * 159={car_num=2222, id=159, guide_price=32.00, produce_time=2000-10-10, brand=比亚迪秦, car_type=新能源} * } * @return */ @MapKey("id") // 将查询结果的id值作为整个大Map集合的key。 Map<Long, Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetMap();
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectAllRetMap" resultType="map"> select * from t_car </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectAllRetMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Map<Long, Map<String, Object>> map = mapper.selectAllRetMap(); System.out.println(map); sqlSession.close(); }
11.6 resultMap结果映射
- 查询结果的列名和java对象的属性名对应不上怎么办?
。第一种方式:as给列起别名
。第二种方式:使用resultMap进行结果映射
。第三种方式:是否开启驼峰命名自动映射(配置settings)
使用resultMap进行结果映射 【重要】
select标签的resultMap属性,用来指定使用哪个结果映射。
resultMap:指定数据库表的字段名和Java类的属性名的对应关系
- type属性:用来指定POJO类的类名。
- id属性:指定resultMap的唯一标识。这个id将来要在select标签中使用。
- id标签:如果有主键,建议这里配置一个id标签,注意:这不是必须的。
。但是官方的解释是什么呢?这样的配置可以让mybatis提高效率。
- result标签
。property后面填写POJO类的属性名
。column后面填写数据库表的字段名
。javaType
。jdbcType
- association标签:关联,多对一
一个Student对象关联一个Clazz对象
。property属性:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名
。javaType属性:用来指定要映射的java类型。
。id标签
。result标签
分布查询时需使用的属性
。property属性:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名
。select属性:关联对象中对应的sql语句的id
。column属性:select属性对应的sql语句中的执行条件,上步中返回的结果中所需要的字段名
。fetchType属性:lazy 支持延迟加载
- collection标签:集合;一对多
一个Clazz对象关联一个Student对象
。property属性:提供要映射集合的属性名。
。ofType 属性:用来指定集合当中的元素类型
分布查询时需使用的属性名
。property属性:提供要映射的集合的属性名
。select属性:关联对象中对应的sql语句的id
。column属性:select属性对应的sql语句中的执行条件,上步中返回的结果中所需要的字段名
。fetchType属性:lazy 支持延迟加载
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 查询所有的Car信息。使用resultMap标签进行结果映射。 * @return */ List<Car> selectAllByResultMap();
- mapper.xml
<!-- 1.专门定义一个结果映射,在这个结果映射当中指定数据库表的字段名和Java类的属性名的对应关系。 2. type属性:用来指定POJO类的类名。 3. id属性:指定resultMap的唯一标识。这个id将来要在select标签中使用。 --> <resultMap id="carResultMap" type="Car"> <!--如果数据库表中有主键,一般都是有主键,要不然不符合数据库设计第一范式。--> <!--如果有主键,建议这里配置一个id标签,注意:这不是必须的。但是官方的解释是什么呢?这样的配置可以让mybatis提高效率。--> <id property="id" column="id"/> <!--<result property="id" column="id"/>--> <!--property后面填写POJO类的属性名--> <!--column后面填写数据库表的字段名--> <result property="carNum" column="car_num" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> <!--如果column和property是一样的,这个可以省略。--> <!--<result property="brand" column="brand"/>--> <result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price"/> <result property="produceTime" column="produce_time"/> <result property="carType" column="car_type" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> </resultMap> <!--select标签的resultMap属性,用来指定使用哪个结果映射。resultMap后面的值是resultMap的id--> <select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap"> select * from t_car </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectAllByResultMap(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAllByResultMap(); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
是否开启驼峰命名自动映射
- 使用这种方式的前提是:属性名遵循Java的命名规范,数据库表的列名遵循SQL的命名规范。
。Java命名规范:首字母小写,后面每个单词首字母大写,遵循驼峰命名方式。
。SQL命名规范:全部小写,单词之间采用下划线分割。
- 在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行配置
<!--放在properties标签后⾯--> <settings> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings>
十二、动态SQL
- 需求:有些SQL语句需要进行动态拼接
- 使用场景
。批量删除
。多条件查询
12.1 if 标签
if标签
1.if标签中test属性是必须的。
2.if标签中test属性的值是false或者true。
3.如果test是true,则if标签中的sql语句就会拼接。反之,则不会拼接。
4.test属性中可以使用的是:
。当使用了@Param注解,那么test中要出现的是@Param注解指定的参数名。@Param(“brand”),那么这里只能使用brand
。当没有使用@Param注解,那么test中要出现的是:param1 param2 param3 arg0 arg1 arg2…
。当使用了POJO,那么test中出现的是POJO类的属性名
5.在mybatis的动态SQL当中,不能使用&&,只能使用and。
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 多条件查询 * @param brand 品牌 * @param guidePrice 指导价 * @param carType 汽车类型 * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiCondition(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);
- mapper.xml
。1 = 1使sql语句恒成立
<select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car where 1 = 1 <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByMultiCondition(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 假设三个条件都不是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("比亚迪", 2.0, "新能源"); // 假设三个条件都是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("", null, ""); // 假设后两个条件不为空,第一个条件为空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("", 2.0, "新能源"); // 假设第一个条件不是空,后两个条件是空 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("比亚迪", null, ""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
12.2 where标签
where标签的作用:让where子句更加动态智能。
- 所有条件都为空时,where标签保证不会生成where⼦句。
- 自动去除某些条件前面多余的and或or,后面多余的不会去除
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 使用where标签,让where子句更加的智能。 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithWhere(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectByMultiConditionWithWhere" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <!--where标签是专门负责where子句动态生成的。--> <where> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </where> </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithWhere(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 三个条件都不是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("比亚迪", 2.0, "新能源"); // 三个条件都是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("", null, ""); // 如果第一个条件是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("", 2.0, "新能源"); // 后面两个条件是空 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("比亚迪", null, ""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
12.3 trim标签
trim标签的属性:
- prefix:在trim标签中的语句前添加内容
- suffix:在trim标签中的语句后添加内容
- prefixOverrides:前缀覆盖掉(去掉)
- suffixOverrides:后缀覆盖掉(去掉)
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 使用trim标签 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithTrim(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectByMultiConditionWithTrim" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <!-- prefix:加前缀 suffix:加后缀 prefixOverrides:删除前缀 suffixOverrides:删除后缀 --> <!--prefix="where" 是在trim标签所有内容的前面添加 where--> <!--suffixOverrides="and|or" 把trim标签中内容的后缀and或or去掉--> <trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and|or"> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" or </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price > #{guidePrice} and </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> car_type = #{carType} </if> </trim> </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithTrim(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("比亚迪", null, ""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
12.4 set标签
主要使用在update语句当中,用来生成set关键字,同时去掉最后多余的“,”
比如我们只更新提交的不为空的字段,如果提交的数据是空或者"",那么这个字段我们将不更新。
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 使用set标签 * @param car * @return */ int updateBySet(Car car);
- mapper.xml
<update id="updateBySet"> update t_car <set> <if test="carNum != null and carNum != ''">car_num = #{carNum},</if> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''">brand = #{brand},</if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''">guide_price = #{guidePrice},</if> <if test="produceTime != null and produceTime != ''">produce_time = #{produceTime},</if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''">car_type = #{carType},</if> </set> where id = #{id} </update>
不使用set标签
<update id="updateById"> update t_car set car_num = #{carNum}, brand = #{brand}, guide_price = #{guidePrice}, produce_time = #{produceTime}, car_type = #{carType} where id = #{id} </update>
- test
@Test public void testUpdateBySet(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = new Car(158L, null,"丰田霸道",null,null,null); mapper.updateBySet(car); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
12.5 choose when otherwise
语法格式:等同于 if elseif else
<choose> <when></when> <when></when> <when></when> <otherwise></otherwise> </choose>
- mapper接口
/** * 使用choose when otherwise标签。 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByChoose(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectByChoose" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <where> <choose> <when test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </when> <when test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price > #{guidePrice} </when> <otherwise> car_type = #{carType} </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByChoose(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 三个条件都不为空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose("丰田霸道",1.0,"新能源"); // 第一个条件是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,1.0,"新能源"); // 前两个条件都是空 //List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,null,"新能源"); // 全部都是空 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,null,null); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
12.6 foreach标签
循环数组或集合,动态生成sql
- foreach标签的属性:
。collection:指定数组或者集合
。item:代表数组或集合中的元素
。separator:循环之间的分隔符
。open: foreach循环拼接的所有sql语句的最前面以什么开始。
。close: foreach循环拼接的所有sql语句的最后面以什么结束。
批量删除
- mapper接口
/** * 批量删除。foreach标签 * @param ids * @return */ int deleteByIds(@Param("ids") Long[] ids);
- mapper.xml
<delete id="deleteByIds"> <!-- delete from t_car where id in (id1,id2,id3) --> delete from t_car where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")"> #{id} </foreach> </delete>
<delete id="deleteByIds2"> delete from t_car where <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="or"> id=#{id} </foreach> </delete>
- test
@Test public void testDeleteByIds(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Long[] ids = {158L,159L,160L}; int count = mapper.deleteByIds(ids); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
批量添加
- mapper接口
/** * 批量插入,一次插入多条Car信息 * @param cars * @return */ int insertBatch(@Param("cars") List<Car> cars);
- mapper.xml
<insert id="insertBatch"> insert into t_car values <foreach collection="cars" item="car" separator=","> (null,#{car.carNum},#{car.brand},#{car.guidePrice},#{car.produceTime},#{car.carType}) </foreach> </insert>
- test
@Test public void testInsertBatch(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car1 = new Car(null,"1200", "帕萨特1", 30.0, "2020-11-11", "燃油车"); Car car2 = new Car(null,"1201", "帕萨特2", 30.0, "2020-11-11", "燃油车"); Car car3 = new Car(null,"1202", "帕萨特3", 30.0, "2020-11-11", "燃油车"); List<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>(); cars.add(car1); cars.add(car2); cars.add(car3); mapper.insertBatch(cars); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
12.7 sql标签与include标签
- sql标签用来声明sql片段
- include标签用来将声明的sql片段包含到某个sql语句当中
- 作用:
。代码复用
。易维护
代码
- mapper接口
- mapper.xml
<!--声明一个SQL片段--> <sql id="carColumnNameSql"> id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType </sql> <select id="selectById" resultType="car"> select <!--将声明的sql片段包含进来。--> <include refid="carColumnNameSql"/> from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
- test
十三、MyBatis的高级映射及延迟加载
- 高级映射
。多对一
。一对多
。多对多:分解成两个一对多
。一对一
- 怎么区分主表和副表?
谁在前谁是主表->JVM中的主对象
。多对一:多是主表
。一对多:一是主表
- 多对一
。在主对象类中加一个副对象的属性
- 一对多
。一对多的实现,通常是在一的一方中有List集合属性
比如在Clazz类中添加List<Student> stus; 属性
13.1 多对一
许多学生对应一个班级
- 案例:根据学生的编号查询对应的班级信息【班级id+班级名称】
实现方式有多种,常见的包括三种:
- 第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射
1.在pojo类中添加副对象属性
2.编写sql语句:使用左外连接
3.编写resultMap
- 第二种方式:一条SQL语句,association标签。
1.在pojo类中添加副对象属性
2.编写sql语句:使用左外连接
3.与方式一区别在于resultMap,将关联对象使用association标签进行映射
association:翻译为关联。一个Student对象关联一个Clazz对象
。property:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名。
。javaType:用来指定要映射的java类型。
- 第三种方式:两条SQL语句,分步查询。(这种方式常用:优点一是可复用。优点二是支持懒加载/延迟加载。)
。方法:
1.在pojo类中添加副对象属性
2.编写sql语句:使用左外连接
3.在association标签中映射关联对象,并配置以下属性
- property属性:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名
- select属性:关联对象中对应的sql语句的id
- column属性:select属性对应的sql语句中的执行条件,上步中返回的结果中所需要的字段名
- fetchType属性:lazy 支持延迟加载
。分步查询的优点:
- 第一:复用性增强。可以重复利用。(大步拆成N多个小碎步。每一个小碎步更加可以重复利用。)
- 第二:采用这种分步查询,可以充分利用他们的延迟加载/懒加载机制。
延迟加载
- 什么是延迟加载(懒加载),有什么用?
。延迟加载的核心原理是:用的时候再执行查询语句。不用的时候不查询。
。作用:提高性能。尽可能的不查,或者说尽可能的少查。来提高效率。
- 在mybatis当中怎么开启延迟加载呢?
。association标签中添加fetchType=“lazy”
注意:默认情况下是没有开启延迟加载的。需要设置:fetchType=“lazy”
这种在association标签中配置fetchType=“lazy”,是局部的设置,只对当前的association关联的sql语句起作用。
。在实际的开发中,大部分都是需要使用延迟加载的,所以建议开启全部的延迟加载机制:
在mybatis核心配置文件中添加全局配置:lazyLoadingEnabled=true
- 实际开发中的模式:
。把全局的延迟加载打开。
。如果某一步不需要使用延迟加载,请设置:fetchType=“eager”
- 懒加载执行效果对比:如果需要使用到学生所在班级的名称,这个时候才会执行关联的sql语句
。不使用cname
。使用cname
第一种方式:级联属性映射
代码
- Student pojo类:添加clazz属性
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo; import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.ClazzMapper; /** * 学生信息 */ public class Student { // Student是多的一方 private Integer sid; private String sname; private Clazz clazz; // Clazz是少的一方。 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "sid=" + sid + ", sname='" + sname + '\'' + ", clazz=" + clazz + '}'; } public Clazz getClazz() { return clazz; } public void setClazz(Clazz clazz) { this.clazz = clazz; } //省略其他get set... }
- StudentMapper接口
/** * 根据id获取学生信息。同时获取学生关联的班级信息。 * @param id 学生的id * @return 学生对象,但是学生对象当中含有班级对象。 */ Student selectById(Integer id);
- StudentMapper.xml
<!--多对一映射的第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射。左外连接--> <resultMap id="studentResultMap" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid"/> <result property="sname" column="sname"/> <result property="clazz.cid" column="cid"/> <result property="clazz.cname" column="cname"/> </resultMap> <select id="selectById" resultMap="studentResultMap"> select s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname from t_stu s left join t_clazz c on s.cid = c.cid where s.sid = #{sid} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student student = mapper.selectById(1); System.out.println(student); sqlSession.close(); }
第二种方式:association
代码
- StudentMapper接口
/** * 一条SQL语句,association * @param id * @return */ Student selectByIdAssociation(Integer id);
- StudentMapper.xml
<!--一条SQL语句,association。--> <resultMap id="studentResultMapAssociation" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid"/> <result property="sname" column="sname"/> <!-- association:翻译为关联。一个Student对象关联一个Clazz对象 property:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名。 javaType:用来指定要映射的java类型。 --> <association property="clazz" javaType="Clazz"> <id property="cid" column="cid"/> <result property="cname" column="cname"/> </association> </resultMap> <select id="selectByIdAssociation" resultMap="studentResultMapAssociation"> select s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname from t_stu s left join t_clazz c on s.cid = c.cid where s.sid = #{sid} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByIdAssociation(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student student = mapper.selectByIdAssociation(4); System.out.println(student); sqlSession.close(); }
第三种方式:分步查询
代码
- StudentMapper接口
/** * 根据班级编号查询学生信息。 * @param cid * @return */ List<Student> selectByCidStep2(Integer cid); /** * 分部查询第一步:先根据学生的sid查询学生的信息。 * @param sid * @return */ Student selectByIdStep1(Integer sid);
- StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByCidStep2" resultType="Student"> select * from t_stu where cid = #{cid} </select> <!--两条SQL语句,完成多对一的分步查询。--> <!--这里是第一步:根据学生的id查询学生的所有信息。这些信息当中含有班级id(cid)--> <resultMap id="studentResultMapByStep" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid"/> <result property="sname" column="sname"/> <association property="clazz" select="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.ClazzMapper.selectByIdStep2" column="cid" fetchType="eager"/> </resultMap> <select id="selectByIdStep1" resultMap="studentResultMapByStep"> select sid,sname,cid from t_stu where sid = #{sid} </select>
- ClazzMapper接口
/** * 分步查询第二步:根据cid获取班级信息。 * @param cid * @return */ Clazz selectByIdStep2(Integer cid);
- ClazzMapper.xml
<!--分步查询第二步:根据cid获取班级信息。--> <select id="selectByIdStep2" resultType="Clazz"> select cid,cname from t_clazz where cid = #{cid} </select>
- StudentMapperTest
@Test public void testSelectByIdStep1(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student student = mapper.selectByIdStep1(5); //System.out.println(student); // 只需要看学生的名字 System.out.println(student.getSname()); // 程序执行到这里了,我想看看班级的名字 //System.out.println(student.getClazz().getCname()); sqlSession.close(); }
代码
- mapper接口
- mapper.xml
- test
- StudentMapper接口
- StudentMapper.xml
- ClazzMapper接口
- ClazzMapper.xml
- StudentMapperTest
13.2 一对多
- 注意:实际开发中不能Student包含Clazz,Clazz包含Student,输出为null可以,不能两端都有值
- 案例:根据班级编号查询班级信息【班级中的学生编号及姓名】
- 一对多的实现,通常是在一的一方中有List集合属性。
在Clazz类中添加List<Student> stus; 属性。
- 实现方式
。collection
1.在主对象类中添加List<副对象>属性
2.编写sql语句:使用左外连接
3.将集合对象使用collection标签进行映射
collection:翻译为集合。比如一个Clazz对象对应一个Student集合
- property属性:提供要映射集合的属性名。
- ofType 属性:用来指定集合当中的元素类型。
。分布查询
1.在主对象类中添加List<副对象>属性
2.编写sql语句:使用左外连接
3.将集合对象使用collection标签进行映射并配置以下属性
- property属性:提供要映射的集合的属性名
- select属性:关联对象中对应的sql语句的id
- column属性:select属性对应的sql语句中的执行条件,上步中返回的结果中所需要的字段名
- fetchType属性:lazy 支持延迟加载
- clazz pojo类代码
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo; import java.util.List; /** * 班级信息 */ public class Clazz { private Integer cid; private String cname; private List<Student> stus; @Override public String toString() { return "Clazz{" + "cid=" + cid + ", cname='" + cname + '\'' + ", stus=" + stus + '}'; } public List<Student> getStus() { return stus; } public void setStus(List<Student> stus) { this.stus = stus; } public Integer getCid() { return cid; } public void setCid(Integer cid) { this.cid = cid; } public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } public Clazz() { } public Clazz(Integer cid, String cname) { this.cid = cid; this.cname = cname; } }
第一种方式:collection
代码
- ClazzMapper接口
/** * 根据班级编号查询班级信息。 * @param cid * @return */ Clazz selectByCollection(Integer cid);
- ClazzMapper.xml
<resultMap id="clazzResultMap" type="Clazz"> <id property="cid" column="cid"/> <result property="cname" column="cname"/> <!--一对多,这里是collection。collection是集合的意思。--> <!--ofType 属性用来指定集合当中的元素类型。--> <collection property="stus" ofType="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid"/> <result property="sname" column="sname"/> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="selectByCollection" resultMap="clazzResultMap"> select c.cid,c.cname,s.sid,s.sname from t_clazz c left join t_stu s on c.cid = s.cid where c.cid = #{cid} </select>
- ClazzMapperTest
@Test public void testSelectByCollection(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); ClazzMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ClazzMapper.class); Clazz clazz = mapper.selectByCollection(1000); System.out.println(clazz); sqlSession.close(); }
第二种方式:分步查询
代码
- ClazzMapper接口
/** * 分步查询。第一步:根据班级编号获取班级信息。 * @param cid 班级编号 * @return */ Clazz selectByStep1(Integer cid);
- ClazzMapper.xml
<!--分步查询第一步:根据班级的cid获取班级信息。--> <resultMap id="clazzResultMapStep" type="Clazz"> <id property="cid" column="cid"/> <result property="cname" column="cname"/> <collection property="stus" select="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByCidStep2" column="cid" fetchType="eager" /> </resultMap> <select id="selectByStep1" resultMap="clazzResultMapStep"> select cid,cname from t_clazz where cid = #{cid} </select>
- StudentMapper接口
/** * 根据班级编号查询学生信息。 * @param cid * @return */ List<Student> selectByCidStep2(Integer cid);
- StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByCidStep2" resultType="Student"> select * from t_stu where cid = #{cid} </select>
- ClazzMapperTest
@Test public void testSelectByStep1(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); ClazzMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ClazzMapper.class); Clazz clazz = mapper.selectByStep1(1000); //System.out.println(clazz); // 只访问班级名字。 System.out.println(clazz.getCname()); // 只有用到的时候才会去执行第二步SQL //System.out.println(clazz.getStus()); sqlSession.close(); }
十四、MyBatis的缓存
- 缓存:cache
- 缓存的作用:通过减少IO[读文件和写文件]的方式,来提高程序的执行效率。
。一方面是减少了IO。
。另一方面不再执行繁琐的查找算法。
- mybatis的缓存:将select语句的查询结果放到缓存(内存)当中,下一次还是这条select语句的话,直接从缓存中取,不再查数据库。
- mybatis缓存包括:
范围:一级缓存小于二级缓存
。一级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到SqlSession中。【针对一次会话】
- 一级缓存默认是开启的。不需要做任何配置。
- 只要使用同一个SqlSession对象执行同一条SQL语句,就会走缓存。
。二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到SqlSessionFactory中。【只针对整个数据库】
- <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"> 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。默认就是true,无需设置。
- 在需要使用二级缓存的SqlMapper.xml文件中添加配置:<cache />
- 使用二级缓存的实体类对象必须是可序列化的,也就是必须实现java.io.Serializable接口
- SqlSession对象关闭或提交之后,一级缓存中的数据才会被写入到二级缓存当中。此时二级缓存才可用。
- 因此如果要使用二级缓存,一级缓存一定要失效或者集成其它第三方的缓存:比如EhCache【Java语言开发的】、Memcache【C语言开发的】等。
- 第三方的缓存是为了代替mybatis自带的二级缓存。一级缓存是无法替代的。
- 缓存只针对于DQL语句,也就是说缓存机制只对应select语句。
- 常见的缓存技术
。字符串常量池
。整数型常量池线程池
。连接池
- 思考:什么时候不走缓存?
。SqlSession对象不是同一个,肯定不走缓存。
。查询条件不一样,肯定也不走缓存。
- 思考:什么时候一级缓存失效?
第一次DQL和第二次DQL之间你做了以下两件事中的任意一件,都会让一级缓存清空:
1.执行了sqlSession的clearCache()方法,这是手动清空缓存。
2.执行了INSERT或DELETE或UPDATE语句。不管你是操作哪张表的,都会清空一级缓存。
- 二级缓存的失效:只要两次查询之间出现了增删改操作。二级缓存就会失效。
14.1 一级缓存
- 思考:什么时候不走缓存?
。SqlSession对象不是同一个,肯定不走缓存。
。查询条件不一样,肯定也不走缓存。
- 思考:什么时候一级缓存失效?
。第一次DQL和第二次DQL之间你做了以下两件事中的任意一件,都会让一级缓存清空:
1.执行了sqlSession的clearCache()方法,这是手动清空缓存。
2.执行了INSERT或DELETE或UPDATE语句。不管你是操作哪张表的,都会清空一级缓存。
- CarMapper接口
/** * 根据id获取Car信息。 * @param id * @return */ Car selectById(Long id);
- CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectById" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car where id = #{id} </select> <select id="selectById2" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
- CarMapperTest
// 思考:什么时候不走缓存? // SqlSession对象不是同一个,肯定不走缓存。 // 查询条件不一样,肯定也不走缓存。 // 思考:什么时候一级缓存失效? // 第一次DQL和第二次DQL之间你做了以下两件事中的任意一件,都会让一级缓存清空: // 1. 执行了sqlSession的clearCache()方法,这是手动清空缓存。 // 2. 执行了INSERT或DELETE或UPDATE语句。不管你是操作哪张表的,都会清空一级缓存。 @Test public void testSelectById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(164L); System.out.println(car1); // 手动清空一级缓存 //sqlSession.clearCache(); // 在这里执行了INSERT DELETE UPDATE中的任意一个语句。并且和表没有关系。 CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); mapper.insertClazz(2000, "高三三班"); CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car2 = mapper2.selectById(164L); System.out.println(car2); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
@Test public void testSelectById() throws Exception{ // 如果要获取不同的SqlSession对象,不能使用以下代码。 //SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car1 = mapper1.selectById(164L); System.out.println(car1); CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car2 = mapper2.selectById(164L); System.out.println(car2); sqlSession1.close(); sqlSession2.close(); }
- 测试结果:同一个Session
14.2 二级缓存
- 二级缓存的失效:只要两次查询之间出现了增删改操作。二级缓存就会失效。【一级缓存也会失效】
- 二级缓存相关的配置[了解]
1.eviction:指定从缓存中移除某个对象的淘汰算法。默认采用LRU策略。
a. LRU:Least Recently Used。最近最少使用。优先淘汰在间隔时间内使用频率最低的对象。(其实还有一种淘汰算法LFU,最不常用。)
b. FIFO:First In First Out。一种先进先出的数据缓存器。先进入二级缓存的对象最先被淘汰。
c. SOFT:软引用。淘汰软引用指向的对象。具体算法和JVM的垃圾回收算法有关。
d. WEAK:弱引用。淘汰弱引用指向的对象。具体算法和JVM的垃圾回收算法有关。
2.flushInterval:
a. 二级缓存的刷新时间间隔。单位毫秒。如果没有设置。就代表不刷新缓存,只要内存足够大,一直会向二级缓存中缓存数据。除非执行了增删改。
3.readOnly::
a. true:多条相同的sql语句执行之后返回的对象是共享的同一个。性能好。但是多线程并发可能会存在安全问题。
b. false:多条相同的sql语句执行之后返回的对象是副本,调用了clone方法。性能一般。但安全。
4.size:
a. 设置二级缓存中最多可存储的java对象数量。默认值1024。
- mapper接口
/** * 测试二级缓存 * @param id * @return */ Car selectById2(Long id);
- mapper.xml
<!-- 默认情况下,二级缓存机制是开启的。 只需要在对应的SqlMapper.xml文件中添加以下标签。用来表示“我”使用该二级缓存。 --> <!--<cache/>--> <select id="selectById2" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car where id = #{id} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectById2() throws Exception{ // 这里只有一个SqlSessionFactory对象。二级缓存对应的就是SqlSessionFactory。 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CarMapper.class); CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 这行代码执行结束之后,实际上数据是缓存到一级缓存当中了。(sqlSession1是一级缓存。) Car car1 = mapper1.selectById2(164L); System.out.println(car1); // 如果这里不关闭SqlSession1对象的话,二级缓存中还是没有数据的。 // 如果执行了这行代码,sqlSession1的一级缓存中的数据会放到二级缓存当中。 sqlSession1.close(); // 这行代码执行结束之后,实际上数据会缓存到一级缓存当中。(sqlSession2是一级缓存。) Car car2 = mapper2.selectById2(164L); System.out.println(car2); // 程序执行到这里的时候,会将sqlSession1这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中。 //sqlSession1.close(); // 程序执行到这里的时候,会将sqlSession2这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中。 sqlSession2.close(); }
14.3 MyBatis集成EhCache
按照以下步骤操作,就可以完成集成:
1.引入mybatis整合ehcache的依赖。
<!--mybatis集成ehcache的组件--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId> <version>1.2.2</version> </dependency>
2.在类的根路径下新建echcache.xml文件,并提供以下配置信息。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <!--磁盘存储:将缓存中暂时不使用的对象,转移到硬盘,类似于Windows系统的虚拟内存--> <diskStore path="e:/ehcache"/> <!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略--> <!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断--> <!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目--> <!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上--> <!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false--> <!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问--> <!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问--> <!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略--> <!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)--> <!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存--> <!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存--> <defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/> </ehcache>
3.修改SqlMapper.xml文件中的<cache/>标签,添加type属性。
<!--集成Ehcache组件--> <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
4.编写测试程序使用
@Test public void testSelectById2() throws Exception{ // 这里只有一个SqlSessionFactory对象。二级缓存对应的就是SqlSessionFactory。 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")); SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); CarMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CarMapper.class); CarMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 这行代码执行结束之后,实际上数据是缓存到一级缓存当中了。(sqlSession1是一级缓存。) Car car1 = mapper1.selectById2(164L); System.out.println(car1); // 如果这里不关闭SqlSession1对象的话,二级缓存中还是没有数据的。 // 如果执行了这行代码,sqlSession1的一级缓存中的数据会放到二级缓存当中。 sqlSession1.close(); // 这行代码执行结束之后,实际上数据会缓存到一级缓存当中。(sqlSession2是一级缓存。) Car car2 = mapper2.selectById2(164L); System.out.println(car2); // 程序执行到这里的时候,会将sqlSession1这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中。 //sqlSession1.close(); // 程序执行到这里的时候,会将sqlSession2这个一级缓存中的数据写入到二级缓存当中。 sqlSession2.close(); }
十五、MyBatis的逆向工程
- 逆向工程:根据数据库表逆向生成Java的pojo类,SqlMapper.xml文件,以及Mapper接口类等。
- 思考:使用这个插件的话,需要给这个插件配置哪些信息?
。pojo类名、包名以及生成位置。
。SqlMapper.xml文件名以及生成位置。
。Mapper接口名以及生成位置。
。连接数据库的信息。
。指定哪些表参与逆向工程。
。…
15.1 逆向工程配置与生成
第一步:基础环境准备
- 新建模块:mybatis-011-generator
- 打包方式:jar
第二步:在pom中添加逆向工程插件
<!--配置mybatis逆向工程的插件--> <!--定制构建过程--> <build> <!--可配置多个插件--> <plugins> <!--其中的一个插件:mybatis逆向工程插件--> <plugin> <!--插件的GAV坐标--> <groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.4.1</version> <!--允许覆盖--> <configuration> <overwrite>true</overwrite> </configuration> <!--插件的依赖--> <dependencies> <!--mysql驱动依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.30</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
第三步:配置generatorConfig.xml
- 该文件名必须叫做:generatorConfig.xml
- 该文件必须放在类的根路径下。
- MyBatis3Simple版本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration> <!-- targetRuntime有两个值: MyBatis3Simple:生成的是基础版,只有基本的增删改查。 MyBatis3:生成的是增强版,除了基本的增删改查之外还有复杂的增删改查。 --> <context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3Simple"> <!--防止生成重复代码--> <plugin type="org.mybatis.generator.plugins.UnmergeableXmlMappersPlugin"/> <commentGenerator> <!--是否去掉生成日期--> <property name="suppressDate" value="true"/> <!--是否去除注释--> <property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/> </commentGenerator> <!--连接数据库信息--> <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/powernode" userId="root" password="root"> </jdbcConnection> <!-- 生成pojo包名和位置 --> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo" targetProject="src/main/java"> <!--是否开启子包--> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> <!--是否去除字段名的前后空白--> <property name="trimStrings" value="true"/> </javaModelGenerator> <!-- 生成SQL映射文件的包名和位置 --> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper" targetProject="src/main/resources"> <!--是否开启子包--> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> </sqlMapGenerator> <!-- 生成Mapper接口的包名和位置 --> <javaClientGenerator type="xmlMapper" targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper" targetProject="src/main/java"> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> </javaClientGenerator> <!-- 表名和对应的实体类名--> <table tableName="t_car" domainObjectName="Car"/> </context> </generatorConfiguration>
- MyBatis3
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration> <!-- targetRuntime有两个值: MyBatis3Simple:生成的是基础版,只有基本的增删改查。 MyBatis3:生成的是增强版,除了基本的增删改查之外还有复杂的增删改查。 --> <context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3"> <!--防止生成重复代码--> <plugin type="org.mybatis.generator.plugins.UnmergeableXmlMappersPlugin"/> <commentGenerator> <!--是否去掉生成日期--> <property name="suppressDate" value="true"/> <!--是否去除注释--> <property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/> </commentGenerator> <!--连接数据库信息--> <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/powernode" userId="root" password="root"> </jdbcConnection> <!-- 生成pojo包名和位置 --> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo" targetProject="src/main/java"> <!--是否开启子包--> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> <!--是否去除字段名的前后空白--> <property name="trimStrings" value="true"/> </javaModelGenerator> <!-- 生成SQL映射文件的包名和位置 --> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper" targetProject="src/main/resources"> <!--是否开启子包--> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> </sqlMapGenerator> <!-- 生成Mapper接口的包名和位置 --> <javaClientGenerator type="xmlMapper" targetPackage="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper" targetProject="src/main/java"> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/> </javaClientGenerator> <!-- 表名和对应的实体类名--> <table tableName="t_car" domainObjectName="Car"/> </context> </generatorConfiguration>
第四步:运行插件
双击运行即可,会自动生成pojo类、mapper接口、mapper.xml文件
15.2 测试逆向工程生成的是否好用
第一步:环境准备
- 依赖:mybatis依赖、mysql驱动依赖、junit依赖、logback依赖
- jdbc.properties
- mybatis-config.xml
- logback.xml
第二步:编写测试程序
- MyBatis3Simple版本
package com.powernode.mybatis.test; import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper; import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car; import com.powernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; public class CarMapperTest { @Test public void testSelectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAll(); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void testDeleteByPrimaryKey(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int count = mapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(164L); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } }
- MyBatis3
。CarExample :封装查询条件
。按照条件进行查询
。QBC 风格:Query By Criteria 一种查询方式,比较面向对象,看不到sql语句。
。封装条件,通过CarExample对象来封装查询条件
package com.powernode.mybatis.test; import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper; import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car; import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.CarExample; import com.powernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.util.List; public class CarMapperTest { // CarExample类负责封装查询条件的。 @Test public void testSelect(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 执行查询 // 1. 查询一个 Car car = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(165L); System.out.println(car); // 2. 查询所有(selectByExample,根据条件查询,如果条件是null表示没有条件。) List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByExample(null); cars.forEach(car1 -> System.out.println(car1)); System.out.println("========================================="); // 3. 按照条件进行查询 // QBC 风格:Query By Criteria 一种查询方式,比较面向对象,看不到sql语句。 // 封装条件,通过CarExample对象来封装查询条件 CarExample carExample = new CarExample(); // 调用carExample.createCriteria()方法来创建查询条件 carExample.createCriteria() .andBrandLike("帕萨特") .andGuidePriceGreaterThan(new BigDecimal(20.0)); // 添加or carExample.or().andCarTypeEqualTo("燃油车"); // 执行查询 List<Car> cars2 = mapper.selectByExample(carExample); cars2.forEach(car2 -> System.out.println(car2)); sqlSession.close(); } }
十六、MyBatis使用PageHelper
16.1 limit分页
- mysql的limit后面两个数字:
。第一个数字:startIndex(起始下标;下标从0开始;默认也为0)
。第二个数字:pageSize(每页显示的记录条数)
- 假设已知页码pageNum,还有每页显示的记录条数pageSize,第一个数字可以动态的获取吗?
。startIndex = (pageNum - 1) * pageSize
- 所以,标准通用的mysql分页SQL:
select * from tableName ...... limit (pageNum - 1) * pageSize, pageSize
- 使用mybatis应该怎么做?
。mapper接口
/** * 分页查询 * @param startIndex 起始下标。 * @param pageSize 每页显示的记录条数 * @return */ List<Car> selectByPage(@Param("startIndex") int startIndex, @Param("pageSize") int pageSize);
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectByPage" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize} </select>
- test
@Test public void testSelectByPage(){ // 获取每页显示的记录条数 int pageSize = 3; // 显示第几页:页码 int pageNum = 3; // 计算开始下标 int startIndex = (pageNum - 1) * pageSize; SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByPage(startIndex, pageSize); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); sqlSession.close(); }
获取数据不难,难的是获取分页相关的数据比较难。->插件
16.3 PageHelper插件
- 使用PageHelper插件进行分页,更加的便捷。
- 关键点:
。在查询语句之前开启分页功能
。在查询语句之后封装PageInfo对象。(PageInfo对象将来会存储到request域当中。在页面上展示。)
第一步:引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId> <artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId> <version>5.3.1</version> </dependency>
第二步:在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置插件
typeAliases标签下面进行配置:
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin> </plugins>
第三步:编写Java代码
关键点:
- 在查询语句之前开启分页功能。
- 在查询语句之后封装PageInfo对象。(PageInfo对象将来会存储到request域当中。在页面上展示。)
代码
- mapper接口
/** * 查询所有的Car,通过分页查询插件PageHelper完成。 * @return */ List<Car> selectAll();
- mapper.xml
<select id="selectAll" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car </select>
test
@Test public void testSelectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 一定一定一定要注意:在执行DQL语句之前。开启分页功能。 int pageNum = 2; int pageSize = 3; PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAll(); //cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); // 封装分页信息对象new PageInfo() // PageInfo对象是PageHelper插件提供的,用来封装分页相关的信息的对象。 PageInfo<Car> carPageInfo = new PageInfo<>(cars, 3); System.out.println(carPageInfo); sqlSession.close(); /* PageInfo{pageNum=2, pageSize=3, size=3, startRow=4, endRow=6, total=7, pages=3, list=Page{count=true, pageNum=2, pageSize=3, startRow=3, endRow=6, total=7, pages=3, reasonable=false, pageSizeZero=false} [Car{id=168, carNum='1204', brand='奥迪Q7', guidePrice=3.0, produceTime='2009-10-11', carType='燃油车'}, Car{id=169, carNum='1205', brand='朗逸', guidePrice=4.0, produceTime='2001-10-11', carType='新能源'}, Car{id=170, carNum='1206', brand='奔驰E300L', guidePrice=50.0, produceTime='2003-02-03', carType='新能源'}], prePage=1, nextPage=3, isFirstPage=false, isLastPage=false, hasPreviousPage=true, hasNextPage=true, navigatePages=3, navigateFirstPage=1, navigateLastPage=3, navigatepageNums=[1, 2, 3]} */ }
十七、MyBatis的注解式开发
- 注解式开发方式
。mybatis中也提供了注解式开发方式,采用注解可以减少Sql映射文件的配置。
。使用注解式开发的话,sql语句是写在java程序中的,这种方式也会给sql语句的维护带来成本。
官方:
使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java 注解不仅力不从心,还会让你本就复杂的 SQL 语句更加混乱不堪。 因此,如果你需要做一些很复杂的操作,最好用 XML 来映射语句。
。复杂的sql语句
。原则:简单sql可以注解。复杂sql使用xml。
17.1 @Insert
- mapper接口
@Insert("insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})") int insert(Car car);
- test
@Test public void testInsert(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = new Car(null,"6666","丰田霸道",32.0,"2020-11-11","燃油车"); int count = mapper.insert(car); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
17.2 @Delete
- mapper接口
@Delete("delete from t_car where id = #{id}") int deleteById(Long id);
- test
@Test public void testDeleteById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int count = mapper.deleteById(170L); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
17.3 @Update
- mapper接口
@Update("update t_car set car_num=#{carNum},brand=#{brand},guide_price=#{guidePrice},produce_time=#{produceTime},car_type=#{carType} where id=#{id}") int update(Car car);
- test
@Test public void testUpdate(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = new Car(165L,"6666","丰田霸道",32.0,"2020-11-11","燃油车"); int count = mapper.update(car); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
17.4 @Select
- mapper接口
需要开启驼峰命名自动映射
@Select("select * from t_car where id = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(property = "id", column = "id"), @Result(property = "carNum", column = "car_num"), @Result(property = "brand", column = "brand"), @Result(property = "guidePrice", column = "guide_price"), @Result(property = "produceTime", column = "produce_time"), @Result(property = "carType", column = "car_type") }) Car selectById(Long id);
- test
@Test public void testSelectById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = mapper.selectById(171L); System.out.println(car); sqlSession.close(); }