跳跃表
跳表是基于链表的,在链表的基础上加了多层索引结构。
跳表这种特殊的数据结果是有 Willam Pugh 发明的。最早出现在1990 年发表的论文《Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees》
论文中有个描述:
Skip lists are a data structure that can be used in place of balanced trees.Skip lists use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing and as a result the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
简单的说,跳表是基于概率型的表。
先看个普通有序链表的结构:
如果要查找 23 那么起码需要比较 2次,查找 43 比较 4次,查找 59 比较 6次。有什么办法解决这个问题呢?容易想到二分搜索。
采用分层链表结构,以一些节点作为索引,
比如,提取了 14 34 50 72 作为一层链表,查找 59 的时候,就可以通过比较 14 24 50 59 共5次找到 59 来减少查找次数。
如果加一层,基本上就可以采用类似二分的方式进行查找了
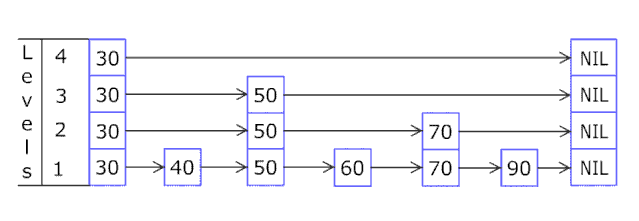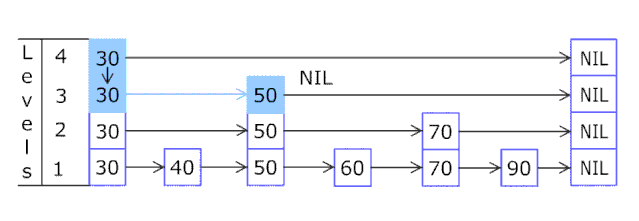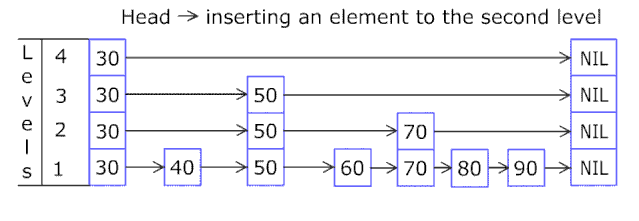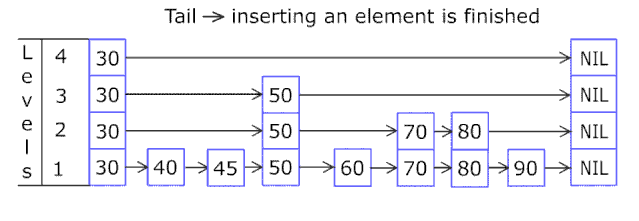
现在看给完整的 快表插入一个新元素的过程:
参考代码:
public class SkipList { private static class SkipListNode { int data; SkipListNode[] next; SkipListNode(int d, int level) { data = d; next = new SkipListNode[level + 1]; } } private int maxLevel; SkipListNode header; private static final int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE; SkipList(int maxLevel) { this.maxLevel = maxLevel; header = new SkipListNode(0, maxLevel); SkipListNode sentinel = new SkipListNode(INFINITY, maxLevel); for (int i = 0; i <= maxLevel; i++) header.next[i] = sentinel; } public boolean find(int key) { SkipListNode current = header; for (int i = maxLevel; i >= 0; i--) { SkipListNode next = current.next[i]; while (next.data < key) { current = next; next = current.next[i]; } } current = current.next[0]; if (current.data == key) return true; else return false; } public void insert(int searchKey, int newValue) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[maxLevel + 1]; SkipListNode current = header; for (int i = maxLevel; i >= 0; i--) { SkipListNode next = current.next[i]; while (next.data < searchKey) { current = next; next = current.next[i]; } update[i] = current; } current = current.next[0]; if (current.data == searchKey) current.data = newValue; else { int v = generateRandomLevel(); SkipListNode node = new SkipListNode(newValue, maxLevel); for (int i = 0; i <= v; i++) { node.next[i] = update[i].next[i]; update[i].next[i] = node; } update = null; } } private int generateRandomLevel() { int newLevel = 0; while (newLevel < maxLevel && Math.random() < 0.5) newLevel++; return newLevel; } public boolean delete(int searchKey) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[maxLevel + 1]; SkipListNode current = header; for (int i = maxLevel; i >= 0; i--) { SkipListNode next = current.next[i]; while (next.data < searchKey) { current = next; next = current.next[i]; } update[i] = current; } current = current.next[0]; if (current.data == searchKey) { for (int i = 0; i <= maxLevel; i++) { if (update[i].next[i] == current) { update[i].next[i] = current.next[i]; current.next[i] = null; } else current.next[i] = null; } return true; } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { } }