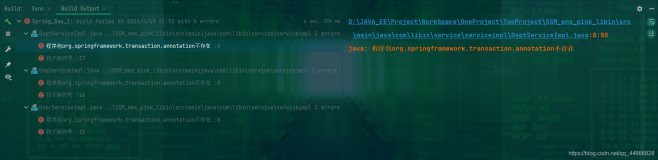
这个包的说明是说主要是包括用于操作JavaBean的类和接口,将被大部分spring包使用。在读这个包的代码前,我特意将JavaBean规范读了一遍。JavaBean规范不仅仅是getter、setter,定义了一个完整的轻量级组件模型,事件、方法、属性、持久化等等支持均包含在内。JavaBean规范很明显是学习Delphi的组件模型,sun希望通过它来形成一个java组件的市场,可惜结果不如人意,JavaBean在GUI方面并未形成一个类似delphi控件市场;随着spring等轻量级框架的流行,而EJB重量级的组件模型被越来越多的人放弃,JavaBean反而在服务端模型方面占据了主流 。废话不提,这个包的核心接口和类就是BeanWrapper和BeanWrapperImpl,顾名思义,这个接口就是用于包装JavaBean的行为,诸如设置和获取属性,设置属性编辑器等(PropertyEditor)。看下这个包的核心类图:

BeanWrapper接口继承了PropertyAccessor(用于属性访问和设置)和PropertyEditorRegistry(属性编辑器的获取和设置),而BeanWrapperImpl除了实现BeanWrapper接口外还继承自PropertyEditorRegistrySupport 类。在PropertyEditorRegistrySupport 类中可以看到spring默认设置的一系列自定义PropertyEditor。比如:
PropertyEditor的概念就是属性编辑器,或者说属性转换器,比如我们在spring的配置文件中设置某个bean的class,这是一个字符串,怎么转换为一个Class对象呢?通过上面注册的ClassEditor,看看这个类是怎么实现的:
因为缓存使用的key是bean的Class对象(以保证唯一性),因此在应用存在多个class loaders的时候,为了保证垃圾收集的进行,不出现内存泄露而采用WeakHashMap,为了理解这一点,我用JProfiler测试了自定义ClassLoader情况下,内存堆的使用情况,从快照上看。在使用HashMap的情况下,因为测试的bean的Class对象被载入它的ClassLoader以及java.beans.BeanInfo,java.beans.PropertyDescriptor,java.lang.reflect.Method这四个对象强引用,而导致不可回收。而在使用WeakHashMap时,判断当载入bean的ClassLoader和载入CachedIntrospectionResults的ClassLoader是不同的时候,使用弱引用包装缓存对象,当垃圾收集起发现弱引用时将马上清除弱引用对象,该弱引用也将加入一个队列,而WeakHashMap将定时检查这个队列,当有新的弱引用达到时(意味着已经被回收)就清除相应的键值。请看:

BeanWrapper接口继承了PropertyAccessor(用于属性访问和设置)和PropertyEditorRegistry(属性编辑器的获取和设置),而BeanWrapperImpl除了实现BeanWrapper接口外还继承自PropertyEditorRegistrySupport 类。在PropertyEditorRegistrySupport 类中可以看到spring默认设置的一系列自定义PropertyEditor。比如:
protected
void
registerDefaultEditors() {
this .defaultEditors = new HashMap( 32 );
// Simple editors, without parameterization capabilities.
// The JDK does not contain a default editor for any of these target types.
this .defaultEditors.put(Class. class , new ClassEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(File. class , new FileEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(InputStream. class , new InputStreamEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Locale. class , new LocaleEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Properties. class , new PropertiesEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Resource[]. class , new ResourceArrayPropertyEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(String[]. class , new StringArrayPropertyEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(URL. class , new URLEditor());
。。。。。。。
this .defaultEditors = new HashMap( 32 );
// Simple editors, without parameterization capabilities.
// The JDK does not contain a default editor for any of these target types.
this .defaultEditors.put(Class. class , new ClassEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(File. class , new FileEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(InputStream. class , new InputStreamEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Locale. class , new LocaleEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Properties. class , new PropertiesEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(Resource[]. class , new ResourceArrayPropertyEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(String[]. class , new StringArrayPropertyEditor());
this .defaultEditors.put(URL. class , new URLEditor());
。。。。。。。
PropertyEditor的概念就是属性编辑器,或者说属性转换器,比如我们在spring的配置文件中设置某个bean的class,这是一个字符串,怎么转换为一个Class对象呢?通过上面注册的ClassEditor,看看这个类是怎么实现的:
public
class
ClassEditor
extends
PropertyEditorSupport {
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
/**
* Create a default ClassEditor, using the given ClassLoader.
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use
* (or <code>null</code> for the thread context ClassLoader)
*/
public ClassEditor(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this .classLoader =
(classLoader != null ? classLoader : Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (StringUtils.hasText(text)) {
try {
//调用辅助类,得到Class对象
setValue(ClassUtils.forName(text.trim(), this .classLoader));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( " Class not found: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
setValue( null );
}
}
public String getAsText() {
Class clazz = (Class) getValue();
if (clazz == null ) {
return "" ;
}
if (clazz.isArray()) {
return clazz.getComponentType().getName() + ClassUtils.ARRAY_SUFFIX;
}
else {
return clazz.getName();
}
}
}
代码已经解释了一切,继承javabean的PropertyEditorSupport,自己实现转换即可。这个包另外就是定义了一个完整的异常体系,值的我们参考。另外一个值的注意的地方是CachedIntrospectionResults类的实现,这个类使用了单例模式,它的作用在于缓存JavaBean反省(Introspect)得到的信息,因为每次使用Introspector对获取JavaBean信息是个不小的性能开支。缓存使用的是WeakHashMap,而不是HashMap,看看spring的解释:
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
/**
* Create a default ClassEditor, using the given ClassLoader.
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use
* (or <code>null</code> for the thread context ClassLoader)
*/
public ClassEditor(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this .classLoader =
(classLoader != null ? classLoader : Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (StringUtils.hasText(text)) {
try {
//调用辅助类,得到Class对象
setValue(ClassUtils.forName(text.trim(), this .classLoader));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( " Class not found: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
setValue( null );
}
}
public String getAsText() {
Class clazz = (Class) getValue();
if (clazz == null ) {
return "" ;
}
if (clazz.isArray()) {
return clazz.getComponentType().getName() + ClassUtils.ARRAY_SUFFIX;
}
else {
return clazz.getName();
}
}
}
/**
* Map keyed by class containing CachedIntrospectionResults.
* Needs to be a WeakHashMap with WeakReferences as values to allow
* for proper garbage collection in case of multiple class loaders.
*/
private static final Map classCache = Collections.synchronizedMap( new WeakHashMap());
* Map keyed by class containing CachedIntrospectionResults.
* Needs to be a WeakHashMap with WeakReferences as values to allow
* for proper garbage collection in case of multiple class loaders.
*/
private static final Map classCache = Collections.synchronizedMap( new WeakHashMap());
因为缓存使用的key是bean的Class对象(以保证唯一性),因此在应用存在多个class loaders的时候,为了保证垃圾收集的进行,不出现内存泄露而采用WeakHashMap,为了理解这一点,我用JProfiler测试了自定义ClassLoader情况下,内存堆的使用情况,从快照上看。在使用HashMap的情况下,因为测试的bean的Class对象被载入它的ClassLoader以及java.beans.BeanInfo,java.beans.PropertyDescriptor,java.lang.reflect.Method这四个对象强引用,而导致不可回收。而在使用WeakHashMap时,判断当载入bean的ClassLoader和载入CachedIntrospectionResults的ClassLoader是不同的时候,使用弱引用包装缓存对象,当垃圾收集起发现弱引用时将马上清除弱引用对象,该弱引用也将加入一个队列,而WeakHashMap将定时检查这个队列,当有新的弱引用达到时(意味着已经被回收)就清除相应的键值。请看:
private
static
boolean
isCacheSafe(Class clazz) {
// CachedIntrospectionResults的ClassLoader
ClassLoader cur = CachedIntrospectionResults. class .getClassLoader();
// 载入bean的ClassLoader
ClassLoader target = clazz.getClassLoader();
if (target == null || cur == target) {
return true ;
}
while (cur != null ) {
cur = cur.getParent();
if (cur == target) {
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
public static CachedIntrospectionResults forClass(Class beanClass) throws BeansException {

boolean cacheSafe = isCacheSafe(beanClass);
if (cacheSafe) {
classCache.put(beanClass, results);
}
else {
// 弱引用
classCache.put(beanClass, new WeakReference(results));
}


// CachedIntrospectionResults的ClassLoader
ClassLoader cur = CachedIntrospectionResults. class .getClassLoader();
// 载入bean的ClassLoader
ClassLoader target = clazz.getClassLoader();
if (target == null || cur == target) {
return true ;
}
while (cur != null ) {
cur = cur.getParent();
if (cur == target) {
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
public static CachedIntrospectionResults forClass(Class beanClass) throws BeansException {


boolean cacheSafe = isCacheSafe(beanClass);
if (cacheSafe) {
classCache.put(beanClass, results);
}
else {
// 弱引用
classCache.put(beanClass, new WeakReference(results));
}


不知道我的理解是否有误,如果有误,请不吝指出,谢谢。
文章转自庄周梦蝶 ,原文发布时间5.17