前段时间写了一篇关于实现统一响应信息的博文,根据文中实战操作,能够解决正常响应的一致性,但想要实现优雅响应,还需要优雅的处理异常响应,所以有了这篇内容。
作为后台服务,能够正确的处理程序抛出的异常,并返回友好的异常信息是非常重要的,毕竟我们大部分代码都是为了 处理异常情况。而且,统一的异常响应,有助于客户端理解服务端响应,并作出正确处理,而且能够提升接口的服务质量。
SpringBoot提供了异常的响应,可以通过/error请求查看效果:
这是从浏览器打开的场景,也就是请求头不包括content-type: applicaton/json,大白板一个,和友好完全不搭边。
这是请求头包括content-type: applicaton/json时的响应,格式还行,但是我们还需要加工一下,实现自定义的异常码和异常信息。
本文主要是针对RESTful请求的统一响应,想要实现的功能包括:
自动封装异常,返回统一响应
异常信息国际化
定义异常响应类
当程序发送错误时,不应该将晦涩的堆栈报告信息返回给API客户端,从某种意义将,这是一种不礼貌的和不负责任的行为。
我们在SpringBoot 实战:一招实现结果的优雅响应中,定义了一个响应类,为什么还要再定义一个异常响应类呢?其实是为了语义明确且职责单一。类图如下:
具体代码如下:
基础类BaseResponse:
@Data public abstract class BaseResponse { private Integer code; private String desc; private Date timestamp = new Date(); private String path; public BaseResponse() { } public BaseResponse(final Integer code, final String desc) { this.code = code; this.desc = desc; } public BaseResponse(final Integer code, final String desc, final String path) { this.code = code; this.desc = desc; this.path = path; } }
异常类ErrorResponse:
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true) @Data public class ErrorResponse extends BaseResponse { public ErrorResponse(final Integer code, final String desc) { super(code, desc); } public ErrorResponse(final Integer code, final String desc, final WebRequest request) { super(code, desc, extractRequestURI(request)); } public ErrorResponse(final HttpStatus status, final Exception e) { super(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase() + ": " + e.getMessage()); } public ErrorResponse(final HttpStatus status, final Exception e, final WebRequest request) { super(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase() + ": " + e.getMessage(), extractRequestURI(request)); } private static String extractRequestURI(WebRequest request) { final String requestURI; if (request instanceof ServletWebRequest) { ServletWebRequest servletWebRequest = (ServletWebRequest) request; requestURI = servletWebRequest.getRequest().getRequestURI(); } else { requestURI = request.getDescription(false); } return requestURI; } }
定义异常枚举类
为了能够规范响应码和响应信息,我们可以定义一个枚举类。
枚举接口ResponseEnum:
public interface ResponseEnum { Integer getCode(); String getMessage(); default String getLocaleMessage() { return getLocaleMessage(null); } String getLocaleMessage(Object[] args); }
枚举类CommonResponseEnum:
public enum CommonResponseEnum implements ResponseEnum { BAD_REQUEST(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), "Bad Request"), NOT_FOUND(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), "Not Found"), METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED(HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.value(), "Method Not Allowed"), NOT_ACCEPTABLE(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE.value(), "Not Acceptable"), REQUEST_TIMEOUT(HttpStatus.REQUEST_TIMEOUT.value(), "Request Timeout"), UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE(HttpStatus.UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE.value(), "Unsupported Media Type"), INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), "Server Error"), SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE.value(), "Service Unavailable"), ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT(4000, "Illegal Argument"), DATA_NOT_FOUND(4004, "Data Not Found"), USER_NOT_FOUND(4104, "User Not Found"), MENU_NOT_FOUND(4204, "Menu Not Found"), INTERNAL_ERROR(9999, "Server Error"), ; private final Integer code; private final String message; private MessageSource messageSource; CommonResponseEnum(final Integer code, final String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } @Override public Integer getCode() { return code; } @Override public String getMessage() { return message; } @Override public String getLocaleMessage(Object[] args) { return messageSource.getMessage("response.error." + code, args, message, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()); } public void setMessageSource(final MessageSource messageSource) { this.messageSource = messageSource; } @Component public static class ReportTypeServiceInjector { private final MessageSource messageSource; public ReportTypeServiceInjector(final MessageSource messageSource) { this.messageSource = messageSource; } @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { for (final CommonResponseEnum anEnum : CommonResponseEnum.values()) { anEnum.setMessageSource(messageSource); } } } }
需要注意的是,我们在异常枚举类中定义了ReportTypeServiceInjector类,这个类的作用是为枚举类注入MessageSource对象,是为了实现异常信息的国际化。这部分功能Spring已经封装好了,我们只需要在resources目录中定义一组messages.properties文件就可以了,比如:
message.properties定义默认描述:
response.error.4000=[DEFAULT] Illegal Arguments response.error.4004=[DEFAULT] Not Found
messages_zh_CN.properties定义中文描述:
response.error.4004=对应数据未找到 response.error.9999=系统异常,请求参数: {0}
messages_en_US.properties定义英文描述:
response.error.4004=Not Found
自定义异常类
Java和Spring中提供了很多可用的异常类,可以满足大部分场景,但是有时候我们希望异常类可以携带更多信息,所以还是需要自定义异常类:
可以携带我们想要的信息;
有更加明确语义;
附带效果,可以知道这是手动抛出的业务异常。
上代码:
@Data @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true) public class CodeBaseException extends RuntimeException { private final ResponseEnum anEnum; private final Object[] args;// 打印参数 private final String message;// 异常信息 private final Throwable cause;// 异常栈 public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum) { this(anEnum, null, anEnum.getMessage(), null); } public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final String message) { this(anEnum, null, message, null); } public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final Object[] args, final String message) { this(anEnum, args, message, null); } public CodeBaseException(final ResponseEnum anEnum, final Object[] args, final String message, final Throwable cause) { this.anEnum = anEnum; this.args = args; this.message = message; this.cause = cause; } }
自定义异常信息处理类
前期准备工作完成,接下来定义异常信息处理类。
Spring自带的异常信息处理类往往不能满足我们实际的业务需求,这就需要我们定义符合具体情况的异常信息处理类,在自定义异常信息处理类中,我们可以封装更为详细的异常报告。我们可以扩展Spring提供的ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类定义自己的异常信息处理类,站在巨人的肩膀上,快速封装自己需要的类。
通过源码可以看到,ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类的核心方法是public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleException(Exception ex, WebRequest request),所有的异常都在这个方法中根据类型进行处理,我们只需要实现具体的处理方法即可:
@RestControllerAdvice @Slf4j public class UnifiedExceptionHandlerV2 extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { private static final String ENV_PROD = "prod"; private final MessageSource messageSource; private final Boolean isProd; public UnifiedExceptionHandlerV2(@Value("${spring.profiles.active:dev}") final String activeProfile, final MessageSource messageSource) { this.messageSource = messageSource; this.isProd = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(activeProfile.split(","))).contains(ENV_PROD); } @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(final Exception e, final Object body, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) { log.info("请求异常:" + e.getMessage(), e); if (HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.equals(status)) { request.setAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, e, WebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST); } return new ResponseEntity<>(new ErrorResponse(status, e), headers, HttpStatus.OK); } @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindException(final BindException ex, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) { log.info("参数绑定异常", ex); final ErrorResponse response = wrapperBindingResult(status, ex.getBindingResult()); return new ResponseEntity<>(response, headers, HttpStatus.OK); } @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(final MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, final HttpHeaders headers, final HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) { log.info("参数校验异常", ex); final ErrorResponse response = wrapperBindingResult(status, ex.getBindingResult()); return new ResponseEntity<>(response, headers, HttpStatus.OK); } @ExceptionHandler(value = CodeBaseException.class) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(CodeBaseException e) { log.error("业务异常:" + e.getMessage(), e); final ResponseEnum anEnum = e.getAnEnum(); return new ErrorResponse(anEnum.getCode(), anEnum.getLocaleMessage(e.getArgs())); } @ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleExceptionInternal(Exception e) { log.error("未捕捉异常:" + e.getMessage(), e); final Integer code = INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode(); return new ErrorResponse(code, getLocaleMessage(code, e.getMessage())); } /** * 包装绑定异常结果 * * @param status HTTP状态码 * @param bindingResult 参数校验结果 * @return 异常对象 */ private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(HttpStatus status, BindingResult bindingResult) { final List<String> errorDesc = new ArrayList<>(); for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) { final StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder(); if (error instanceof FieldError) { msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": "); } msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage()); errorDesc.add(msg.toString()); } final String desc = isProd ? getLocaleMessage(status.value(), status.getReasonPhrase()) : String.join(", ", errorDesc); return new ErrorResponse(status.value(), desc); } private String getLocaleMessage(Integer code, String defaultMsg) { try { return messageSource.getMessage("" + code, null, defaultMsg, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()); } catch (Throwable t) { log.warn("本地化异常消息发生异常: {}", code); return defaultMsg; } } }
如果感觉Spring的ResponseEntityExceptionHandler类不够灵活,也可以完全自定义异常处理类:
@RestControllerAdvice @Slf4j public class UnifiedExceptionHandler { private static final String ENV_PROD = "prod"; private final MessageSource messageSource; private final Boolean isProd; public UnifiedExceptionHandler(@Value("${spring.profiles.active:dev}") final String activeProfile, final MessageSource messageSource) { this.messageSource = messageSource; this.isProd = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(activeProfile.split(","))).contains(ENV_PROD); } @ExceptionHandler({ MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,// 缺少servlet请求参数异常处理方法 ServletRequestBindingException.class,// servlet请求绑定异常 TypeMismatchException.class,// 类型不匹配 HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,// 消息无法检索 MissingServletRequestPartException.class// 缺少servlet请求部分 }) public ErrorResponse badRequestException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ NoHandlerFoundException.class// 没有发现处理程序异常 }) public ErrorResponse noHandlerFoundException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(NOT_FOUND.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class// 不支持的HTTP请求方法异常信息处理方法 }) public ErrorResponse httpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class// 不接受的HTTP媒体类型异常处方法 }) public ErrorResponse httpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(NOT_ACCEPTABLE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class// 不支持的HTTP媒体类型异常处理方法 }) public ErrorResponse httpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class// 异步请求超时异常 }) public ErrorResponse asyncRequestTimeoutException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.info(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ MissingPathVariableException.class,// 请求路径参数缺失异常处方法 HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,// HTTP消息不可写 ConversionNotSupportedException.class,// 不支持转换 }) public ErrorResponse handleServletException(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.error(e.getMessage(), e); return new ErrorResponse(INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode(), e.getMessage(), request); } @ExceptionHandler({ BindException.class// 参数绑定异常 }) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleBindException(BindException e, WebRequest request) { log.error("参数绑定异常", e); return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult(), request); } /** * 参数校验异常,将校验失败的所有异常组合成一条错误信息 */ @ExceptionHandler({ MethodArgumentNotValidException.class// 方法参数无效 }) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e, WebRequest request) { log.error("参数校验异常", e); return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult(), request); } /** * 包装绑定异常结果 */ private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(BindingResult bindingResult, WebRequest request) { final List<String> errorDesc = new ArrayList<>(); for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) { final StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder(); if (error instanceof FieldError) { msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": "); } msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage()); errorDesc.add(msg.toString()); } final String desc = isProd ? getLocaleMessage(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), "") : String.join(", ", errorDesc); return new ErrorResponse(BAD_REQUEST.getCode(), desc, request); } /** * 业务异常 */ @ExceptionHandler(value = CodeBaseException.class) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(CodeBaseException e, WebRequest request) { log.error("业务异常:" + e.getMessage(), e); final ResponseEnum anEnum = e.getAnEnum(); return new ErrorResponse(anEnum.getCode(), anEnum.getLocaleMessage(e.getArgs()), request); } /** * 未定义异常 */ @ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class) @ResponseBody public ErrorResponse handleExceptionInternal(Exception e, WebRequest request) { log.error("未捕捉异常:" + e.getMessage(), e); final Integer code = INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode(); return new ErrorResponse(code, getLocaleMessage(code, e.getMessage()), request); } private String getLocaleMessage(Integer code, String defaultMsg) { try { return messageSource.getMessage("" + code, null, defaultMsg, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()); } catch (Throwable t) { log.warn("本地化异常消息发生异常: {}", code); return defaultMsg; } } }
从上面两个类可以看出,比较核心的是这么几个注解:
@ExceptionHandle:负责处理controller标注的类中抛出的异常的注解
@RestControllerAdvice:能够将@ExceptionHandler标注的方法集中到一个地方进行处理的注解,这个注解是复合注解,实现了@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseBody的功能。
借用谭朝红博文中的图片(蓝色箭头表示正常的请求和响应,红色箭头表示发生异常的请求和响应):
写个Demo测试一下
接下来我们写个demo测试一下是否能够实现异常的优雅响应:
@RestController @RequestMapping("index") @Slf4j public class IndexController { private final IndexService indexService; public IndexController(final IndexService indexService) { this.indexService = indexService; } @GetMapping("hello1") public Response<String> hello1() { Response<String> response = new Response<>(); try { response.setCode(200); response.setDesc("请求成功"); response.setData(indexService.hello()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("hello1方法请求异常", e); response.setCode(500); response.setDesc("请求异常:" + e.getMessage()); } finally { log.info("执行controller的finally结构"); } return response; } @GetMapping("hello2") public Response<String> hello2(@RequestParam("ex") String ex) { switch (ex) { case "ex1": throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.USER_NOT_FOUND, "用户信息不存在"); case "ex2": throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.MENU_NOT_FOUND, "菜单信息不存在"); case "ex3": throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, "请求参数异常"); case "ex4": throw new CodeBaseException(CommonResponseEnum.DATA_NOT_FOUND, "数据不存在"); } throw new CodeBaseException(INTERNAL_ERROR, new Object[]{ex}, "请求异常", new RuntimeException("运行时异常信息")); } }
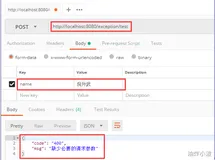
启动服务之后,传入不同参数获取不同的异常信息:
// 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex1 { "code": 4104, "desc": "User Not Found", "timestamp": "2020-10-10T05:58:39.433+00:00", "path": "/index/hello2" } // 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex2 { "code": 4204, "desc": "Menu Not Found", "timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:34.141+00:00", "path": "/index/hello2" } // 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex3 { "code": 4000, "desc": "[DEFAULT] Illegal Arguments", "timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:44.233+00:00", "path": "/index/hello2" } // 请求 /index/hello2?ex=ex4 { "code": 4004, "desc": "对应数据未找到", "timestamp": "2020-10-10T06:00:54.178+00:00", "path": "/index/hello2" }
设置标签
附上文中的代码:https://github.com/howardliu-cn/effective-spring/tree/main/spring-exception-handler,收工。