总览
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double cbrt (double x) |
计算 x 的立方根(double) |
float cbrtf (float x) |
计算 x 的立方根(float) |
long double cbrtl (long double x) |
计算 x 的立方根(long double) |
double ceil (double x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(double) |
float ceilf (float x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(float) |
long double ceill (long double x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(long double) |
double copysign (double x, double y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(double) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
float copysignf (float x, float y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(float) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
long double copysignl (long double x, long double y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(long double) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
int chdir(const char *path); |
更改当前的工作目录。如果成功返回 0,否则返回 -1 |
int chmod( const char *filename, int pmode); |
变更文件或目录的权限。如果改变成功返回0,否则返回-1 |
int chsize(int handle, long size); |
改变文件大小 |
void circle(int x, int y, int radius); |
在给定半径radius,以(x, y)为圆心画圆 |
void cleardevice(void); |
清除图形屏幕 |
void clearerr(FILE *stream); |
复位错误标志,使用它可以使文件错误标志和文件结束标志置为 0。 |
void clearviewport(); |
清除图形视区 |
int close(int handle); |
通过文件描述符handle,来关闭文件,成功返回0,出错返回-1 |
long clock(void); |
确定处理器调用某个进程或函数所用的时间 |
void closegraph(); |
关闭图形系统 |
double cos(double x); |
计算x的余弦(double) |
float cosf(float x); |
计算x的余弦(float) |
long double cosl(long double x); |
计算x的余弦(long double) |
double cosh(double x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(double) |
float coshf(float x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(float) |
long double coshl(long double x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(long double) |
int creat (const char *filename, int mode); |
创建一个新文件或重写一个已存在的文件 |
char *ctime(const time_t *time); |
把日期和时间转换为字符串 |
1. cbrt,cbrtf,cbrtl
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double cbrt (double x) |
计算 x 的立方根(double) |
float cbrtf (float x) |
计算 x 的立方根(float) |
long double cbrtl (long double x) |
计算 x 的立方根(long double) |
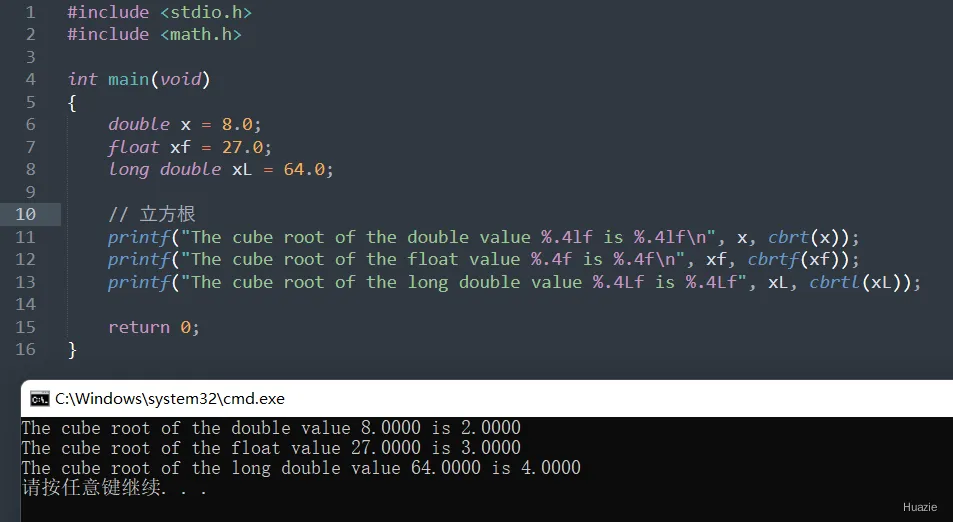
1.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x = 8.0;
float xf = 27.0;
long double xL = 64.0;
// 立方根
printf("The cube root of the double value %.4lf is %.4lf\n", x, cbrt(x));
printf("The cube root of the float value %.4f is %.4f\n", xf, cbrtf(xf));
printf("The cube root of the long double value %.4Lf is %.4Lf", xL, cbrtl(xL));
return 0;
}
1.3 运行结果
2. ceil,ceilf,ceill
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double ceil (double x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(double) |
float ceilf (float x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(float) |
long double ceill (long double x) |
计算大于或等于x的最小整数(long double) |
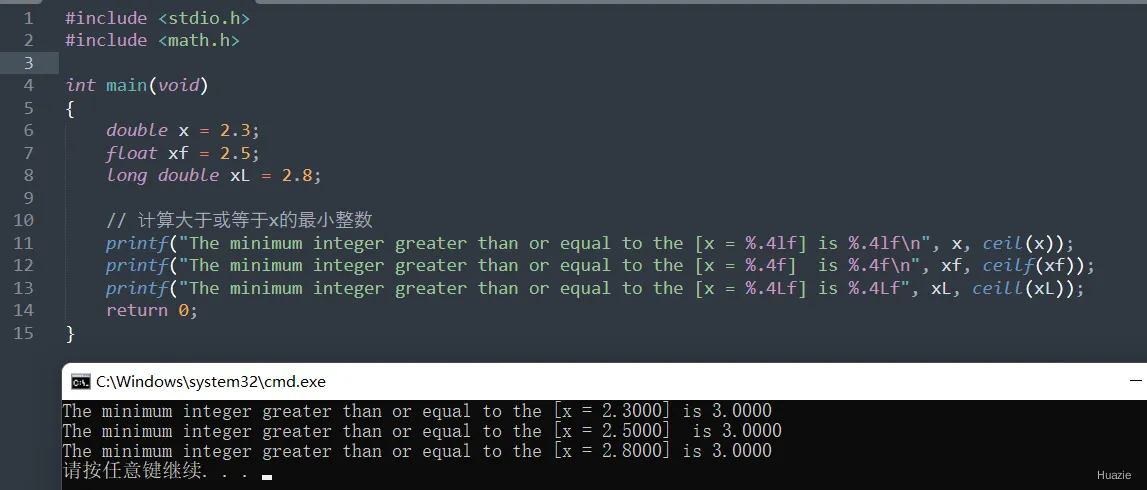
2.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x = 2.3;
float xf = 2.5;
long double xL = 2.8;
// 计算大于或等于x的最小整数
printf("The minimum integer greater than or equal to the [x = %.4lf] is %.4lf\n", x, ceil(x));
printf("The minimum integer greater than or equal to the [x = %.4f] is %.4f\n", xf, ceilf(xf));
printf("The minimum integer greater than or equal to the [x = %.4Lf] is %.4Lf", xL, ceill(xL));
return 0;
}
2.3 运行结果
3. copysign,copysignf,copysignl
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double copysign (double x, double y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(double) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
float copysignf (float x, float y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(float) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
long double copysignl (long double x, long double y); |
通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值。(long double) 例如,如果x为2.0,y为-1.0,则将生成值-2.0。 |
copysign 是一个数学函数,用于返回一个具有特定绝对值和符号的浮点数。它接受两个参数:第一个参数x是数值,第二个参数y是符号。该函数返回一个新的数,其值大小与x相同,但符号与y相同。这意味着如果y是正数,则结果与x相同;如果y是负数,则结果为x的相反数。
copysign 函数在数值分析和信号处理等领域非常有用,因为它允许程序员根据需要修改数据的符号而不改变其绝对大小。
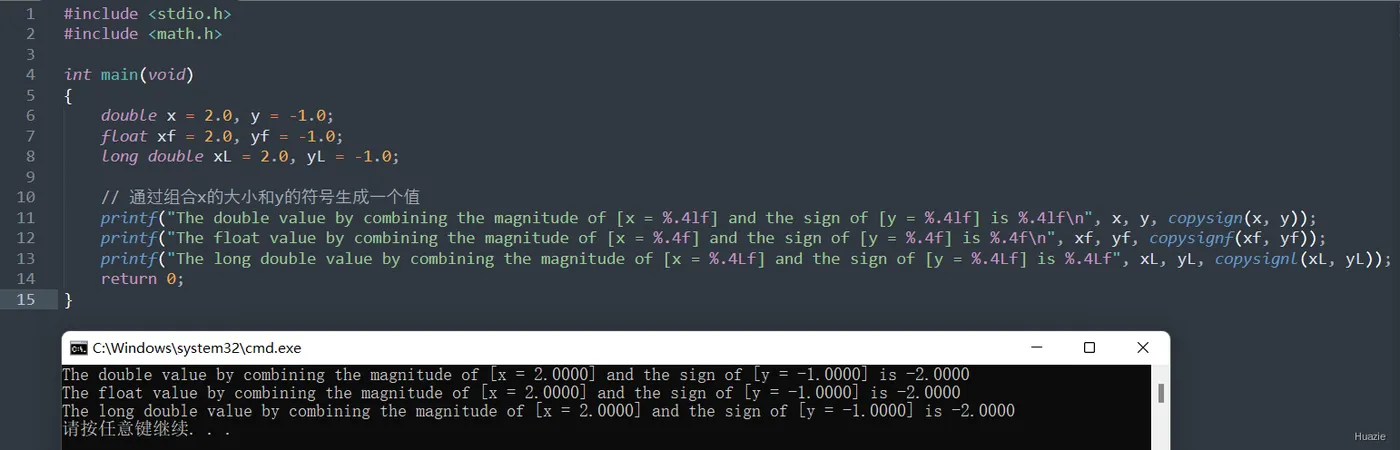
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x = 2.0, y = -1.0;
float xf = 2.0, yf = -1.0;
long double xL = 2.0, yL = -1.0;
// 通过组合x的大小和y的符号生成一个值
printf("The double value by combining the magnitude of [x = %.4lf] and the sign of [y = %.4lf] is %.4lf\n", x, y, copysign(x, y));
printf("The float value by combining the magnitude of [x = %.4f] and the sign of [y = %.4f] is %.4f\n", xf, yf, copysignf(xf, yf));
printf("The long double value by combining the magnitude of [x = %.4Lf] and the sign of [y = %.4Lf] is %.4Lf", xL, yL, copysignl(xL, yL));
return 0;
}
3.3 运行结果
4. chdir
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int chdir(const char *path); |
更改当前的工作目录。如果成功返回 0,否则返回 -1 |
4.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dir.h>
#define MAXDIR 1000
char old_dir[MAXDIR];
char new_dir[MAXDIR];
int main()
{
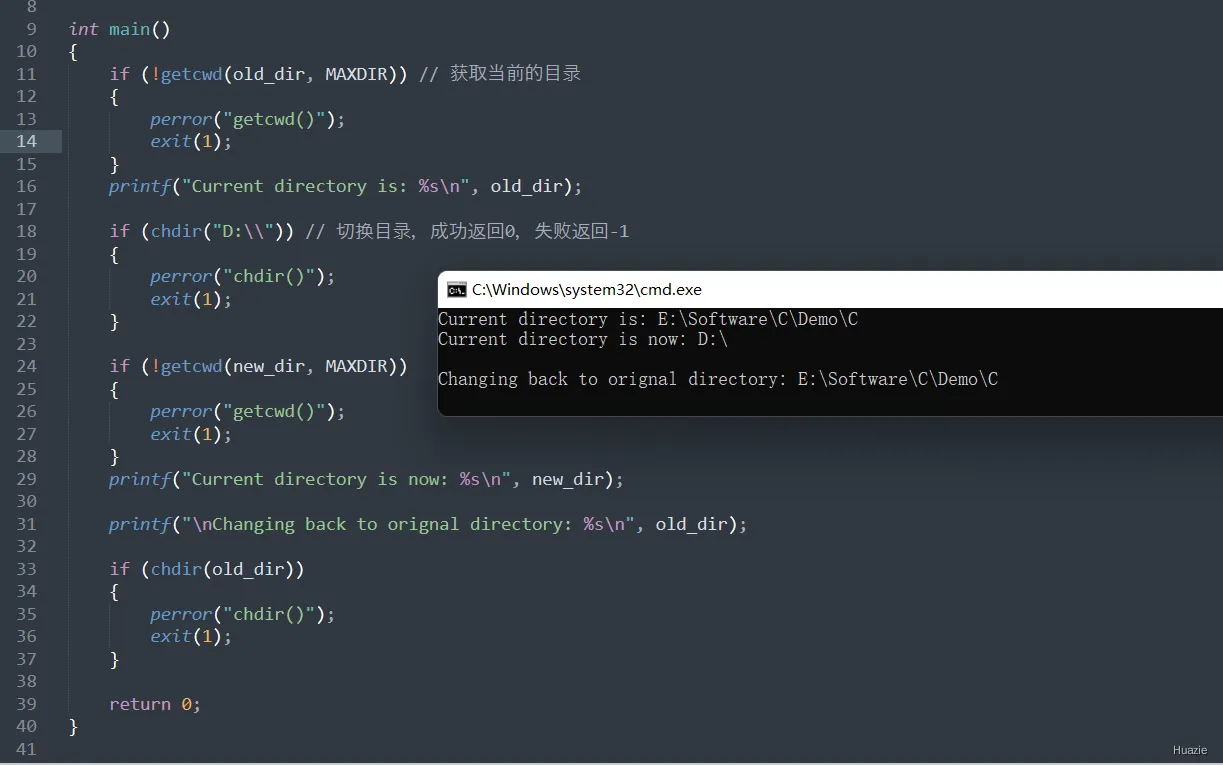
if (!getcwd(old_dir, MAXDIR)) // 获取当前的目录
{
perror("getcwd()");
exit(1);
}
printf("Current directory is: %s\n", old_dir);
if (chdir("D:\\")) // 切换目录,成功返回0,失败返回-1
{
perror("chdir()");
exit(1);
}
if (!getcwd(new_dir, MAXDIR))
{
perror("getcwd()");
exit(1);
}
printf("Current directory is now: %s\n", new_dir);
printf("\nChanging back to orignal directory: %s\n", old_dir);
if (chdir(old_dir))
{
perror("chdir()");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
4.3 运行结果
5. chmod
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int chmod( const char *filename, int pmode); |
变更文件或目录的权限。如果改变成功返回0,否则返回-1 |
5.2 演示示例
#include <sys\stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <io.h>
void make_read_only(char *filename);
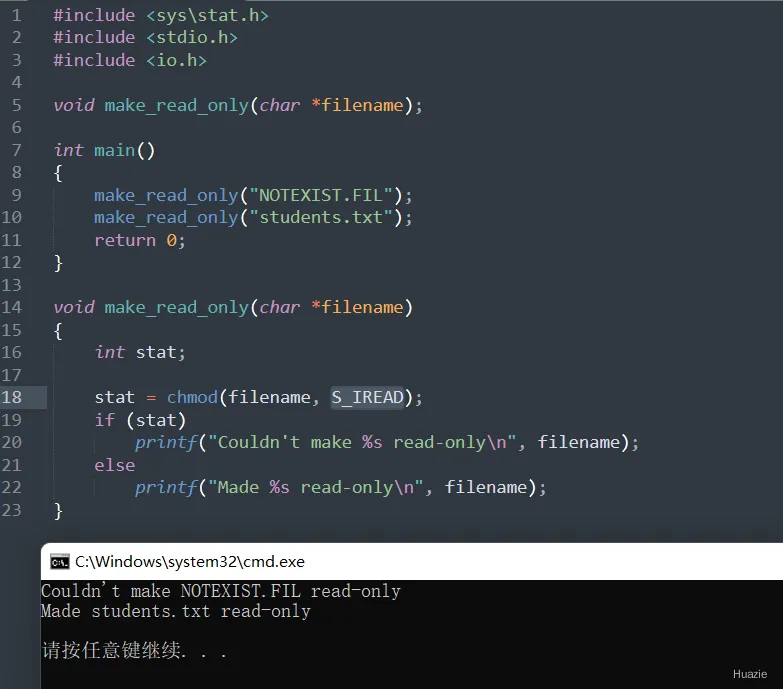
int main(void)
{
make_read_only("NOTEXIST.FIL");
make_read_only("students.txt");
return 0;
}
void make_read_only(char *filename)
{
int stat;
stat = chmod(filename, S_IREAD);
if (stat)
printf("Couldn't make %s read-only\n", filename);
else
printf("Made %s read-only\n", filename);
}
5.3 运行结果
6. chsize
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int chsize(int handle, long size); |
改变文件大小 |
6.2 演示示例
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
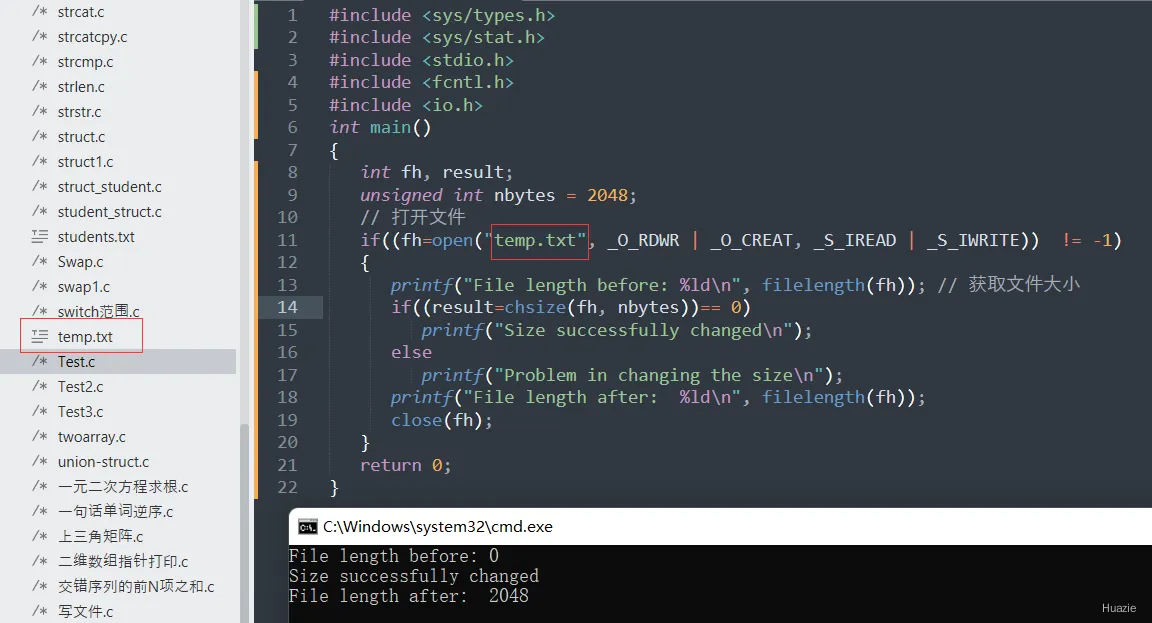
int main()
{
int fh, result;
unsigned int nbytes = 2048;
// 打开文件
if((fh=open("temp.txt", _O_RDWR | _O_CREAT, _S_IREAD | _S_IWRITE)) != -1)
{
printf("File length before: %ld\n", filelength(fh)); // 获取文件大小
if((result=chsize(fh, nbytes))== 0)
printf("Size successfully changed\n");
else
printf("Problem in changing the size\n");
printf("File length after: %ld\n", filelength(fh));
close(fh);
}
return 0;
}
6.3 运行结果
7. circle
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
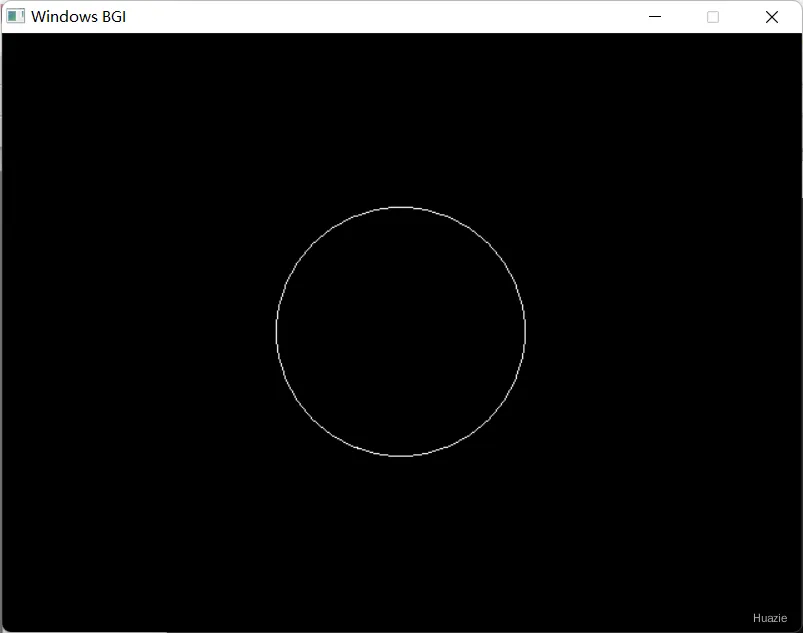
void circle(int x, int y, int radius); |
在给定半径radius,以(x, y)为圆心画圆 |
7.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main(void)
{
/* request auto detection */
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int midx, midy;
int radius = 100;
/* initialize graphics and local variables */
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk) /* an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
midx = getmaxx() / 2;
midy = getmaxy() / 2;
setcolor(getmaxcolor());
/* draw the circle */
circle(midx, midy, radius);
/* clean up */
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
7.3 运行结果
8. cleardevice
8.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void cleardevice(void); |
清除图形屏幕 |
8.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main(void)
{
/* request auto detection */
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int midx, midy;
/* initialize graphics and local variables */
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk) /* an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
midx = getmaxx() / 2;
midy = getmaxy() / 2;
setcolor(getmaxcolor());
/* for centering screen messages */
settextjustify(CENTER_TEXT, CENTER_TEXT);
/* output a message to the screen */
outtextxy(midx, midy, "press any key to clear the screen:");
/* wait for a key */
getch();
/* clear the screen */
cleardevice();
/* output another message */
outtextxy(midx, midy, "press any key to quit:");
/* clean up */
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
8.3 运行结果

9. clearerr
9.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void clearerr(FILE *stream); |
复位错误标志,使用它可以使文件错误标志和文件结束标志置为 0。 |
9.2 演示示例
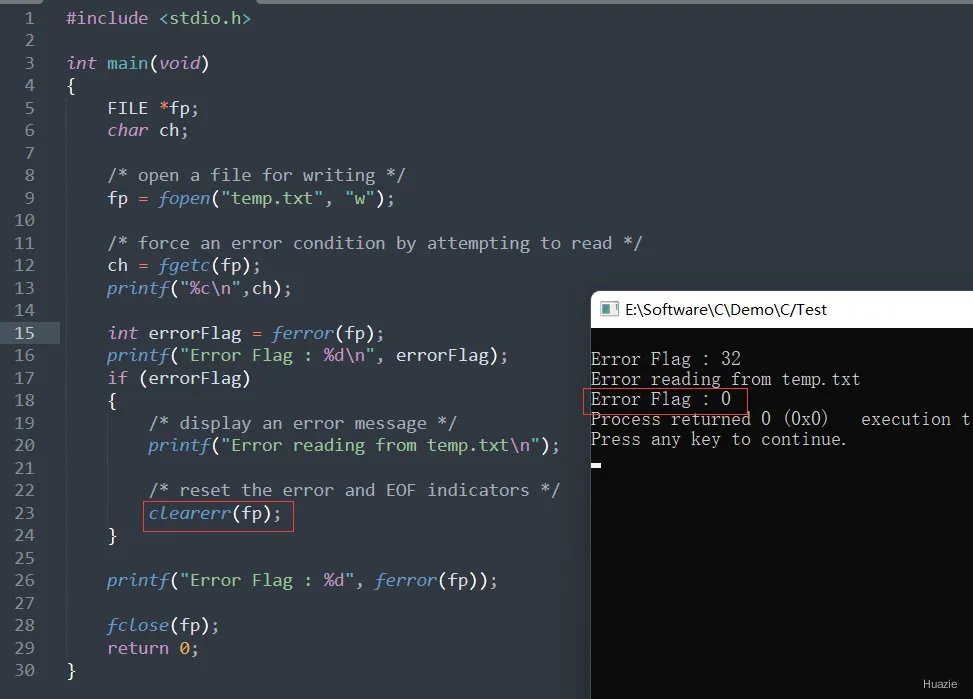
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
char ch;
/* open a file for writing */
fp = fopen("temp.txt", "w");
/* force an error condition by attempting to read */
ch = fgetc(fp);
printf("%c\n",ch);
int errorFlag = ferror(fp);
printf("Error Flag : %d\n", errorFlag);
if (errorFlag)
{
/* display an error message */
printf("Error reading from temp.txt\n");
/* reset the error and EOF indicators */
clearerr(fp);
}
printf("Error Flag : %d", ferror(fp));
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
9.3 运行结果
10. clearviewport
10.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void clearviewport(); |
清除图形视区 |
10.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define CLIP_ON 1 /* activates clipping in viewport */
int main(void)
{
/* request auto detection */
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int ht;
/* initialize graphics and local variables */
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk) /* an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
setcolor(getmaxcolor());
ht = textheight("W");
/* message in default full-screen viewport */
outtextxy(0, 0, "* <-- (0, 0) in default viewport");
/* create a smaller viewport */
setviewport(50, 50, getmaxx()-50, getmaxy()-50, CLIP_ON);
/* display some messages */
outtextxy(0, 0, "* <-- (0, 0) in smaller viewport");
outtextxy(0, 2*ht, "Press any key to clear viewport:");
/* wait for a key */
getch();
/* clear the viewport */
clearviewport();
/* output another message */
outtextxy(0, 0, "Press any key to quit:");
/* clean up */
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
10.3 运行结果

11. close
11.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int close(int handle); |
通过文件描述符handle,来关闭文件,成功返回0,出错返回-1 |
11.2 演示示例
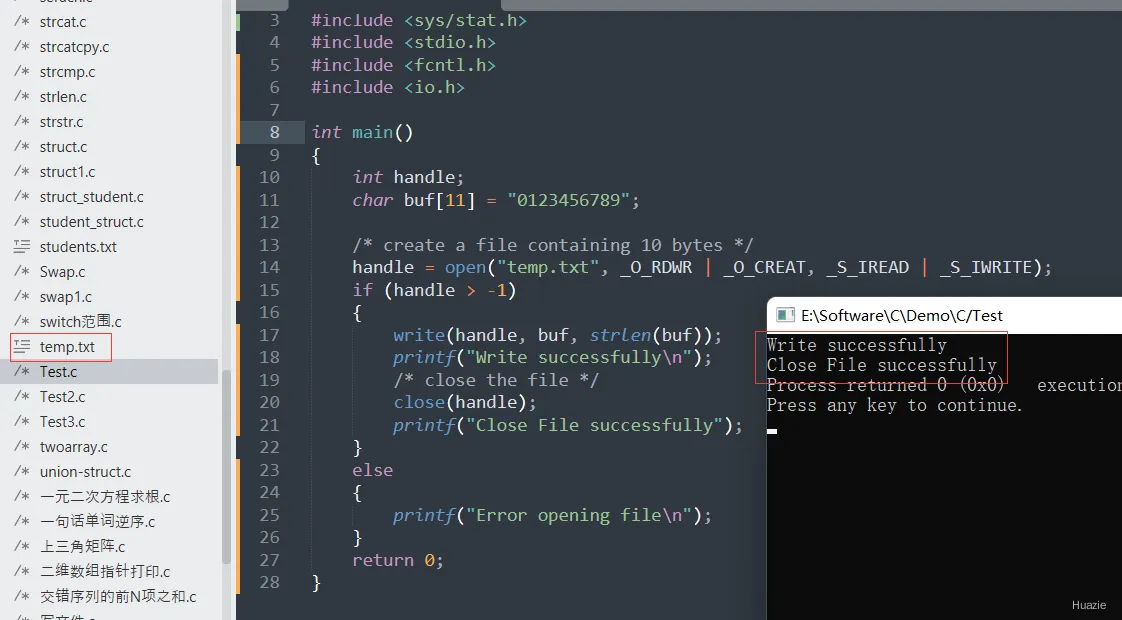
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
int main()
{
int handle;
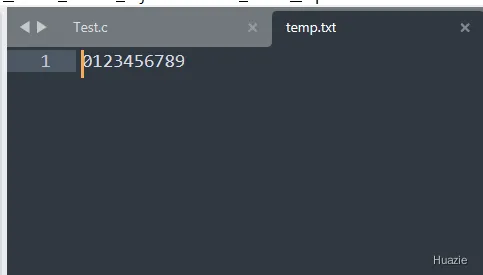
char buf[11] = "0123456789";
/* create a file containing 10 bytes */
handle = open("temp.txt", _O_RDWR | _O_CREAT, _S_IREAD | _S_IWRITE);
if (handle > -1)
{
write(handle, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("Write successfully\n");
/* close the file */
close(handle);
printf("Close File successfully");
}
else
{
printf("Error opening file\n");
}
return 0;
}
11.3 运行结果
12. clock
12.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
long clock(void); |
确定处理器调用某个进程或函数所用的时间 |
12.2 演示示例
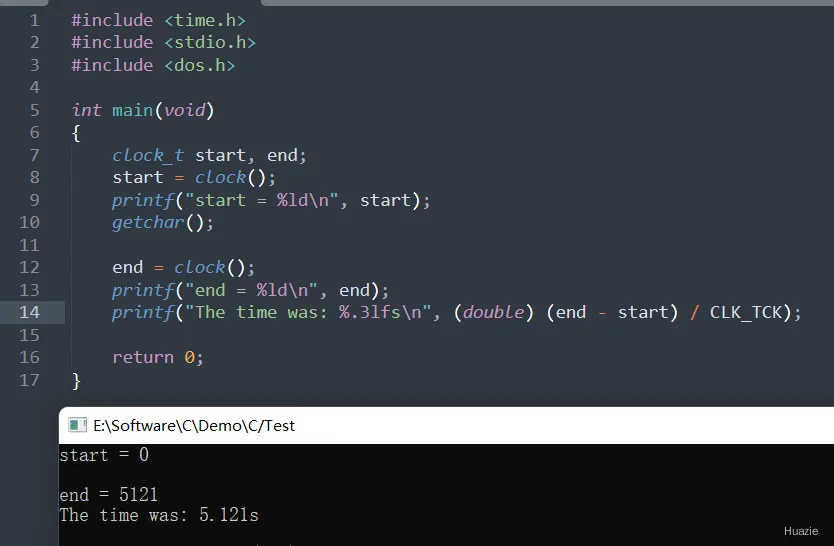
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
int main(void)
{
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
printf("start = %ld\n", start);
getchar();
end = clock();
printf("end = %ld\n", end);
printf("The time was: %.3lfs\n", (double) (end - start) / CLK_TCK);
return 0;
}
12.3 运行结果
13. closegraph
13.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void closegraph(); |
关闭图形系统 |
13.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main(void)
{
/* request auto detection */
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int x, y;
/* initialize graphics mode */
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk) /* an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
x = getmaxx() / 2;
y = getmaxy() / 2;
/* output a message */
settextjustify(CENTER_TEXT, CENTER_TEXT);
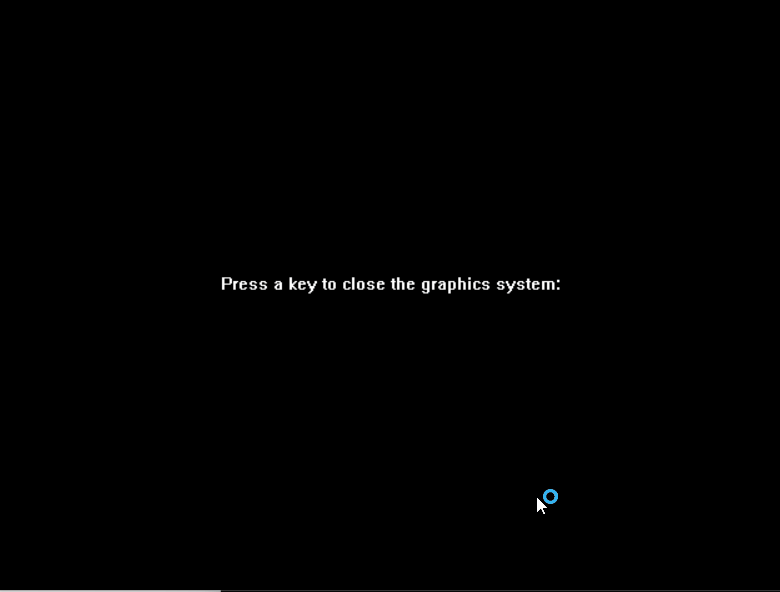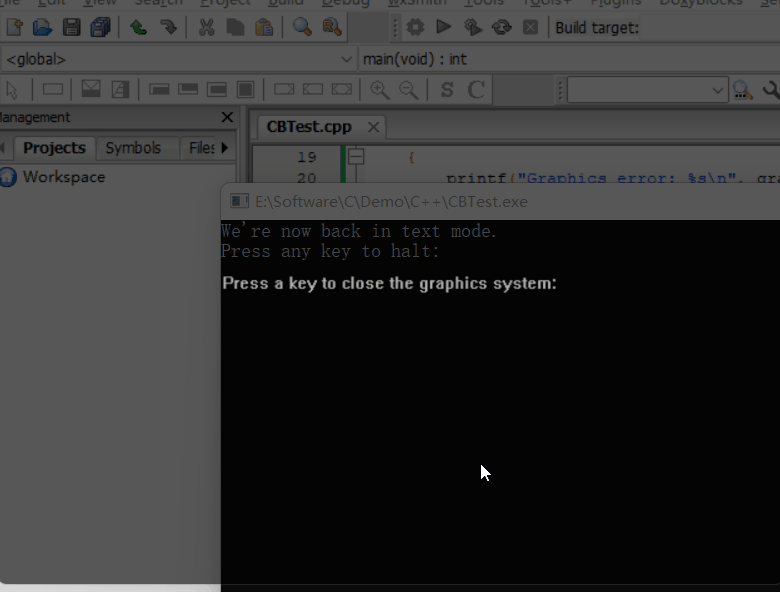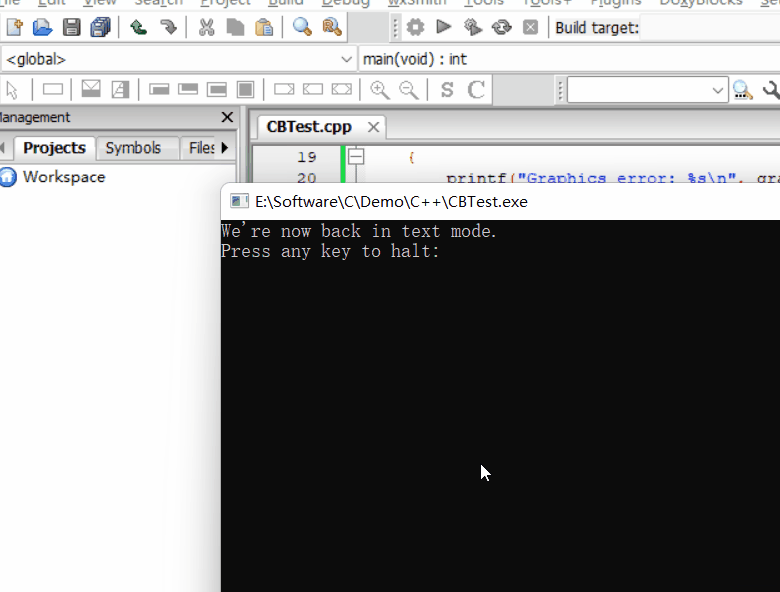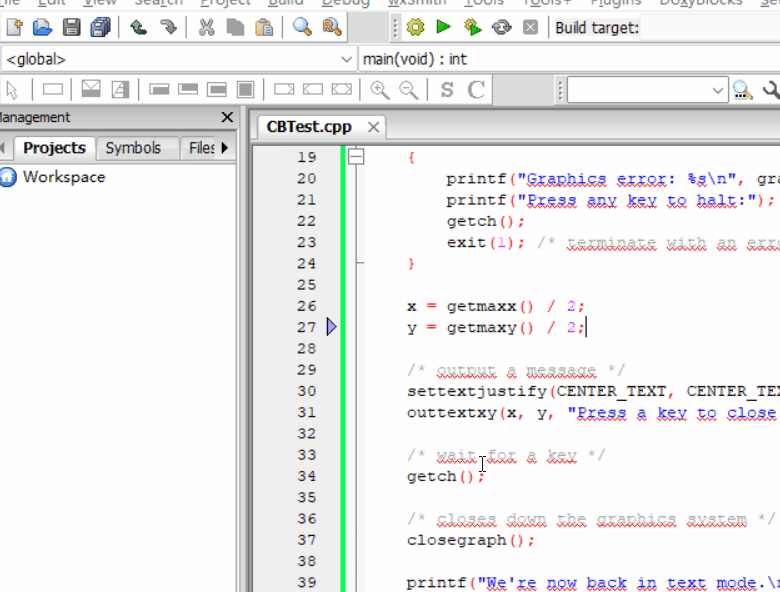
outtextxy(x, y, "Press a key to close the graphics system:");
/* wait for a key */
getch();
/* closes down the graphics system */
closegraph();
printf("We're now back in text mode.\n");
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getchar();
return 0;
}
13.3 运行结果
14. cos,cosf,cosl
14.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double cos(double x); |
计算x的余弦(double) |
float cosf(float x); |
计算x的余弦(float) |
long double cosl(long double x); |
计算x的余弦(long double) |
14.2 演示示例
// Huazie
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x = 1.0;
double result = cos(x); // 余弦
float xf = 1.0f;
float resultf = cosf(xf);
long double xL = 1.0;
long double resultL = cosl(xL);
printf("The cosine of %lf is %.16lf\n", x, result);
printf("The cosine of %f is %.16f\n", xf, resultf);
printf("The cosine of %Lf is %.16Lf\n", xL, resultL);
return 0;
}
14.3 运行结果
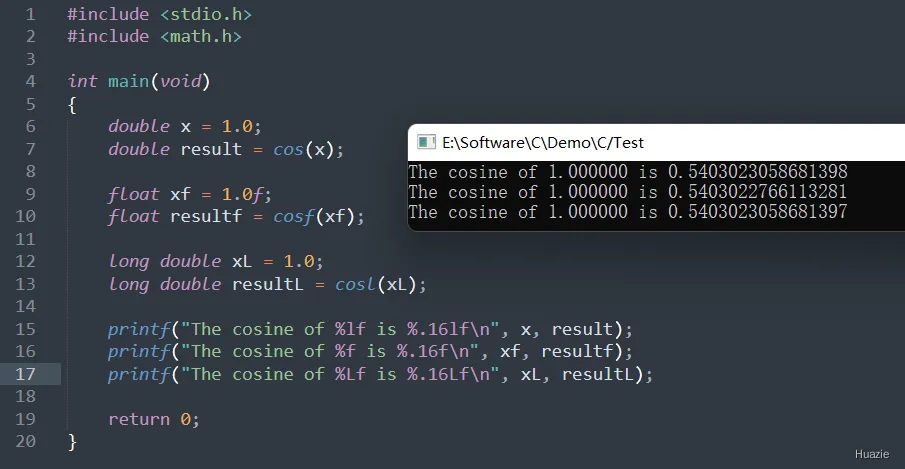
15. cosh,coshf,coshl
15.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double cosh(double x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(double) |
float coshf(float x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(float) |
long double coshl(long double x); |
计算x的双曲余弦(long double) |
15.2 演示示例
// Huazie
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x = 1.0;
double result = cosh(x); // 双曲余弦
float xf = 1.0f;
float resultf = coshf(xf);
long double xL = 1.0;
long double resultL = coshl(xL);
printf("The hyperbolic coshine of %lf is %.16lf\n", x, result);
printf("The hyperbolic coshine of %f is %.16f\n", xf, resultf);
printf("The hyperbolic coshine of %Lf is %.16Lf\n", xL, resultL);
return 0;
}
15.3 运行结果
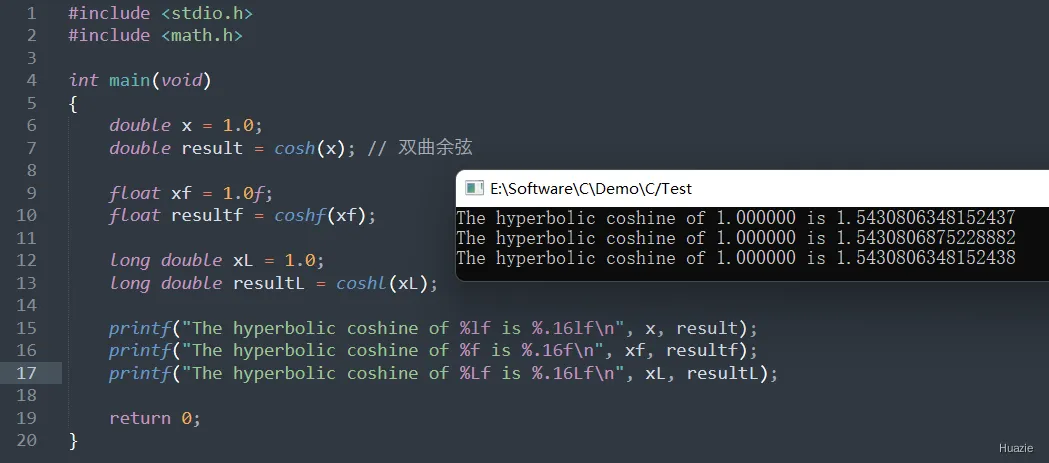
16. creat
16.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int creat (const char *filename, int mode); |
创建一个新文件或重写一个已存在的文件 |
16.2 演示示例
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
int handle;
char buf[11] = "0123456789";
handle = creat("temp1.txt", S_IREAD | S_IWRITE);
printf("Create file successfully");
/* write 10 bytes to the file */
write(handle, buf, strlen(buf));
/* close the file */
close(handle);
return 0;
}
16.3 运行结果
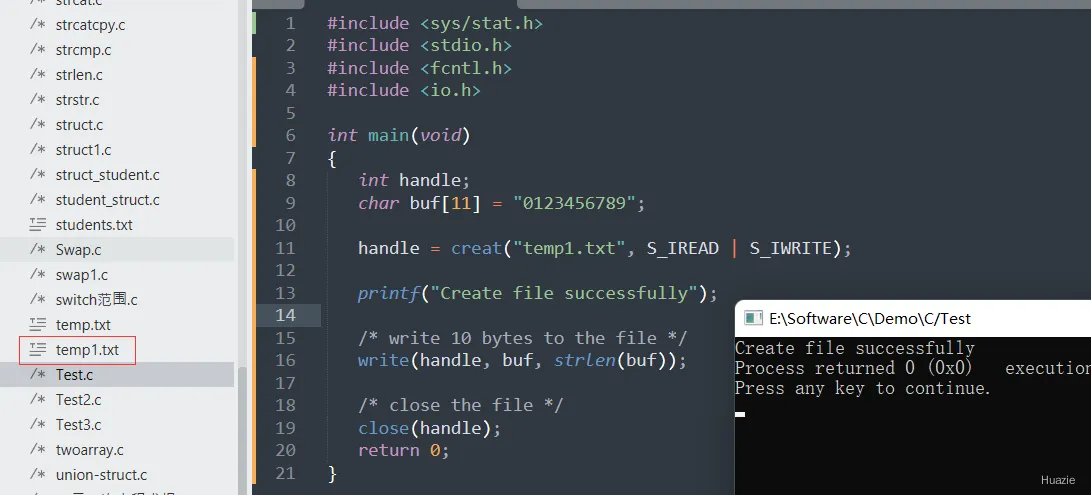
17. ctime
17.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
char *ctime(const time_t *time); |
把日期和时间转换为字符串 |
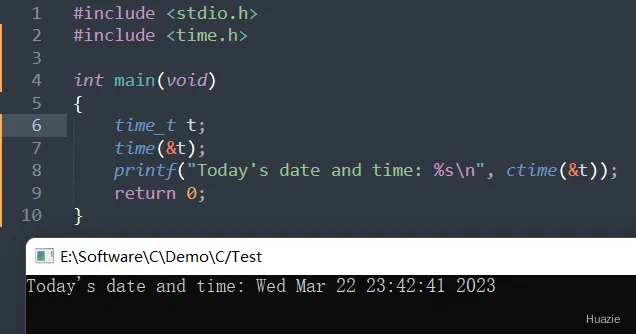
17.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(void)
{
time_t t;
time(&t);
printf("Today's date and time: %s\n", ctime(&t));
return 0;
}
17.3 运行结果