CreateCollection API执行流程(addCollectionMetaStep)源码解析
milvus版本:v2.3.2
CreateCollection这个API流程较长,也是milvus的核心API之一,涉及的内容比较复杂。这里介绍和channel相关的流程。
整体架构:
CreateCollection(addCollectionMetaStep)的数据流向:
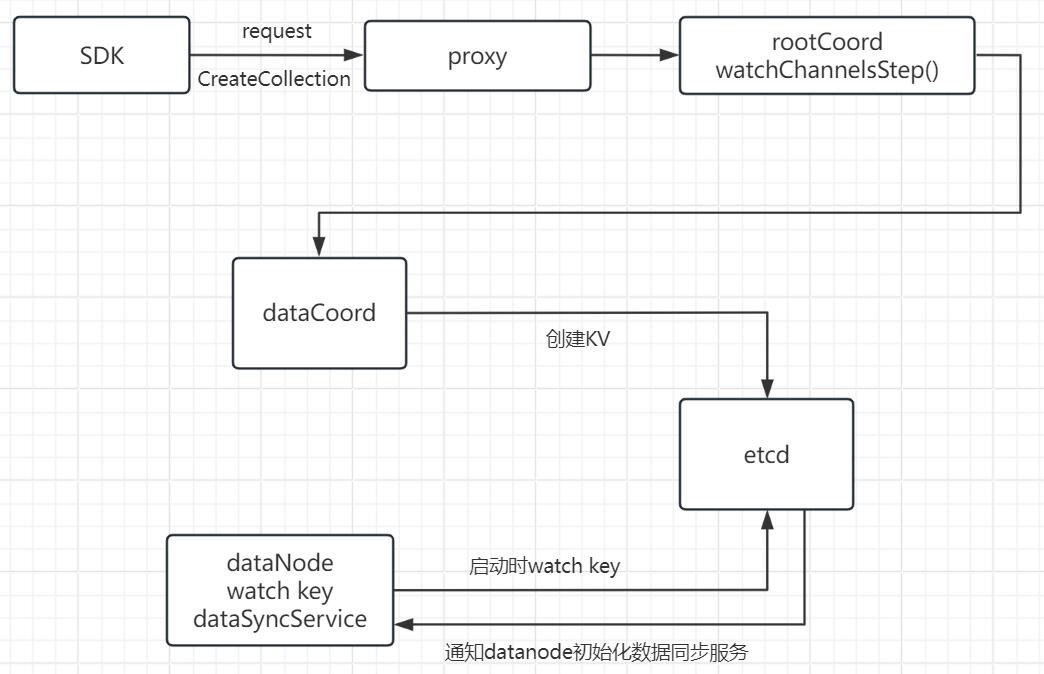
1.客户端sdk发出CreateCollection API请求。
from pymilvus import (
connections,
FieldSchema, CollectionSchema, DataType,
Collection,
)
num_entities, dim = 3000, 1024
print("start connecting to Milvus")
connections.connect("default", host="192.168.230.71", port="19530")
fields = [
FieldSchema(name="pk", dtype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, auto_id=False, max_length=100),
FieldSchema(name="random", dtype=DataType.DOUBLE),
FieldSchema(name="embeddings", dtype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=dim)
]
schema = CollectionSchema(fields, "hello_milvus is the simplest demo to introduce the APIs")
print("Create collection `hello_milvus`")
hello_milvus = Collection("hello_milvus", schema, consistency_level="Strong",shards_num=2)
客户端SDK向proxy发送一个CreateCollection API请求,创建一个名为hello_milvus的collection。
2.客户端接受API请求,将request封装为createCollectionTask,并压入ddQueue队列。
代码路径:internal\proxy\impl.go
func (node *Proxy) CreateCollection(ctx context.Context, request *milvuspb.CreateCollectionRequest) (*commonpb.Status, error) {
......
// request封装为task
cct := &createCollectionTask{
ctx: ctx,
Condition: NewTaskCondition(ctx),
CreateCollectionRequest: request,
rootCoord: node.rootCoord,
}
......
// 将task压入ddQueue队列
if err := node.sched.ddQueue.Enqueue(cct); err != nil {
......
}
......
// 等待cct执行完
if err := cct.WaitToFinish(); err != nil {
......
}
......
}
3.执行createCollectionTask的3个方法PreExecute、Execute、PostExecute。
PreExecute()一般为参数校验等工作。
Execute()一般为真正执行逻辑。
PostExecute()执行完后的逻辑,什么都不做,返回nil。
代码路径:internal\proxy\task.go
func (t *createCollectionTask) Execute(ctx context.Context) error {
var err error
t.result, err = t.rootCoord.CreateCollection(ctx, t.CreateCollectionRequest)
return err
}
从代码可以看出调用了rootCoord的CreateCollection接口。
4.进入rootCoord的CreateCollection接口。
代码路径:internal\rootcoord\root_coord.go
继续将请求封装为rootcoord里的createCollectionTask
func (c *Core) CreateCollection(ctx context.Context, in *milvuspb.CreateCollectionRequest) (*commonpb.Status, error) {
......
// 封装为createCollectionTask
t := &createCollectionTask{
baseTask: newBaseTask(ctx, c),
Req: in,
}
// 加入调度
if err := c.scheduler.AddTask(t); err != nil {
......
}
// 等待task完成
if err := t.WaitToFinish(); err != nil {
......
}
......
}
5.执行createCollectionTask的Prepare、Execute、NotifyDone方法。
Execute()为核心方法。
代码路径:internal\rootcoord\create_collection_task.go
func (t *createCollectionTask) Execute(ctx context.Context) error {
// collID为collectionID,在Prepare()里分配
// partIDs为partitionID,在Prepare()里分配
collID := t.collID
partIDs := t.partIDs
// 产生时间戳
ts, err := t.getCreateTs()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// vchanNames为虚拟channel,在Prepare()里分配
// chanNames为物理channel,在Prepare()里分配
vchanNames := t.channels.virtualChannels
chanNames := t.channels.physicalChannels
startPositions, err := t.addChannelsAndGetStartPositions(ctx, ts)
if err != nil {
t.core.chanTimeTick.removeDmlChannels(t.channels.physicalChannels...)
return err
}
// 填充partition,创建collection的时候,默认只有一个名为"Default partition"的partition。
partitions := make([]*model.Partition, len(partIDs))
for i, partID := range partIDs {
partitions[i] = &model.Partition{
PartitionID: partID,
PartitionName: t.partitionNames[i],
PartitionCreatedTimestamp: ts,
CollectionID: collID,
State: pb.PartitionState_PartitionCreated,
}
}
// 填充collection
// 可以看出collection由collID、dbid、schemaName、fields、vchanName、chanName、partition、shardNum等组成
collInfo := model.Collection{
CollectionID: collID,
DBID: t.dbID,
Name: t.schema.Name,
Description: t.schema.Description,
AutoID: t.schema.AutoID,
Fields: model.UnmarshalFieldModels(t.schema.Fields),
VirtualChannelNames: vchanNames,
PhysicalChannelNames: chanNames,
ShardsNum: t.Req.ShardsNum,
ConsistencyLevel: t.Req.ConsistencyLevel,
StartPositions: toKeyDataPairs(startPositions),
CreateTime: ts,
State: pb.CollectionState_CollectionCreating,
Partitions: partitions,
Properties: t.Req.Properties,
EnableDynamicField: t.schema.EnableDynamicField,
}
clone := collInfo.Clone()
existedCollInfo, err := t.core.meta.GetCollectionByName(ctx, t.Req.GetDbName(), t.Req.GetCollectionName(), typeutil.MaxTimestamp)
if err == nil {
equal := existedCollInfo.Equal(*clone)
if !equal {
return fmt.Errorf("create duplicate collection with different parameters, collection: %s", t.Req.GetCollectionName())
}
log.Warn("add duplicate collection", zap.String("collection", t.Req.GetCollectionName()), zap.Uint64("ts", ts))
return nil
}
// 分为多个step执行,每一个undoTask由todoStep和undoStep构成
// 执行todoStep,报错则执行undoStep
undoTask := newBaseUndoTask(t.core.stepExecutor)
undoTask.AddStep(&expireCacheStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
dbName: t.Req.GetDbName(),
collectionNames: []string{
t.Req.GetCollectionName()},
collectionID: InvalidCollectionID,
ts: ts,
}, &nullStep{
})
undoTask.AddStep(&nullStep{
}, &removeDmlChannelsStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
pChannels: chanNames,
})
undoTask.AddStep(&addCollectionMetaStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
coll: &collInfo,
}, &deleteCollectionMetaStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
collectionID: collID,
ts: ts,
})
undoTask.AddStep(&nullStep{
}, &unwatchChannelsStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
collectionID: collID,
channels: t.channels,
isSkip: !Params.CommonCfg.TTMsgEnabled.GetAsBool(),
})
undoTask.AddStep(&watchChannelsStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
info: &watchInfo{
ts: ts,
collectionID: collID,
vChannels: t.channels.virtualChannels,
startPositions: toKeyDataPairs(startPositions),
schema: &schemapb.CollectionSchema{
Name: collInfo.Name,
Description: collInfo.Description,
AutoID: collInfo.AutoID,
Fields: model.MarshalFieldModels(collInfo.Fields),
},
},
}, &nullStep{
})
undoTask.AddStep(&changeCollectionStateStep{
baseStep: baseStep{
core: t.core},
collectionID: collID,
state: pb.CollectionState_CollectionCreated,
ts: ts,
}, &nullStep{
})
return undoTask.Execute(ctx)
}
创建collection涉及多个步骤,可以看出这里依次分为expireCacheStep、addCollectionMetaStep、watchChannelsStep、changeCollectionStateStep这几个步骤,addCollectionMetaStep是关于etcd元数据的step,已在另一篇文章对其进行详细解析。本篇幅对watchChannelsStep进行解析。
6.进入watchChannelsStep,执行其Execute()方法。
代码路径:internal\rootcoord\step.go
func (s *watchChannelsStep) Execute(ctx context.Context) ([]nestedStep, error) {
err := s.core.broker.WatchChannels(ctx, s.info)
return nil, err
}
在这里重点研究s.core.broker.WatchChannels()这个方法做了什么事情。
调用栈如下:
s.core.broker.WatchChannels()
|--WatchChannels()(internal\rootcoord\broker.go)
|--b.s.dataCoord.WatchChannels()
|--WatchChannels()(internal\datacoord\services.go)
|--s.channelManager.Watch()
|--c.updateWithTimer()(internal\datacoord\channel_manager.go)
|--c.store.Update()
|--c.update()(internal\datacoord\channel_store.go)
|--c.txn()(同上)
|--c.store.MultiSaveAndRemove()(同上)
|--MultiSaveAndRemove()(internal\kv\etcd\etcd_kv.go)
|--s.meta.catalog.MarkChannelAdded()

WatchChannels这个操作最终是在etcd写入kv。那么我们研究写入的kv是什么。
根据堆栈顺序来进行分析。
1.WatchChannels()方法
代码路径:internal\datacoord\services.go
// WatchChannels notifies DataCoord to watch vchannels of a collection.
func (s *Server) WatchChannels(ctx context.Context, req *datapb.WatchChannelsRequest) (*datapb.WatchChannelsResponse, error) {
log := log.Ctx(ctx).With(
zap.Int64("collectionID", req.GetCollectionID()),
zap.Strings("channels", req.GetChannelNames()),
)
log.Info("receive watch channels request")
resp := &datapb.WatchChannelsResponse{
Status: merr.Success(),
}
if err := merr.CheckHealthy(s.GetStateCode()); err != nil {
return &datapb.WatchChannelsResponse{
Status: merr.Status(err),
}, nil
}
// req.GetChannelNames()得到的值为:
// by-dev-rootcoord-dml_2_445674962009727985v0
// by-dev-rootcoord-dml_3_445674962009727985v1
for _, channelName := range req.GetChannelNames() {
ch := &channel{
Name: channelName,
CollectionID: req.GetCollectionID(),
StartPositions: req.GetStartPositions(),
Schema: req.GetSchema(),
CreateTimestamp: req.GetCreateTimestamp(),
}
// 循环执行watch()
err := s.channelManager.Watch(ctx, ch)
if err != nil {
log.Warn("fail to watch channelName", zap.Error(err))
resp.Status = merr.Status(err)
return resp, nil
}
// 向etcd写入另外一个kv
if err := s.meta.catalog.MarkChannelAdded(ctx, ch.Name); err != nil {
// TODO: add background task to periodically cleanup the orphaned channel add marks.
log.Error("failed to mark channel added", zap.Error(err))
resp.Status = merr.Status(err)
return resp, nil
}
}
return resp, nil
}
函数入参req的值如下:
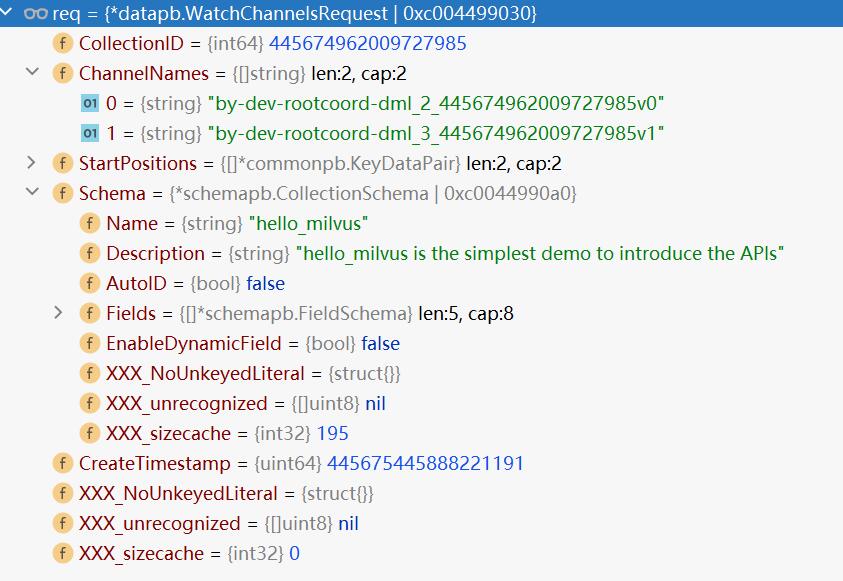
在这里有2个channelName,是虚拟channel,为什么是2个channel?因为客户端SDK创建collection传入了shards_num=2。一个shard对应一个虚拟channel。
channel名称by-dev-rootcoord-dml_2_445674962009727985v0中的445674962009727985是collectionID。
2.进入到s.channelManager.Watch()
代码路径:internal\datacoord\channel_manager.go
// Watch tries to add the channel to cluster. Watch is a no op if the channel already exists.
func (c *ChannelManager) Watch(ctx context.Context, ch *channel) error {
log := log.Ctx(ctx)
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// 使用分配策略:datacoord.AverageAssignPolicy
updates := c.assignPolicy(c.store, []*channel{
ch})
if len(updates) == 0 {
return nil
}
log.Info("try to update channel watch info with ToWatch state",
zap.String("channel", ch.String()),
zap.Array("updates", updates))
// 操作etcd
err := c.updateWithTimer(updates, datapb.ChannelWatchState_ToWatch)
if err != nil {
log.Warn("fail to update channel watch info with ToWatch state",
zap.String("channel", ch.String()), zap.Array("updates", updates), zap.Error(err))
}
return err
}
updates的值为:
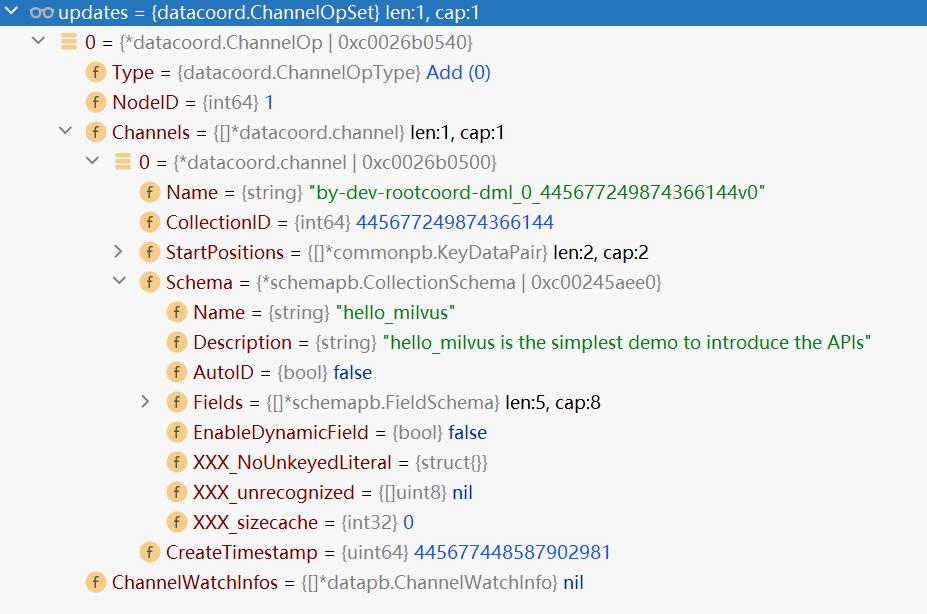
updates变量是一个ChannelOpSet类型。这时候ChannelWatchInfos为空。
type ChannelOpSet []*ChannelOp
type ChannelOp struct {
Type ChannelOpType
NodeID int64
Channels []*channel
ChannelWatchInfos []*datapb.ChannelWatchInfo
}
3.进入c.updateWithTimer()
代码路径:internal\datacoord\channel_manager.go
func (c *ChannelManager) updateWithTimer(updates ChannelOpSet, state datapb.ChannelWatchState) error {
channelsWithTimer := []string{
}
// updates此时数组长度为1
for _, op := range updates {
if op.Type == Add {
// 填充ChannelWatchInfos
channelsWithTimer = append(channelsWithTimer, c.fillChannelWatchInfoWithState(op, state)...)
}
}
// 操作etcd
err := c.store.Update(updates)
if err != nil {
log.Warn("fail to update", zap.Array("updates", updates), zap.Error(err))
c.stateTimer.removeTimers(channelsWithTimer)
}
c.lastActiveTimestamp = time.Now()
return err
}
4.进入c.store.Update()
代码路径:internal\datacoord\channel_store.go
// Update applies the channel operations in opSet.
func (c *ChannelStore) Update(opSet ChannelOpSet) error {
totalChannelNum := 0
for _, op := range opSet {
totalChannelNum += len(op.Channels)
}
// totalChannelNum = 1
// maxOperationsPerTxn = 64
if totalChannelNum <= maxOperationsPerTxn {
// 走这条路径
return c.update(opSet)
}
// 如果超过则分批执行
......
}
5.进入c.update(opSet)
代码路径:internal\datacoord\channel_store.go
// update applies the ADD/DELETE operations to the current channel store.
func (c *ChannelStore) update(opSet ChannelOpSet) error {
// Update ChannelStore's kv store.
// 操作etcd
if err := c.txn(opSet); err != nil {
return err
}
// Update node id -> channel mapping.
for _, op := range opSet {
switch op.Type {
case Add:
for _, ch := range op.Channels {
if c.checkIfExist(op.NodeID, ch) {
continue // prevent adding duplicated channel info
}
// Append target channels to channel store.
c.channelsInfo[op.NodeID].Channels = append(c.channelsInfo[op.NodeID].Channels, ch)
}
case Delete:
// Remove target channels from channel store.
del := make(map[string]struct{
})
for _, ch := range op.Channels {
del[ch.Name] = struct{
}{
}
}
prev := c.channelsInfo[op.NodeID].Channels
curr := make([]*channel, 0, len(prev))
for _, ch := range prev {
if _, ok := del[ch.Name]; !ok {
curr = append(curr, ch)
}
}
c.channelsInfo[op.NodeID].Channels = curr
default:
return errUnknownOpType
}
metrics.DataCoordDmlChannelNum.WithLabelValues(strconv.FormatInt(op.NodeID, 10)).Set(float64(len(c.channelsInfo[op.NodeID].Channels)))
}
return nil
}
6.进入c.txn(opSet)
代码路径:internal\datacoord\channel_store.go
// txn updates the channelStore's kv store with the given channel ops.
func (c *ChannelStore) txn(opSet ChannelOpSet) error {
saves := make(map[string]string)
var removals []string
for _, op := range opSet {
for i, ch := range op.Channels {
// 构建key的规则
k := buildNodeChannelKey(op.NodeID, ch.Name)
switch op.Type {
case Add:
// 构建value,ChannelWatchInfo
info, err := proto.Marshal(op.ChannelWatchInfos[i])
if err != nil {
return err
}
saves[k] = string(info)
case Delete:
removals = append(removals, k)
default:
return errUnknownOpType
}
}
}
return c.store.MultiSaveAndRemove(saves, removals)
}
因为op.Type是Add,所以removals是nil。
key的值:
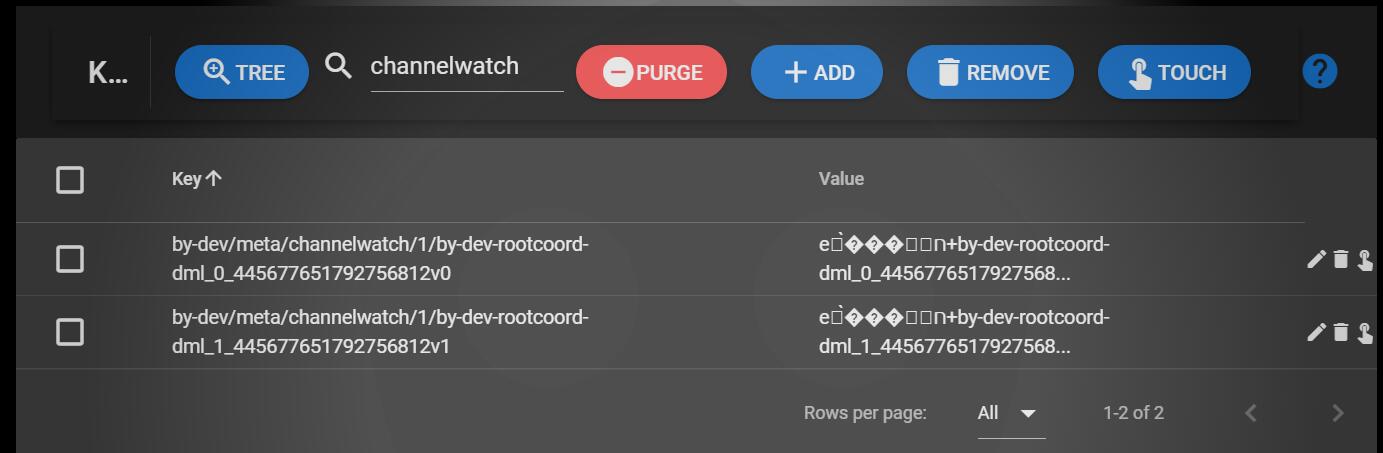
channelwatch/1/by-dev-rootcoord-dml_2_445674962009727985v0
规则为:channelwatch/{nodeID}/{chName}
saves变量的值:
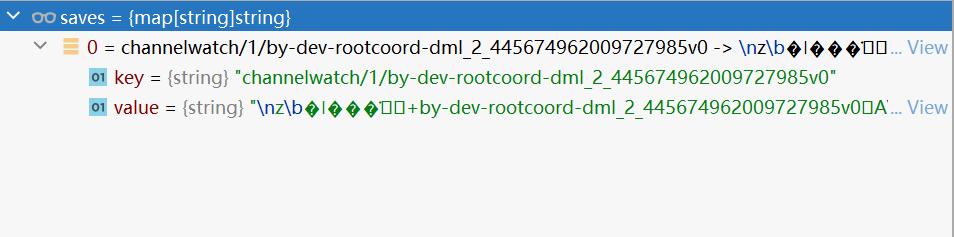
后面已经不用再跟踪下去。
使用etcd-manager查看etcd。
7.进入s.meta.catalog.MarkChannelAdded()
代码路径:internal\metastore\kv\datacoord\kv_catalog.go
func (kc *Catalog) MarkChannelAdded(ctx context.Context, channel string) error {
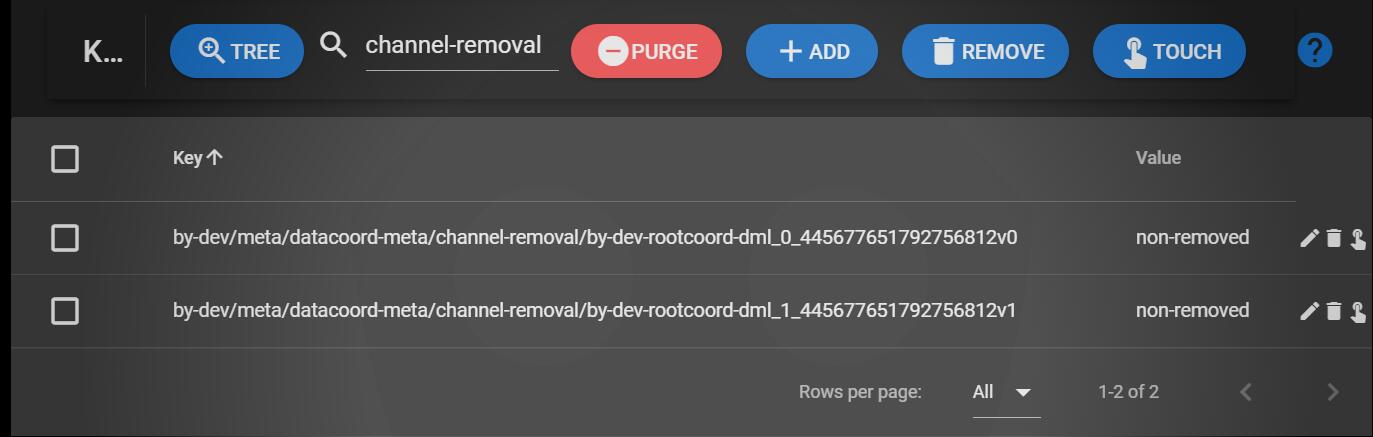
// 构建key的规则:datacoord-meta/channel-removal/{channelName}
key := buildChannelRemovePath(channel)
// 构建value:NonRemoveFlagTomestone = "non-removed"
err := kc.MetaKv.Save(key, NonRemoveFlagTomestone)
if err != nil {
log.Error("failed to mark channel added", zap.String("channel", channel), zap.Error(err))
return err
}
log.Info("NON remove flag tombstone added", zap.String("channel", channel))
return nil
}
构建key的规则:
datacoord-meta/channel-removal/{channelName}
总结:
1.CreateCollection的addCollectionMetaStep会创建2种类型的key。
- channelwatch/{nodeID}/{chName}
- datacoord-meta/channel-removal/{channelName}