前言
时间就像海绵里的水,只要愿挤,总还是有的。
TextView组件
TextView直接继承了View,它的作用就是在界面上显示文本。
代码示例
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<!-- 设置文本框内文字居中 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:text="halo_加油"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<!-- 设置字号为20pt,在文本框结尾处绘制图片 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="HALO_加油"
android:textSize="20pt"
android:drawableEnd="@drawable/ic_launcher"
/>
<!-- 设置结尾省略,所有字母大写 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
android:text="halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油halo_加油"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:textAllCaps="true"
/>
<!-- 对邮箱、电话增加链接 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
android:text="邮箱是halo_andriod@163.com,电话是010666666"
android:autoLink="email|phone"
/>
<!-- 设置文字颜色、大小,并使用阴影 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Halo_加油"
android:shadowColor="#00f"
android:shadowDx="10.0"
android:shadowDy="8.0"
android:shadowRadius="3.0"
android:textColor="#f00"
android:textSize="18pt"
/>
<!-- 密码框 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="halo_加油"
android:password="true"
/>
</LinearLayout>
效果
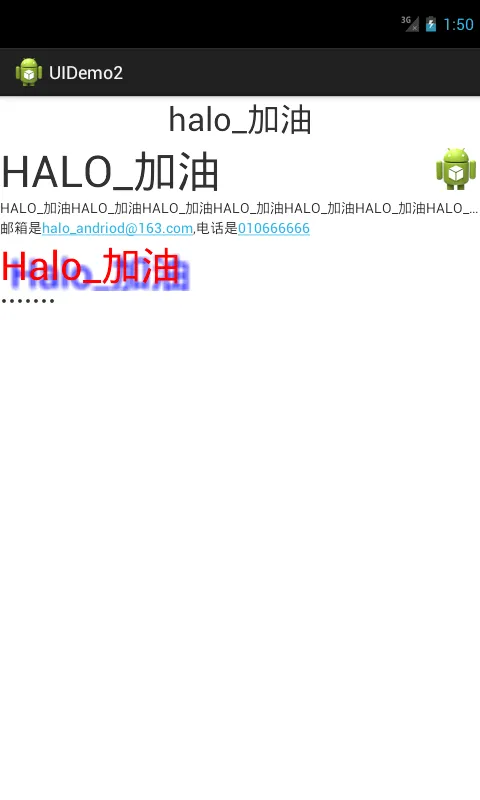
Screenshot_20171018-095040.png
提示
andriod:drawableBottom属性,在文本框内文本的底端绘制指定图像。
andriod:drawableTop属性,在文本框内文本的顶端绘制指定图像。
andriod:drawableLeft属性,在文本框内文本的左边绘制指定图像。
andriod:drawableRight属性,在文本框内文本的右边绘制指定图像。
andriod:drawableEnd属性,在文本框内文本的结尾处绘制指定图像。
andriod:drawableStart属性,在文本框内文本的开始处绘制指定图像。
andriod:ellipsize属性,设置当显示文本超过了TextView的长度时,如何处理文本内容。(none,start,middle,end,marquee)。
andriod:lines属性,设置该文本框默认占几行。
andriod:linksClickable属性,控制该文本框的URL、E-mail等链接是否可点击。
andriod:maxLines属性,设置该文本框最多占几行。
andriod:singleLine属性,设置该文本框是否为单行模式。
andriod:textAllCaps属性,设置是否将文本框的所有字母显示为大写字母。
andriod:autoLink属性,是否将符合指定格式的文本转换为可单击的超链接形式。
andriod:shadowColor属性,设置文本框内文本的阴影颜色。
自定义TextView组件
在有的时候,系统自带TextView满足不了你的要求,比如说在默认情况下,TextView是不带边框的,如果想为TextView添加边框,我们可以考虑为TextView设置一个背景Drawable,该Drawable只是一个边框,这样就实现了带边框的TextView。
代码示例
drawable\bg_border.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<!-- 设置背景色为透明色 -->
<solid android:color="#0000"/>
<!-- 设置红色边框 -->
<stroke android:width="4px" android:color="#f00"/>
</shape>
drawable\bg_border2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle">
<!-- 指定圆角矩形的4个圆角的半径 -->
<corners
android:topLeftRadius="20px"
android:topRightRadius="20px"
android:bottomLeftRadius="20px"
android:bottomRightRadius="20px"
/>
<!-- 指定边框线条的宽度和颜色 -->
<stroke android:width="4px" android:color="#f0f"/>
<!-- 指定使用渐变背景色,使用sweep类型的渐变。颜色从红色->绿色->蓝色 -->
<gradient
android:startColor="#f00"
android:centerColor="#0f0"
android:endColor="#00f"
android:type="sweep"
/>
</shape>
layout\textview.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="带边框的文本1"
android:textSize="22pt"
android:background="@drawable/bg_border"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="圆角边框、渐变背景的文本"
android:textSize="22pt"
android:background="@drawable/bg_border2"
/>
</LinearLayout>
效果

Screenshot_20171018-102316.png
EditText组件
EditText与TextView非常相似,它甚至与TextView共用了绝大部分XML属性和方法。EditText与TextView的最大区别在于:EditText可以接受用户输入。
代码示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="1">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="用户名:"
android:textSize="16sp"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请填写登陆账号"
android:selectAllOnFocus="true"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密码:"
android:textSize="16sp"
/>
<!-- andriod:inputType="numberPassword"表明只能接受数字密码 -->
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="numberPassword"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="年龄:"
android:textSize="16sp"
/>
<!-- inputType="number"表明是数值输入框 -->
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="number"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="生日:"
android:textSize="16sp"
/>
<!-- inputType="date"表明是日期输入框 -->
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="date"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="电话号码:"
android:textSize="16sp"
/>
<!-- inputType="phone"表明是输入电话号码的输入框 -->
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请填写您的电话号码"
android:selectAllOnFocus="true"
android:inputType="phone"
/>
</TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="注册"
/>
</TableLayout>
效果
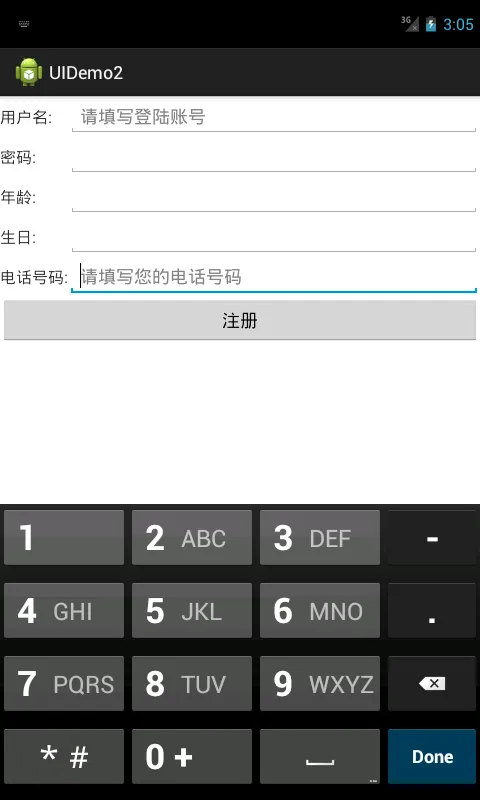
Screenshot_20171018-110532.png
提示
android:hint属性,设置当该文本框内容为空时,文本框内默认显示的提示文本。
android:inputType属性,指定文本框的类型。类似于HTML中<input.../>元素的type属性。
Button组件
Button继承了TextView,它主要是在UI界面上生成一个按钮,该按钮可以供用户单击,当用户单击按钮时,按钮会触发一个onClick事件。
示例代码
\layout\button.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!-- 文字带阴影的按钮 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="文字带阴影的按钮"
android:textSize="12pt"
android:shadowColor="#aa5"
android:shadowRadius="1"
android:shadowDx="5"
android:shadowDy="5"
/>
<!-- 普通文字按按钮 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮"
android:textSize="10pt"
android:background="@drawable/red"
/>
<!-- 带文字的图片按钮 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="11px"
android:text="带文字的图片按钮"
android:background="@drawable/button_selector"
/>
</LinearLayout>
\drawable\button_selector.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<!-- 指定按钮按下时的图片 -->
<item android:state_pressed="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/red"
/>
<!-- 指定按钮松开时的图片 -->
<item android:state_pressed="false"
android:drawable="@drawable/blue"
/>
</selector>
效果

Screenshot_20171018-123121.png
提示
这里只是简单的介绍了Button组件的生成方式,Button是一个很强大的组件,使用Button生成的按钮不仅可以是普通的文字按钮,也可以定制成任意形状。另外,Button的点击事件将在后面的章节介绍。
RadioButton组件和CheckBox组件
单选钮(RadioButton)和复选框(CheckBox)继承了Button类,因此可以直接使用Button支持的各种属性和方法。
代码示例
\layout\radio_check.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="性别:"
/>
<!-- 定义一组单选按钮 -->
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rg"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
>
<!-- 定义两个单选按钮 -->
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/male"
android:text="男"
android:checked="true"
/>
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/female"
android:text="女"
/>
</RadioGroup>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="喜欢的颜色:"/>
<!-- 定义一个垂直的现线性布局 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<!-- 定义三个复选框 -->
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="红色"
android:checked="true"
/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="蓝色"
/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="绿色"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/show"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</TableLayout>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
RadioGroup rg;
TextView show;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.radio_check);
//获取rg、show两个组件
rg = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.rg);
show = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.show);
//为RadioGroup组件的OnCheckedChanged事件绑定事件监听器
rg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String tip = checkedId == R.id.male?"您的性别是男人":"您的性别是女人";
show.setText(tip);
}
});
}
}
效果

Screenshot_20171018-131021.png
提示
andriod:checked属性,用于指定RadioButton、CheckBox初始时是否被选中。
RadioButton与CheckBox的不同之处在于,一组RadioButton只能选中其中一个,因此RadioButton通常要与RadioGroup一起使用。
ToggleButton组件和Switch组件
状态开关按钮(ToggleButton)和开关(Switch)由Button派生出来,因此它们的本质也是按钮,只不过它们通常用于切换程序中的某种状态。
代码示例
/layout/togglebutton_switch.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!-- 定义一个ToggleButton按钮 -->
<ToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textOff="横向排列"
android:textOn="纵向排列"
android:checked="true"
/>
<!-- 定义一个Switch按钮 -->
<Switch
android:id="@+id/switcher"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textOff="横向排列"
android:textOn="纵向排列"
android:checked="true"
/>
<!-- 定义一个可以动态改变方向的线性布局 -->
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/test"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button2"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button3"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
ToggleButton toggle;
Switch switcher;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.togglebutton_switch);
toggle = (ToggleButton) findViewById(R.id.toggle);
switcher = (Switch) findViewById(R.id.switcher);
final LinearLayout test = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.test);
OnCheckedChangeListener listener = new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(isChecked)
{
//设置LinearLayout垂直布局
test.setOrientation(1);
toggle.setChecked(true);
switcher.setChecked(true);
}
else
{
//设置LinearLayout水平布局
test.setOrientation(0);
toggle.setChecked(false);
switcher.setChecked(false);
}
}
};
toggle.setOnCheckedChangeListener(listener);
switcher.setOnCheckedChangeListener(listener);
}
}
效果

Screenshot_20171018-133244.png
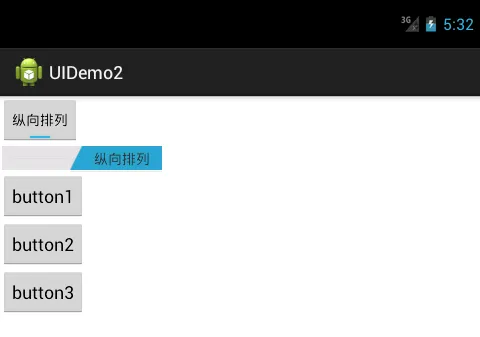
Screenshot_20171018-133246.png
提示
andriod:textOff属性,设置当前按钮的状态关闭时显示的文本。
andriod:textOn属性,设置当前按钮的状态关打开时显示的文本。
AnalogClock组件和TextClock组件
时钟UI组件是两个非常简单的组件,直接上代码。
代码示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center_horizontal" >
<!-- 定义模拟时钟 -->
<AnalogClock
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<!-- 定义数字时钟-->
<DigitalClock
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="10pt"
android:textColor="#f0f"
/>
</LinearLayout>
效果

Screenshot_20171018-135214.png
提示
目前TextClock已经取代了早期的DigitalClock组件,需要API17以上才能使用。TextClock组件能以24小时制或12小时制来显示时间,而且可以由程序员来指定时间格式。
Chronometer组件
计时器(Chronometer)组件继承自TextView,它显示的是从某个起始时间开始,一共过去了多长时间。
Chronometer的用法也很简单,它只提供了一个andriod:format属性,用于指定计时器的计时格式。除此之外,还支持如下常用方法。
- setBase(long base):设置计时器的起始时间。
- setFormat(String format):设置显示时间的格式。
- start():开始计时。
- stop():停止计时。
- setOnChronometerTickListener(Chronometer.OnChronometerTickListener listener):为计时器绑定事件监听器,当计时器改变时触发该监听器。
代码示例
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Chronometer ch;
Button start;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.chronometer);
ch = (Chronometer) findViewById(R.id.test);
start = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start);
start.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//设置开始计时时间
ch.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
//启动计时器
ch.start();
start.setEnabled(false);
}
});
//为Chronometer绑定监听事件
ch.setOnChronometerTickListener(new OnChronometerTickListener() {
@Override
public void onChronometerTick(Chronometer ch) {
//如果从现在开始计时到现在超过了20s
if(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - ch.getBase() > 20 * 1000)
{
ch.stop();
start.setEnabled(true);
}
}
});
}
}
效果
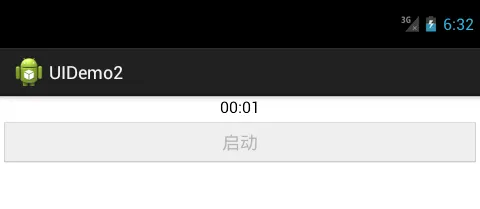
Screenshot_20171018-143258.png