1. 下载源代码
git clone https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin.git
2. 返回到0.1版本
3. 找到程序入口
4. 找到程序主干
表1
| IMPLEMENT_APP()->整个程序的入口,详见Ref[1],Ref[2]. ->OnInit2 --->LoadAddresses() --->LoadBlockIndex() --->LoadWallet() --->ReacceptWalletTransactions(); --->StartNode ----->ThreadIRCSeed ----->ThreadSocketHandler ----->ThreadOpenConnections ----->ThreadMessageHandler --->ThreadBitcoinMiner() |
5. 解析挖矿的代码函数ThreadBitcoinMiner(),再加强一些区块链的技术概念,详见Ref[3],Ref[4]。参考文献中写了挖矿的主要流程:
表2
| 收集广播中还没有被记录账本的原始交易信息 检查每个交易信息中付款地址有没有足够的余额 验证交易是否有正确的签名 把验证通过的交易信息进行打包记录 添加一个奖励交易:给自己的地址增加12.5比特币 |
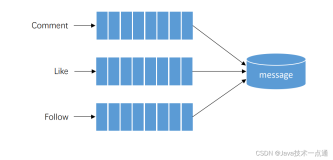
那么关于A,问题来了,如果没有人交易的话,是不是意味着矿机没有矿可以挖?比特币刚诞生的时候,确实有这样的问题,但是我们这里先不做讨论,这里我们主要的目的是研究产生交易的时候,挖矿的流程是如何进行。所以当你有一笔交易要做的时候,如下图所示,软件会将这笔交易告诉网络的中的其他矿机。这儿又有一个问题,其他矿机的IP地址是如何知道的?为了解决这个问题,软件上有个地址簿,告诉软件所有其他挖矿机的IP地址。

回到代码中,主要由ThreadBitcoinMiner中的mapTransactions决定是不是有足够的交易。这里碰到一个问题,就是程序启动的时候,是如何初始化并获得这些交易信息的?建议参考Ref[5]的文章,得到下表3。
表3
| ->OnInit2 LoadAddresses() LoadBlockIndex() LoadWallet() ReacceptWalletTransactions();// Add wallet transactions that aren't already in a block to mapTransactions |
特别要注意表3中红色的这句话(在源代码中可以找到),意思就是将wallet transactions中,但没有在block的交易内容放到mapTransactions中去。这里涉及到wallet 和block两个内容,必须要去了解一下两者的初始化和相关的含义、作用。
表4 LoadBlockIndex()
| CTxDB txdb("cr"); ->CDB("blkindex.dat") --->pdb->open()//将"blkindex.dat"读入到了数据库 ->txdb.LoadBlockIndex() --->InsertBlockIndex() ----->mapBlockIndex.insert(make_pair(hash, pindexNew))//建立mapBlockIndex |
表5 LoadWallet()
| CWalletDB("cr") ->CDB("wallet.dat") --->pdb->open()//将"wallet.dat"读入到了数据库 CWalletDB("cr").LoadWallet() ->CWalletTx& wtx = mapWallet[hash]; ->ssValue >> wtx;//建立mapWallet |
表6 LoadAddresses()
| CAddrDB("cr+") ->CDB("addr.dat") --->pdb->open()//将"addr.dat"读入到了数据库 CAddrDB("cr+").LoadAddresses() ->mapIRCAddresses.insert(make_pair(addr.GetKey(), addr));//建立mapIRCAddresses |
上面三个表格就是完成了mapIRCAddresses,mapBlockIndex和mapWallet的初始化。
这里出现的一个疑问,blkindex.dat的文件内容如果并不是最新的怎么办?
怀着这样的疑问在网络上寻找,我们找到一份完整的资料,关于下载最新blkindex.dat,详见Ref[6].
表7 消息流程
| local node ----->version message-----> <-----version message<----- remote node local node ----->getblocks message-----> <-----inv message<----- remote node local node ----->getdata message-----> <-----blocks message<----- remote node |

表7的内容解释了消息传递的过程。因为随着交易的增加,Block中的交易会越来越多,为了能够减少网络传输的内容,如果本地已经有的block的不会被重复传递。简单地讲本地的挖矿机会告诉另外的挖矿机哪些block我已经有了,你把我没有的block发送过来。
不管获得blkindex.dat的过程如何复杂,其核心的思想是加快获得全部的block。这部分的代码流程如下:
表8. 获得blkindex.dat的启动过程
| ThreadSocketHandler() ->void ThreadSocketHandler2(void* parg) --->CNode* pnode = new CNode(hSocket, addr, true); ----->PushMessage("version", VERSION, nLocalServices, nTime, addr);//启动表7的第一个消息包 ThreadOpenConnections() ->ThreadOpenConnections2() --->pnode=ConnectNode() --->pnode->PushMessage("addr", vAddrToSend);// Advertise our address --->pnode->PushMessage("getaddr");// Get as many addresses as we can |
现在搞清楚block的获取,接下来回过去讨论表3里面的那句话:
Add wallet transactions that aren't already in a block to mapTransactions
这句话其实告诉了我们mapTransactions的初始化,意思就是将我们自己的钱包里面的交易(Ref[7]里面有句话"Add to wallet if mine")但是还没有在block中加入到mapTransactions,见下面的流程:
表9
| AcceptWalletTransaction() ->wtx.AcceptWalletTransaction(txdb, false) --->AcceptTransaction(txdb, fCheckInputs, pfMissingInputs)//本3参函数唯一调用了下面的函数 ----->AddToMemoryPool() ------->mapTransactions[hash] = *this; |
通过查阅代码,只找到两处调用AcceptTransaction(arg1,arg2,arg3)这个函数,分别是ProcessMessage()和Reorganize()。从字面上理解,ProcessMessage就是收到了别人的交易记录,而Reorganize()只是重新组织。所以说有两种情况的交易可以加入mapTransactions,一种是自己产生的交易,另一种是别的挖矿机发送过来的交易。
接下去要了解的内容就是“满足什么样的条件后可以开始挖矿?”。兜兜转转一圈发现现在必须要对transaction进行深入了解,请看Ref[8]和Ref[9]两篇文章。这两篇文章最为关键的是如何认定transaction是有效的。这里先解释一个概念:
The coinbase is the content of the 'input' of a generation transaction. While regular transactions use the 'inputs' section to refer to their parent transaction outputs, a generation transaction has no parent, and creates new coins from nothing.
表10
| 1. bool CTransaction::AcceptTransaction(CTxDB& txdb, bool fCheckInputs, bool* pfMissingInputs) 2. { 3. if (pfMissingInputs) 4. *pfMissingInputs = false; 5. 6. // Coinbase is only valid in a block, not as a loose transaction 7. if (IsCoinBase()) 8. return error("AcceptTransaction() : coinbase as individual tx"); 9. 10. if (!CheckTransaction()) 11. return error("AcceptTransaction() : CheckTransaction failed"); 12. 13. // Do we already have it? 14. uint256 hash = GetHash(); 15. CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_mapTransactions) 16. if (mapTransactions.count(hash)) 17. return false; 18. if (fCheckInputs) 19. if (txdb.ContainsTx(hash)) 20. return false; 21. 22. // Check for conflicts with in-memory transactions 23. CTransaction* ptxOld = NULL; 24. for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 25. { 26. COutPoint outpoint = vin[i].prevout; 27. if (mapNextTx.count(outpoint)) 28. { 29. // Allow replacing with a newer version of the same transaction 30. if (i != 0) 31. return false; 32. ptxOld = mapNextTx[outpoint].ptx; 33. if (!IsNewerThan(*ptxOld)) 34. return false; 35. for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 36. { 37. COutPoint outpoint = vin[i].prevout; 38. if (!mapNextTx.count(outpoint) || mapNextTx[outpoint].ptx != ptxOld) 39. return false; 40. } 41. break; 42. } 43. } 44. 45. // Check against previous transactions 46. map<uint256, CTxIndex> mapUnused; 47. int64 nFees = 0; 48. if (fCheckInputs && !ConnectInputs(txdb, mapUnused, CDiskTxPos(1,1,1), 0, nFees, false, false)) 49. { 50. if (pfMissingInputs) 51. *pfMissingInputs = true; 52. return error("AcceptTransaction() : ConnectInputs failed %s", hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 53. } 54. 55. // Store transaction in memory 56. CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_mapTransactions) 57. { 58. if (ptxOld) 59. { 60. printf("mapTransaction.erase(%s) replacing with new version\n", ptxOld->GetHash().ToString().c_str()); 61. mapTransactions.erase(ptxOld->GetHash()); 62. } 63. AddToMemoryPool(); 64. } 65. 66. ///// are we sure this is ok when loading transactions or restoring block txes 67. // If updated, erase old tx from wallet 68. if (ptxOld) 69. EraseFromWallet(ptxOld->GetHash()); 70. 71. printf("AcceptTransaction(): accepted %s\n", hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 72. return true; 73. } 74. |
表11
| 1. Check syntactic correctness 2. Make sure neither in or out lists are empty 3. Size in bytes <= MAX_BLOCK_SIZE 4. Each output value, as well as the total, must be in legal money range 5. Make sure none of the inputs have hash=0, n=-1 (coinbase transactions) 6. Check that nLockTime <= INT_MAX[1], size in bytes >= 100[2], and sig opcount <= 2[3] 7. Reject "nonstandard" transactions: scriptSig doing anything other than pushing numbers on the stack, or scriptPubkey not matching the two usual forms[4] 8. Reject if we already have matching tx in the pool, or in a block in the main branch 9. For each input, if the referenced output exists in any other tx in the pool, reject this transaction.[5] 10. For each input, look in the main branch and the transaction pool to find the referenced output transaction. If the output transaction is missing for any input, this will be an orphan transaction. Add to the orphan transactions, if a matching transaction is not in there already. 11. For each input, if the referenced output transaction is coinbase (i.e. only 1 input, with hash=0, n=-1), it must have at least COINBASE_MATURITY (100) confirmations; else reject this transaction 12. For each input, if the referenced output does not exist (e.g. never existed or has already been spent), reject this transaction[6] 13. Using the referenced output transactions to get input values, check that each input value, as well as the sum, are in legal money range 14. Reject if the sum of input values < sum of output values 15. Reject if transaction fee (defined as sum of input values minus sum of output values) would be too low to get into an empty block 16. Verify the scriptPubKey accepts for each input; reject if any are bad 17. Add to transaction pool[7] |
表10是认定transaction 合法的源代码,表11是认定transaction 合法的规则,表10实现了表11的规则。最终,符合条件的transaction 进入mapTransactions。
验证交易是否合规,这里面有“非对称加密”和“签名”两个重要的概念。为了能够很好的理解这两个概念,这里做个解释。
| 7、187是公钥(大家都知道),23、187是私钥(只有自己知道),用公钥7、187加密明文数字88: C = 887 mod 187 = 11 (mod就是取余的意思) 得到密文数字11,解密的一方用私钥23、187解密文数字11 M = 1123 mod 187 = 88 得到明文数字88。这样就完成了加密和解密的过程。 |
签名的过程其实有点类同,不过先使用私钥去完成签名,然后公钥用来验证。拥有私钥的人发出一个消息,这个消息同时拥有签名,如果验证通过,拥有公钥的人就知道这个消息肯定是由拥有私钥的人发出来的消息。

用刚才的数字套进去可以到如下的解释,先用私钥23、187去签名11这个数字,得到签名数字88,把11和88这两个数字一起发给其他人,其他用有公钥7、187的人解密88得到某个数字A,如果A等于11,那么就可以确认这个消息是某个拥有私钥的人做的签名。
讲了这么多,实现了初始化,mapTransactions中也有了足够的交易,我们回归到挖矿的代码BitcoinMiner(),看它是如何处理mapTransactions并挖到矿。
在BitcoinMiner()中有一句注解:
// Collect the latest transactions into the block
这句话提示了在这之后的程序要开始选择mapTransactions中的交易,并加入到区块中(用来计算)?
Mempool ("memory pool" or "transaction pool")
A set of transactions which the node knows about and chooses to store in memory and relay to other nodes, and which have not yet been included in a block. In many cases, this may be the full set of transactions that the node has received and validated. If the node has received transactions that violate its policy, however, the mempool will be a subset. In any event, when the node receives and validates a block, it deletes any transactions in the block from its mempool.
这里有两篇参考文章Ref[10],Ref[11]讲得很好,总结起来就是将交易费高的交易优先加入到Mempool中等待挖矿。
接下去要开始挖矿了,最近有太多的事情要处理,具体挖矿的代码另外再找时间研究......
Ref[1]. IMPLEMENT_APP的详解 - CSDN博客.pdf
Ref[2]. wxWidgets:wxApp概述 - CSDN博客.pdf
Ref[3]. 区块链记账原理 _ 深入浅出区块链.pdf,https://learnblockchain.cn/2017/10/25/whatbc/
Ref[4]. 比特币如何挖矿(挖矿原理)-工作量证明 _ 深入浅出区块链.pdf,https://learnblockchain.cn/2017/11/04/bitcoin-pow/
Ref[5]. 比特币bitcoin源码解析之整体架构和流程 - CSDN博客.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/yujiak/article/details/80101467
Ref[6]. Block chain download - Bitcoin Wiki.pdf
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Block_chain_download
Ref[7]. Network - Bitcoin Wiki.pdf
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_rules#.22tx.22_messages
Ref[8]. Transaction - Bitcoin Wiki.pdf
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Transaction
Ref[9]. Protocol rules - Bitcoin Wiki.pdf
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_rules#Block_creation_fee
Ref[10]. Bitcoin Mempool - CSDN博客.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/yyxyong/article/details/77969423
Ref[11]. 交易连接输入ConnectInputs - CSDN博客.pdf