1.写在前面
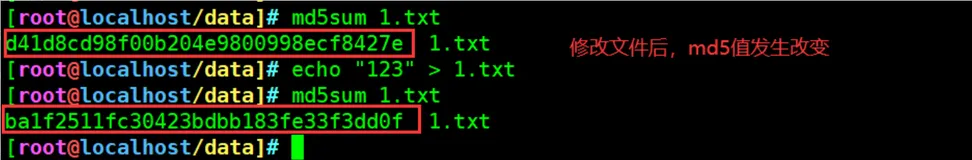
一直以来,虽然知道有问题问男人,对LINUX的帮助没有认真使用过,不会了就baidu,google,今天认真学习了下各种帮助命令,才知道自己的基本功有多么差。
2.使用帮助前
如果,我们想查看命令的帮助,应该首先确定这个命令的类型。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@localhost /]
# type cd
cd
is a shell
builtin
[root@localhost /]
# type su
su
is
/bin/su
[root@localhost /]
#
|
Linux的命令分为两种:
内置命令(SHELL内置)
外部命令(文件系统上必定存在相应可执行文件)
使用type COMMAND的方式获取命令类型。
3.help or --help or man or info
通过确定命令类型后,我们就要选择命令来查看帮助了。
4.结论一:help COMMAND
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
[root@localhost /]
# type cd
cd
is a shell
builtin
[root@localhost /]
# help cd
cd
:
cd
[-L|-P] [
dir
]
Change the current directory to DIR. The variable $HOME is the
default DIR. The variable CDPATH defines the search path
for
the directory containing DIR. Alternative directory names
in
CDPATH
are separated by a colon (:). A null directory name is the same as
the current directory, i.e. `.'. If DIR begins with a slash (/),
then
CDPATH is not used. If the directory is not found, and the
shell option `cdable_vars' is
set
,
then
try the word as a variable
name. If that variable has a value,
then
cd
to the value of that
variable. The -P option says to use the physical directory structure
instead of following symbolic links; the -L option forces symbolic links
to be followed.
[root@localhost /]
#
|
如果是内置命令,我们可以通过:
| help COMMAND |
来查看COMMAND命令的帮助。如果我们对内置命令使用man,则会出现:
|
上面实际上不是cd的帮助,而是BASH的介绍。
也就是说,对于内置命令,寻求帮助的途径是:
| help COMMAND |
5.结论二:man COMMAND
|
对于外部命令,应该使用man,或者长选项--help的方式获取帮助。
|
6.man NUMBER COMMAND
|
1
|
man is manual
|
就像我们买了一些家电设备一样,都会有一个使用手册,这些手册都有一个目录结构,这样会方便用户查找。其实man也是分章节的。
|
查看具体的章节,直接man NUMBER COMMAND即可。
7.如何快速定位
通过前面的知识,我们知道,可以使用man来指定章节查看,可是如果内容过多,如何有效,快速定位到我们想要的内容呢?
|
8.关于info
info COMMAND
偏向命令的一些历史信息。如果可以man,就不用info了。
9.总结
学习完如何使用帮助后,然后独立解决了设置时间,感觉很好。
就算工作再怎么满,我也要挤出点时间学习,我相信我的LINUX水平会不断提高的~
本文转自zfz_linux_boy 51CTO博客,原文链接:http://blog.51cto.com/zhangfengzhe/1405530,如需转载请自行联系原作者