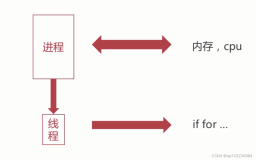
题目描述
三个线程循环打印A、B、C。
解题思路
主要考虑的是线程间同步问题,可以通过线程间等待/通知模型来解决顺序性。
代码实现
方案一
通过thread.join()来控制线程间的顺序性,表示在当前线程中执行另一个线程的thread.join()方法,可以等待另一个线程执行完成之后,当前线程才执行,通过这样的方式来控制两个线程的先后顺序。
/**
* @author yangnk
* @desc
* @date 2023/08/26 15:30
**/
public class JoinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new MyTask1());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new MyTask2(thread1));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new MyTask3(thread2));
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread3.join();
}
}
}
class MyTask1 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("A");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyTask2 implements Runnable {
Thread thread;
public MyTask2(Thread thread) {
this.thread = thread;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread.join();
System.out.println("B");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyTask3 implements Runnable {
Thread thread;
public MyTask3(Thread thread) {
this.thread = thread;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread.join();
System.out.println("C");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
方案二
通过wait()/notiyf()来实现等待/通知模型,首先线程A获取锁后执行线程A中的打印逻辑,然后线程A调用了lock对象的notifyAll()方法进入释放lock对象,线程B获取到锁后执行线程B中的打印逻辑,然后线程B调用了lock对象的notifyAll()方法进入释放lock对象,线程C获取到锁后执行线程C中的打印逻辑,然后线程C调用了lock对象的notifyAll()方法进入释放lock对象。
适合该场景的等待/通知模型:
(1) 获取全局对象锁。
(2) 如果条件不满足,那么调用对象的wait()方法,此时会释放锁。
(3) 竞争到锁并且条件满足,则执行对应的逻辑。
(4) 释放全局对象锁,其他线程可以开始竞争锁。
synchronized(lock){
while(条件不满足){
lock.wait()
}
业务逻辑
lock.notiyfAll()
}
代码实现:
/**
* @author yangnk
* @desc
* @date 2023/08/27 09:40
**/
public class WaitNotifyTest {
private static Object lock = new Object();
private static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
while (true) {
while (num % 3 != 0) {
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
num++;
System.out.println("A");
lock.notifyAll();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
while (true) {
while (num % 3 != 1) {
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
num++;
System.out.println("B");
lock.notifyAll();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
while (true) {
while (num % 3 != 2) {
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
num++;
System.out.println("C");
lock.notifyAll();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
方案三
通过ReentrantLock+Condition方法来顺序打印,其中Condition可以实现全局锁的多条件控制。
/**
* @author yangnk
* @desc
* @date 2023/08/27 00:16
**/
public class ReentrantLockLockTest {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
private static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (num % 3 != 0) {
condition1.await();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("A");
num++;
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (num % 3 != 1) {
condition2.await();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("B");
num++;
condition3.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (num % 3 != 2) {
condition3.await();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("C");
num++;
condition1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}