基于2018年Stack Overflow Developer的调研,TypeScript作为编程语言比JavaScript更受“喜爱”。TypeScript在js开发者中这么受喜爱的原因是:在你运行代码前,添加到javascript中的类型有助你发现错误(代码)。TypeScript编译器提供的错误可以很好的引导你如何修复代码错误。往javascript中添加类型同时有助代码编辑器提供一些高级的功能,例如代码完成,项目范围的重构和自动模块的导入。
如果你认为TypeScript是一门全新的编程语言,那么学习它可能令人生畏。然而,TypeScript只是JavaScript的一个附加层(超集),在使用TypeScript前,你无需了解它的每个语法。TypeScript允许你通过更改文件的后缀名.js为.ts来轻松的转换javascript文件,并且所有的代码将作为TypeScript来正确编译。如果你想在TypeScript文件中强制执行更广的类型覆盖百分比,你可以将TypeScript配置得更具局限性,一旦你熟悉该语言了,你就可以完成此操作。
本文旨在带你快速了解一个标准的TypeScript项目中会遇到的95%的场景。剩余的5%,嗯,你可以google,还有,我会在本文底部放些有用的TypeScript资源链接。
配置TypeScript
当然,要开始编写能正确编译的TypeScript(文件),正确配置开发环境是必要的。
1、安装TypeScript编译器
首先,为了能够将TypeScript文件转换成JavaScript文件,我们需要安装TypeScript编译器。安装TypeScript可全局安装(文件系统中安装,可以在任何位置使用)或者本地安装(仅在项目级别可使用)。【个人偏向后者】
# NPM Installation Method npm install --global typescript # Global installation npm install --save-dev typescript # Local installation # Yarn Installation Method yarn global add typescript # Global installation yarn add --dev typescript # Local installation
2、确保你的编辑器设置为支持TypeScript
你需要确保正确配置了你的编辑器以使用TypeScript。比如,为了在编辑器中能更好得使用TypeScript,你需要安装一个插件(如果你使用atom,你可以安装 atom-typescript)。如果你使用的是VS Code编辑器,那么你不需要安装额外的插件了,因为它内置了TypeScript的支持。😎
3、新建tsconfig.json文件
tsconfig.json文件是用来配置TypeScript项目设置。它应该放在项目的根目录中。该文件允许你使用不同的选项配置TypeScript编译器。
如果你仅仅是想TypeScript生效的话,你只需要tsconfig.json文件中包含一个空JSON对象,但是,如果你需要TypeScript编译器的有不同的行为(比如在特定的输出目录中输出编译后的JavaScript文件),你可以阅读更多有关可以配置哪些设置的(内容)。
备注:你也可以通过运行
tsc --init去生成一个tsconfig.json文件,其中为你设置了些默认选项,还有一些被注释掉的其他选项。
4、将TypeScript转化为JavaScript
为了将你的TypeScript代码转化成JavaScript代码,需要在控制台上跑tsc命令。运行tsc命令将告诉TypeScript编译器去搜索tsconfig.json文件,该文件将确定项目的根目录以及编译TypeScript并将.ts文件转换为.js文件时用的选项。
为了快速验证设置生效,你可以创建一个测试的TypeScript文件,然后在命令行中运行tsc,之后查看下TypeScript文件旁边是否生成了JavaScript文件。
举个例子,TypeScript文件如下...
const greeting = (person: string) => { console.log('Good day ' + person); }; greeting('Daniel');
应该被转换为下面这个JavaScript文件了...
var greeting = function(person) { console.log('Good day ' + person); }; greeting('Daniel');
如果你想TypeScript编译器(动态)监视TypeScript文件内容的变更,并自动将.ts文件转换成.js文件,你可以在你项目的仓库(命令行)中运行tsc -p。
在VS Code(编辑器)中,你可以使用⌘⇧B调出一个菜单,该菜单(包含)可以在正常模式和监视模式下运行转换程序(分别对应tsc:build和tsc:watch)。
了解静态和动态类型
JavaScript附带7种动态类型:
- Undefined
- Null
- Boolean
- Number
- String
- Symbol
- Object
上面的类型被称为动态类型,因为它们在运行时使用。
TypeScript为JavaScript语言带来了静态类型,并且这些类型在编译时(无需运行代码)被确定。静态类型可以预测动态类型的值,这可以帮助在无需运行代码的情况下警告你可能出现的错误。
基本静态类型
好吧,我们来深入研究下TypeScript的语法。以下是TypeScript中最常见的类型。
备注:我遗漏了never和object类型,因为根据我的经验,它们并不被经常使用。
boolean
你已经很了解true和false值了。
let isAwesome: boolean = true;
string
文本数据用单引号('')或双引号("")或后标记(``)【也称模版字符】包围。
let name: string = 'Chris'; let breed: string = 'Border Collie';
如果你使用后标志,该字符串被称为模版文字,可以在里面插入表达式。
let punchline: string = 'Because it was free-range.'; let joke: string = ` Q: Why did the chicken cross the road? A: ${punchline} `;
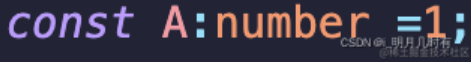
number
任何浮点数都给定为数字类型。作为TypeScript的一部分,支持的四种类型的数字文字是二进制,十进制,八进制和十六进制。
let decimalNumber: number = 42; let binaryNumber: number = 0b101010; // => 42 let octalNumber: number = 0o52; // => 42 let hexadecimalNumber: number = 0x2a; // => 42
备注:并不是只有你一个人对二进制,八进制和十六进制数字感到困惑。
array
TypeScript中有两种书写数组类型的方式。第一种是[]后缀在需要查找的数组元素类型。
let myPetFamily: string[] = ['rocket', 'fluffly', 'harry'];
另一种可替代的方式是,Array后跟要查找的数组元素类型的Array类型(使用尖括号包含)。
let myPetFamily: Array<string> = ['rocket', 'fluffly', 'harry'];
tuple
元组是一个包含固定数量的元素和相关类型的数组。
let myFavoriteTuple: [string, number, boolean]; myFavoriteTuple = ['chair', 20, true]; // ✅ myFavoriteTuple = [5, 20, true]; // ❌ - The first element should be a string, not a number
enum
枚举将名称和常量值关联,可以是数字或者字符串。当你想一组具有关联性的描述名称的不同值,枚举就很有用处了。
默认,为枚举分配从0开始的值,接下来的值为(上一个枚举值)加1。
enum Sizes { Small, Medium, Large, } Sizes.Small; // => 0 Sizes.Medium; // => 1 Sizes.Large; // => 2 复制代码
第一个值也可以设置为非0的值。
enum Sizes { Small = 1, Medium, Large, } Sizes.Small; // => 1 Sizes.Medium; // => 2 Sizes.Large; // => 3
枚举默认是被分配数字,然而,字符串也可以被分配到一个枚举中的。
enum ThemeColors { Primary = 'primary', Secondary = 'secondary', Dark = 'dark', DarkSecondary = 'darkSecondary', }
any
如果变量的类型未知,并且我们并不希望类型检查器在编译时抱怨,则可以使用any类型。
let whoKnows: any = 4; // assigned a number whoKnows = 'a beautiful string'; // can be reassigned to a string whoKnows = false; // can be reassigned to a boolean
在开始使用TypeScript的时,可能会频繁使用any类型。然而,最好尝试减少any的使用,因为当编译器不知道与变量相关的类型时,TypeScript的有用性会降低。
void
当没有与事物相关类型的时候,void类型应该被使用。在指定不返回任何内容的函数返回值时,最常用它。
const darkestPlaceOnEarth = (): void => { console.log('Marianas Trench'); };
null和undefined
null和undefined都对应你在javascript中看到的null和undefined值的类型。这些类型在单独使用的时候不是很有用。
let anUndefinedVariable: undefined = undefined; let aNullVariable: null = null;
默认情况下,null和undefined类型是其他类型的子类型,这意味着可以为string类型的变量赋值为null或者undefined。这通常是不合理的行为,所以通常建议将tsconfig.json文件中的strictNullChecks编译器选项设置为true。将strictNullChecks设置为true,会使null和undefined需要显示设置为变量的类型。
类型推断
幸运的是,你不需要在代码中全部位置指定类型,因为TypeScript具有类型推断。类型推断是TypeScript编译器用来自行决定类型的(内容)。
基本类型推断
TypeScript可以在变量初始化期间,设置默认参数以及确定函数返回值时推断类型。
// Variable initialization let x = 10; // x is given the number type
在上面的例子中,x被分配了数字,TypeScript会以number类型将x变量关联起来。
// Default function parameters const tweetLength = (message = 'A default tweet') => { return message.length; };
在上面的例子中,message参数被赋予了一个类型为string的默认值,因此TypeScript编译器会推断出message的类型是string,因此在访问length属性的时候并不会抛出编译错误。
function add(a: number, b: number) { return a + b; } const result = add(2, 4); result.toFixed(2); // ✅ result.length; // ❌ - length is not a property of number types
在上面这个例子中,因为TypeScript告诉add函数,它的参数都是number类型,那么可以推断得出返回的类型也应该是number。
最佳通用类型推断
从多种可能的类型中推断类型时,TypeScript使用最佳通用类型算法来选择适用于所有其他候选类型的类型。
let list = [10, 22, 4, null, 5]; list.push(6); // ✅ list.push(null); // ✅ list.push('nope'); // ❌ - type 'string' is neither of type 'number' or 'null'
在上面的例子中,数组(list)是由number或null类型组成的,因此TypeScript只希望number或null类型的值加入数组。
类型注释
当类型推断系统不够用的时,你需要在变量和对象上声明类型。
基本类型
在(上面)基本静态类型章节的介绍中,所有的类型都使用:后跟类型名来声明。
let aBoolean: boolean = true; let aNumber: number = 10; let aString: string = 'woohoo';
Arrays
在(上面)讲到的array类型的章节中,arrays可以通过两种方式的其中一种进行注释。
// First method is using the square bracket notation let messageArray: string[] = ['hello', 'my name is fred', 'bye']; // Second method uses the Array keyword notation let messageArray: Array<string> = ['hello', 'my name is fred', 'bye'];
接口
将多种类型的注释组合到一起的一种方法是使用接口。
interface Animal { kind: string; weight: number; } let dog: Animal; dog = { kind: 'mammal', weight: 10, }; // ✅ dog = { kind: true, weight: 10, }; // ❌ - kind should be a string
类型别名
TypeScript使用Type Alias指定多个类型注释,这事(让人)有些疑惑。【下面讲到】
type Animal = { kind: string; weight: number; }; let dog: Animal; dog = { kind: 'mammal', weight: 10, }; // ✅ dog = { kind: true, weight: 10, }; // ❌ - kind should be a string
在使用接口或类型别名这方面,最佳的做法似乎是,在代码库保持一致情况下,通常选择接口类型或类型别名。但是,如果编写其他人可以使用的第三方的公共API,就要使用接口类型了。
如果你想了解更多关于type alias和interface的比较的话,我推荐你看Martin Hochel的这篇文章。
内联注释
相比创建一个可复用的接口,有时内联注释类型可能更合适。
let dog: { kind: string; weight: number; }; dog = { kind: 'mammal', weight: 10, }; // ✅ dog = { kind: true, weight: 10, }; // ❌ - kind should be a string
泛型
某些情况下,变量的特定类型无关紧要,但是应强制执行不同变量和类型之间的关系。针对这些情况,应该使用泛型类型。
const fillArray = <T>(len: number, elem: T) => { return new Array<T>(len).fill(elem); }; const newArray = fillArray<string>(3, 'hi'); // => ['hi', 'hi', 'hi'] newArray.push('bye'); // ✅ newArray.push(true); // ❌ - only strings can be added to the array
上面的示例中有一个泛型类型T,它对应于传递给fillArray函数的第二个参数类型。传递给fillArray函数的第二个参数是一个字符串,因此创建的数组将其所有元素设置为具有字符串类型。
应该注意的是,按照惯例,单个(大写)字母用于泛型类型(比如:T或K)。可是,并不限制你使用更具有描述性的名称来表示你的泛型类型。下面示例就是为所提供的泛型类型使用了更具有描述性的名称:
const fillArray = <ArrayElementType>(len: number, elem: ArrayElementType) => { return new Array<ArrayElementType>(len).fill(elem); }; const newArray = fillArray<string>(3, 'hi'); // => ['hi', 'hi', 'hi'] newArray.push('bye'); // ✅ newArray.push(true); // ❌ - only strings can be added to the array
联合类型
在类型可以是多种类型之一的情况下,使用|分隔符隔开不同类型的选项来使用联合类型。
// The `name` parameter can be either a string or null const sayHappyBirthdayOnFacebook = (name: string | null) => { if (name === null) { console.log('Happy birthday!'); } else { console.log(`Happy birthday ${name}!`); } }; sayHappyBirthdayOnFacebook(null); // => "Happy birthday!" sayHappyBirthdayOnFacebook('Jeremy'); // => "Happy birthday Jeremy!"
交集类型
交集类型使用&符号将多个类型组合在一起。这和(上面的)联合类型不同,因为联合类型是表示结果的类型是列出的类型之一,而交集类型则表示结果的类型是所有列出类型的集合。
type Student = { id: string; age: number; }; type Employee = { companyId: string; }; let person: Student & Employee; person.age = 21; // ✅ person.companyId = 'SP302334'; // ✅ person.id = '10033402'; // ✅ person.name = 'Henry'; // ❌ - name does not exist in Student & Employee
元组类型
元组类型使用一个:符号,其后跟一个使用中括号包含且逗号分隔的类型列表表示。
let list: [string, string, number]; list = ['apple', 'banana', 8.75]; // ✅ list = ['apple', true, 8.75]; // ❌ - the second argument should be of type string list = ['apple', 'banana', 10.33, 3]; // ❌ - the tuple specifies a length of 3, not 4
可选类型
可能存在函数参数或者对象属性是可选的情况。在这些情况下,使用?来表示这些可选值。
// Optional function parameter function callMom(message?: string) { if (!message) { console.log('Hi mom. Love you. Bye.'); } else { console.log(message); } } // Interface describing an object containing an optional property interface Person { name: string; age: number; favoriteColor?: string; // This property is optional }