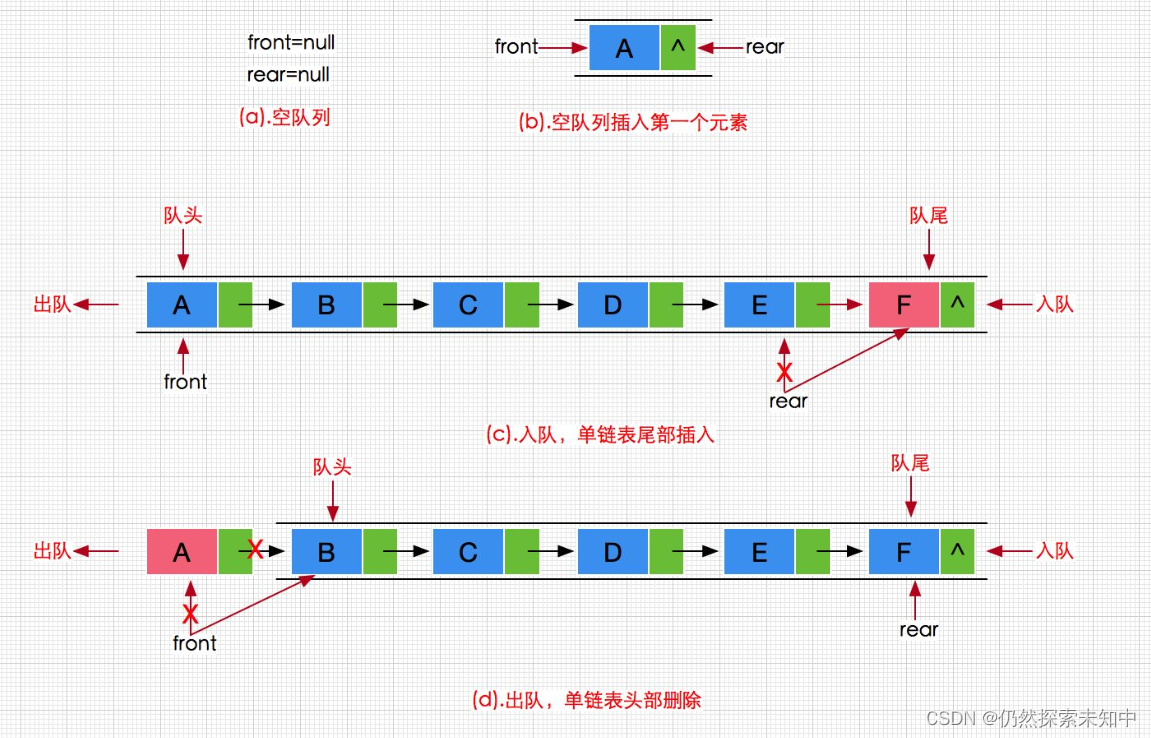
队列的概念及结构
- 队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出
FIFO(First In First Out) - 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
队列的实现
- 队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构, 出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
队列的实现
头文件,需要实现的接口
Queue.h
#pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stdbool.h> typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QListNode { QDataType val; struct QListNode* next; }QNode; // 队列的结构 typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; QDataType size; }Queue; // 初始化队列 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); // 队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); // 队头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); // 获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); // 获取队列队尾元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); // 获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq); // 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0 int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); // 销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }
队尾入队列【重点】
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail!\n"); return; } newnode->val = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->ptail == NULL) { pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; }
队头出队列【重点】
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); QNode* del = pq->phead; pq->phead = pq->phead->next; free(del); del = NULL; if (pq->phead == NULL) pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size--; }
获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; }
获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->ptail); return pq->ptail->val; }
获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }
检测队列是否为空
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == 0; }
销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur != NULL) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }
Queue.c
#include"Queue.h" // 初始化队列 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } // 队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail!\n"); return; } newnode->val = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->ptail == NULL) { pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; } // 队头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); QNode* del = pq->phead; pq->phead = pq->phead->next; free(del); del = NULL; if (pq->phead == NULL) pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size--; } // 获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; } // 获取队列队尾元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->ptail); return pq->ptail->val; } // 获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; } // 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0 int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == 0; } // 销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur != NULL) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }
好了,队列的实现就到这里结束了,有用的话点个赞吧~~