开发者学堂课程【高校精品课-上海交通大学-企业级应用体系架构:Caching】学习笔记,与课程紧密联系,让用户快速学习知识。
课程地址:https://developer.aliyun.com/learning/course/75/detail/15833
Caching (三)
内容介绍:
一、Memcached
二、MemCached - Storage Commands
三、MemCached - Memory Management
四、Redis
五、Clusterina
四、Redis
1、Redis is what is called a key-value store,
often referred to as a NoSQL database.
The essence of a key-value store is the ability to store some data, called a value, inside a key.
2、Redis is an open source, BSD licensed, advanced key-value store.
It is often referred to as a data structure server since keys can
contain strings, hashes, lists, sets and sorted sets.
3、In order to achieve its outstanding performance, Redis works with an in-memory dataset.
Depending on your use case, you can persist it either by dumping the dataset to disk every once in a while, or by appending each command to a log.
4、Redis also supports trivial-to-setup master-slave replication, with very fast non-blocking first synchronization, auto-reconnection on net split and so forth.
memcached 是纯内存,如果崩了,里面的内存就没了,用的更多 redis,redis 也是 key value 存储,只要是key value,就一定是 nosql,
值是打包存储,不再做更犀利的结构化的设置,值比 memcached 复杂一点,里面可以包含不同的类型,看起来像是内存里面的数据集,可以把数据写到硬盘上,如果 redis 关闭或者崩溃,数据还在,把它从硬盘上读到内存里,再存到硬盘里,现在所有的开发不再笔记本上做,所以看不出来,但是实际的开发是数据库在一台机器上,机器在内网里,tomcat 在另外一台机器上,memcached 或者 redis 可能跟 tomcat 在一起,跨过网络找服务器上的数据库,读进数据写入到 redis 中,redis 又会写硬盘,注意硬盘在本地,读本地硬盘的速度一定比读远程硬盘的速度快,通过网络访问,瓶颈在网络的带宽上,直接读本地硬盘,它的瓶颈在硬盘的 io 上,io 比网络的 io 大,拿回之后写的是本地的硬盘,如果不是这种情况,是三台机器,访问,都是网络问题,拿一个非常远的机器做缓存显然不合适,从物理的部署上尽管是三台机器,也许在同一个网段里,都在1204.40的网段里,也许在另外一台网段里,比如有很大的系统,数据库是集中存放在某一个位置,在软件学院在电信大楼,在不同的大楼里面都摆个应用服务器,在应用服务器的旁边,在同一个局域网里并排再摆个缓存服务器,数据库在行政大楼,每次在行政大楼读数据之后马上就放到局域网里面,靠在一起的 redis 服务器的缓存里,也会写硬盘,未来 redis 崩了,再从硬盘里读数据,速度会比到行政大楼重新抓的数据快,redis 往硬盘上写的意义,tomcat 和 redis 跑在一起以及跑在不同的上面,靠的数据库服务器要近的两种情况。
redis 下载好之后,安装,windows 和 linux 上差不多,只要下载之后,在平台上编译。
Download, extract and compile Redis with:
$ wget http://download . redis. io/releases/redis-5.0.7.tar.gz
$ tar xzf
redis-5.0.7.tar .gz
$cd redis-5.0.7
$make
Run redis server
$ src/redis-server 运行方法
redis-server. Exe Windows 上的文件可以跑
Run redis Client
$ src/redis-cli 客户端
redis> set foo bar
OK
redis> get foo 利用命令进行操作
"bar"
最好使用代码访问。
Structure type |
What it contains |
Structure read/ write ability |
STRING |
Strings, integers, or floating-point values |
Operate on the whole string, parts, increment/decrement the integers and floats |
LIST |
Linked list of strings |
Push or pop items from both ends, trim based on offsets, read individual or multiple items, find or remove items by value |
SET |
Unordered collection of unique strings |
Add, fetch, or remove individual items, check membership, intersect, union, difference, fetch random items |
HASH |
Unordered hash table of keys to values |
Add, fetch, or remove individual items, fetch the whole hash |
ZSET (sorted set) |
Ordered mapping of string members to floating-point scores, ordered by score |
Add, fetch, or remove individual values, fetch items based on score ranges or member value |
redis 值可以是字符串,列表,级,排序的级。
STRING in Redis
key 是 hello,值是字符串类型,world,对它可以进行 get set del 操作。
Command |
What it does |
GET |
Fetches the data stored at the given key |
SET |
Sets the value stored at the given key |
DEL |
Deletes the value stored at the given key (works for all types) |
List in Redis
Key 名字,list 里面有若干对 item。
Command |
What it does |
RPUSH |
Pushes the value onto the right end of the list右段末尾 |
LRANGE |
Fetches a range of values from the list范围 |
LINDEX |
Fetches an item at a given position in the list索引 |
LPOP |
Pops the value from the left end of the list and returns it左端是开口 |
Set in Redis
Set 跟 list 差不多,但是 set 的特点是没有重复元素,安全认证有提到过。
Command |
What it does |
SADD |
Adds the item to the set |
SMEMBERS |
Returns the entire set of items |
SISMEMBER |
Checks if an item is in the set检查所有元素 |
SREM |
Removes the item from the set, if it exists |
Sorted set in Redis
hash 需要掌握的是 map,相当于 json 的值是另外的 json,会有一堆的 key 和 value,有获取所有和删除的操作。
Command |
What it does |
HSET |
Stores the value at the key in the hash |
HGET |
Fetches the value at the given hash key |
HGETALL |
Fetches the entire hash |
HDEL |
Removes a key from the hash, if it exists |
Sorted set in Redis
有排序的一列值,竖着类型进行排序,达到一定条件进行排序。
Command |
What it does |
ZADD |
Adds member with the given score to the ZSET |
ZRANGE |
Fetches the items in the ZSET from their positions in sorted order |
ZRANGEBYSCORE |
Fetches items in the ZSET based on a range of scores |
ZREM |
Removes the item from the ZSET, if it exists |
比较 redis 和 memcached 以及关系型数据库,非关系型数据库的差异,前两个是内存里的,后面是硬盘上的,关联型数据库非常多,查询都有自己的一些语句,查询语句比较多,扩展的一些特性和常用的缓存没太大关联,查询都有自己的语句,关系型数据库是最强大的,还有扩展的特性。
Name |
Type |
Data storage options |
Query types |
Additional fe atures |
Redis |
In-memory non-re lational database |
Strings, lists, sets,hashes, sorted sets |
Commands for each data type for common access patterns, with bulk oper- ations, and partial trans- action support |
Publish/ Subscribe, master/ slave replica- tion, disk persistence, scripting (stored proce- dures) |
memcached |
In-memory key-value cache |
Mapping of keys to values |
Commands for create, read, update, delete, and a few others |
Multithreaded server for additional perfor- mance |
MySQL |
Relational database |
Databases of tables ohrows, views over tables, spatial and third-party extensions |
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, functions, stored procedures |
ACID compliant (with InnoDB), master/slave and master/ master replication |
PostgreSQL |
Relational database |
Databases of tables of rows, views over tables, spatial and third-partyextensions, customizable types |
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, built-in functions, cus- tom stored procedures |
ACID compliant, mas- ter/ slave replication, multi-master replica- tion (third party) |
MongoDB |
On-disk non-re lational document store |
Databases of tables of schema-less BSON documents |
Commands for create, read, update, delete, conditional queries, and more |
Supports map-reduce operations, master/ slave replication, shard- ing, spatial indexes |
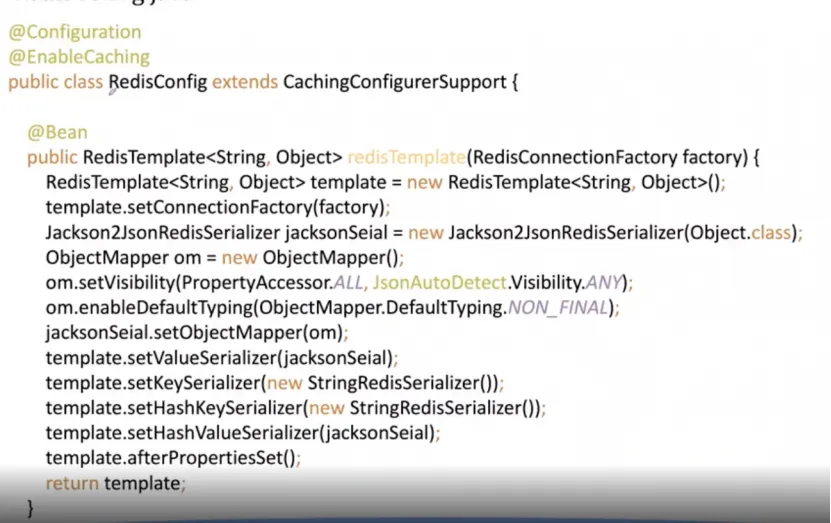
RedisConfig.java
代码和 memcached 特别像,产生 configuration,使用缓存,里面写一堆东西,客户端在操作的时候需要得到spring 里面,产生 redistemlate,可以看到没有特别的地方,产生 template,在里面没有额外的非常复杂的设置。
类没有特殊配制,跟 redis 和 memcached 类似。
PersonDaoImpl.java
从助手类里面获取对象,user+id,到 redis中,如果没取到就调数据库操作,获取,设置到 redis 中,key 就是user+id,值就是把person对象转成 json 对象存进去,如果不为空,从 redis 中能得到 person,但是当时存储的时候是存的 json 对象,所以要把 json 对象按照 person 里的结构解析出来,还原成 person 对象,启动之后找曹操,第一次找不再 redis 中,在数据库里,返回放到 redis,第二次再找,出结果,再找会告诉人就在 redis中。
启动 redis 服务,服务起来之后跑应用,2不在 redis中,再刷新一次,搜索2这个人在 redis,事实证明第一次不再redis中,访问之后在 redis 中,第二次访问时并没有到数据库里面进行抓取,跟 memcached 一样,两个例子都在告诉利用缓存把已经从数据库里读取的内容缓存到本地,不用 jpa。
不能达到内存的充分利用,把缓存专门过滤出来。
memcached 的实现。
既然 redis 做持久化,从已经持久化的数据库拿数据有什么区别,数据库本身离的比较远,开销比较大,而 redis 在一台机器上,即便不在一台机器上一定也是靠很近的一台机器,如果远确实意义不大,无论是 memcached 还是redis,要注意它们的数据一旦在内存里缓存,在写数据库的时候要考虑缓存和数据库的数据要一致,简单的方法是写数据库,就从缓存里删掉,下次再访问的时候又会到数据库里拿一次,写到 redis 或者是 memcached 的系统,复杂的方式是在写入数据库的时候,同时写缓存,两个工具都能实现缓存的目的。但是推荐用 redis,因为 memcached 的更新不如 redis,后续是否有更新不知道,memcached 只写内存,不做持久化,不像 redis 崩了之后还可以从本地的硬盘恢复数据,所以建议用 redis。
五、Clusterina
1、A large-scale system typically:
Has many user, potentially in many different places
Is long-running, that is, required to be "always up"
Processes large numbers of transactions per second
May see increases in both its user population and system load
Represents considerable business value
Is operated and managed by multiple persons
2、Essential requirements on large-scale systems are often
summarized by the following three properties(RAS):
Reliability
Availability
Serviceability
Scalability
缓存服务器可以建集群,应用服务器也可以建集群。