
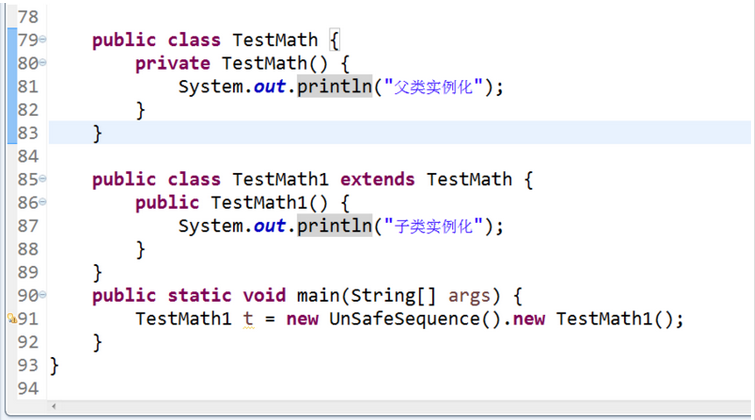

如上图,为什么子类可以调用父类的私有构造方法?
版权声明:本文内容由阿里云实名注册用户自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,阿里云开发者社区不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。具体规则请查看《阿里云开发者社区用户服务协议》和《阿里云开发者社区知识产权保护指引》。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,填写侵权投诉表单进行举报,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
public class UnSafeSequence {
public class TestMath{
private TestMath(){
System.out.println("父类实例化");
}
}
public class TestMath1 extends TestMath{
public TestMath1(){
System.out.println("子类实例化");
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new UnSafeSequence().new TestMath1());
}
}java6语言规范中关于private修饰符的描述,顶级类及内部类的定义
6.6.1
if the member or constructor is declared private, then access is permitted if and only if it occurs within the body of the top level class (§7.6) that encloses the declaration of the member or constructor.
如果一个类的成员或构造器声明为private的,那么只有声明这个成员或构造器的顶级类才有权访问(当然声明这个成员和构造函数的类也是可以访问的)
8.
A top level class is a class that is not a nested class.
A nested class is any class whose declaration occurs within the body of another class or interface. A top level class is a class that is not a nested class.
顶级类不是一个嵌套类(内部类),嵌套类(内部类)是申明在其他类或接口中的类
鉴于以上的规定描述,那么外部类中可以访问构造器标示为private的TestMath内部类。
TestMath1同样是一个内部类,其继承了另一个内部类TestMath,因为一个内部类依赖外部类实例对象而存在,会隐式的关联一个外部类实例
所以
public class TestMath1 extends TestMath{
public TestMath1(){
System.out.println("子类实例化");
}
}可以写成
public class TestMath1 extends UnSafeSequence.TestMath{
public TestMath1(){
UnSafeSequence.this.super();
System.out.println("子类实例化");
}
}这样就可以解释一个内部类的子类为什么可以访问其父类的私有的构造函数了