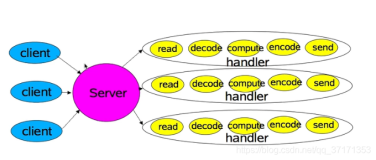
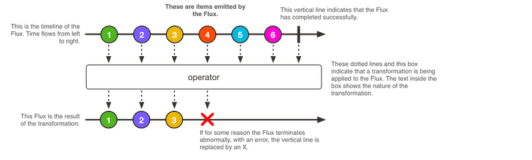
reactor 编程将来会是一种趋势, 就像我们很多年前还不用Lambda 表达式一样,但现在都流行起Lambda表达式编程了。
package com.roy.reactorkit; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class ReactorLeanrn { public static void main(String[] args) { Flux<Integer> ints3 = Flux.range(1, 4); ints3.subscribe(System.out::println, error -> System.err.println("Error " + error), () -> System.out.println("Done"), sub -> sub.request(2)); Flux<String> strflux = Flux.just("foo", "hello"); strflux.subscribe(System.out::println); List<String> strlist = Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd"); Flux<String> sf = Flux.fromIterable(strlist); sf.subscribe(System.out::println); sf.subscribe(System.out::println, error -> System.err.println("error" + error), () -> System.out.println("Done"), sub -> sub.request(2)); } }
输出结果:
package com.roy.reactorkit; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; public class ReactorGoon { public void gentr() { Flux<String> flux = Flux.generate(() -> 0, (state, sink) -> { sink.next(" 2 x" + state + "=" + 2 * state); if (state == 10) { sink.complete(); } return state + 1; }); flux.subscribe(System.out::println); } public static void main(String[] args) { ReactorGoon rec = new ReactorGoon(); rec.gentr(); rec.useHandle(); } public void useHandle() { // sink.next 下一个??? Flux<String> alphabet = Flux.just(-1, 30, 13, 9, 20) .handle((i, sink) -> { String letter = alphabet(i); if (letter != null) { sink.next(letter); } }); alphabet.subscribe(System.out::println); } public String alphabet(int letterNumber) { if (letterNumber < 1 || letterNumber > 26) { return null; } // 13,9,20 System.out.println("letterNumber = " + letterNumber); // 'A' = 65 // 65+13-1 = 77 // 9+65-1 = 73 // 20+65-1 = 84 int letterIndexAscii = 'A' + letterNumber - 1; System.out.println("letterIndexAscii = " + letterIndexAscii); return "" + (char) letterIndexAscii; } }
输出结果:
package com.roy.reactorkit; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; import java.util.Arrays; public class ReactorException { public static void main(String[] args) { Flux flux2 = Flux.just(5, 50, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)); flux2.subscribe(System.out::println, error -> System.out.println(error)); System.out.println("----------------------------------"); Flux flux = Flux.just(10, 20, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorReturn("Divided by zero :("); flux.subscribe(System.out::println); System.out.println("----------------------------------"); Flux flux3 = Flux.just(20, 25, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)); flux3.subscribe(System.out::println, error -> System.err.println("Error: " + error)); System.out.println("----------------------------------"); ReactorException reactorException = new ReactorException(); reactorException.normalErrorHandle(); System.out.println("----------------------------------"); Flux flux4 = Flux.just(10, 25, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorReturn("Divided by zero :("); flux4.subscribe(System.err::println); System.out.println("***********************************"); reactorException.useFallbackMethod(); System.out.println("***********************************"); reactorException.useDynamicFallback(); System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); Flux flux5 = Flux.just(50, 20, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorResume(error -> Flux.error( new RuntimeException("oops, ArithmeticException!", error))); flux5.subscribe(System.out::println); System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); Flux flux6 = Flux.just(50, 10, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorMap(error -> new RuntimeException("oops, ArithmeticException!", error)); flux6.subscribe(System.out::println); } public void normalErrorHandle() { try { Arrays.asList(1, 50, 0).stream().map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).forEach(System.out::println); } catch (Exception e) { System.err.println("Error: " + e); } } public void useDynamicFallback() { Flux flux = Flux.just(25, 20, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorResume(error -> Mono.just( MyWrapper.fromError(error))); flux.subscribe(System.out::println); } public static class MyWrapper { public static String fromError(Throwable error) { return "That is a new Error"; } } public void useFallbackMethod() { Flux flux = Flux.just(1, 20, 0) .map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)) .onErrorResume(e -> System.out::println); flux.subscribe(System.out::println); } }
输出结果:
最后附上一张ASCII码对照表
以上都是些示例,好好看一波,其实也不是那么难。