文章目录:
1.什么是动态SQL?
动态 SQL,通过MyBatis提供的各种标签对条件作出判断以实现动态拼接SQL 语句。这里的条件判断使用的表达式为 OGNL 表达式。常用的动态 SQL标签有<if>、<where>、<foreach>、<sql>等。
MyBatis的动态 SQL 语句,与 JSTL 中的语句非常相似。
动态 SQL,主要用于解决查询条件不确定的情况:在程序运行期间,根据用户提交的查询条件进行查询。提交的查询条件不同,执行的 SQL 语句不同。若将每种可能的情况均逐一列出,对所有条件进行排列组合,将会出现大量的SQL 语句。此时,可使用动态 SQL 来解决这样的问题。
使用动态SQL时,dao接口中方法的形参要使用Java对象。
2.MyBatis中的动态SQL
<if test="boolean判断结果"> <!--要么为true、要么为false--> sql语句的部分 </if> <!-- 对于该标签的执行,当 test 的值为 true 时,会将其包含的 SQL 片段断拼接到其所在的 SQL 语句中。 -->
package com.bjpowernode.dao; import com.bjpowernode.entity.Student; import java.util.List; /** * */ public interface StudentDao { //if List<Student> selectIf(Student student); }
<!-- if test: 使用对象的属性值作为条件 --> <select id="selectIf" resultType="com.bjpowernode.entity.Student"> select * from student where id=-1 <if test="name!=null and name!=''"> or name=#{name} </if> <if test="age>0"> or age=#{age} </if> </select> <!-- <if/>标签的中存在一个比较麻烦的地方:需要在 where 后手工添加 id=-1的子句。 因为,若 where 后的所有<if/>条件均为 false,而 where 后若又没有 id=-1 子句,则 SQL 中就会只剩下一个空的 where,SQL 出错。 所以,在where 后,需要添加子句 id=-1,以防止这种情况的发生。但当数据量很大时,会严重影响查询效率。 -->
@Test public void testSelectIf() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession(); StudentDao studentDao=session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); Student student=new Student(); student.setName("张起灵"); student.setAge(20); List<Student> students=studentDao.selectIf(student); students.forEach( stu -> System.out.println("stu === " + stu) ); session.close(); }
根据上面三个代码块,将其中的内容转为等价的 sql 语句如下:👇👇👇
select * from student where id=-1 or name="张起灵" or age=20
2.2 动态SQL——where标签
<where> 其他动态sql </where>
package com.bjpowernode.dao; import com.bjpowernode.entity.Student; import java.util.List; /** * */ public interface StudentDao { //where List<Student> selectWhere(Student student); }
<!-- where --> <select id="selectWhere" resultType="com.bjpowernode.entity.Student"> select * from student <where> <if test="name!=null and name!=''"> or name=#{name} </if> <if test="age>0"> or age=#{age} </if> </where> </select> <!-- 使用<where/>标签,在有查询条件时,可以自动添加上 where 子句;没有查询条件时,不会添加 where 子句。 需要注意的是,第一个<if/>标签中的SQL 片断,可以不包含 and。不过,写上 and 也不错,where标签会将离它最近的 and 或者 or 删掉。 但其它<if/>中 SQL 片断的 and,必须要求写上。否则 SQL 语句将拼接出错 -->
@Test public void testSelectWhere() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession(); StudentDao studentDao=session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); Student student=new Student(); student.setName("张起灵"); student.setAge(20); List<Student> students=studentDao.selectWhere(student); students.forEach( stu -> System.out.println("stu === " + stu) ); session.close(); }
根据上面三个代码块,将其中的内容转为等价的 sql 语句如下:👇👇👇
select * from student where id=-1 or name="张起灵" or age=20
2.3 动态SQL——foreach标签
<foreach collection="集合类型" open="开始的字符" close="结束的字符" item="集合中的成员" separator="集合成员之间的分隔符"> #{item的值} </foreach> <!-- 如果dao接口中方法的形参是数组,则collection="array" 如果dao接口中方法的形参是List,则collection="list" #item的值}:获取集合成员的值 -->
package com.bjpowernode.dao; import com.bjpowernode.entity.Student; import java.util.List; /** * */ public interface StudentDao { //for-each 1 List<Student> selectForeachOne(List<Integer> idlist); }
<!-- foreach第一种方式,循环简单类型的List: List<Integer> --> <select id="selectForeachOne" resultType="com.bjpowernode.entity.Student"> select * from student <if test="list!=null and list.size>0"> where id in <foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="stuid"> #{stuid} </foreach> </if> </select>
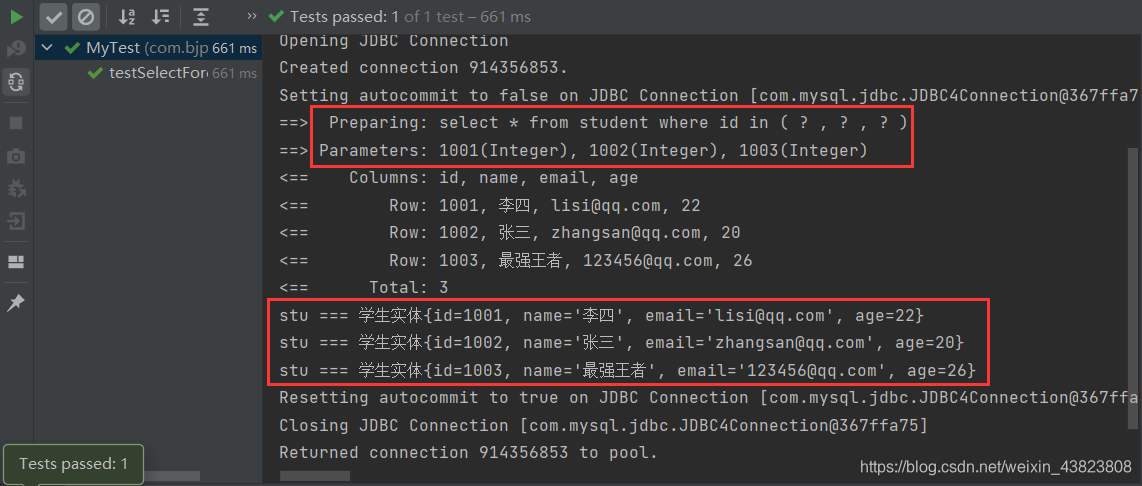
@Test public void testSelectForeachOne() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession(); StudentDao studentDao=session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); List<Integer> idlist=new ArrayList<>(); idlist.add(1001); idlist.add(1002); idlist.add(1003); List<Student> students=studentDao.selectForeachOne(idlist); students.forEach( stu -> System.out.println("stu === " + stu)); session.close(); }
根据上面三个代码块,将其中的内容转为等价的 sql 语句如下:👇👇👇
select * from student where id in (1001,1002,1003)
2.3.2 应用举例2(对象类型)
package com.bjpowernode.dao; import com.bjpowernode.entity.Student; import java.util.List; /** * */ public interface StudentDao { //for-each 2 List<Student> selectForeachTwo(List<Student> studentList); }
<!-- foreach第二种方式,循环对象类型的List: List<Student> --> <select id="selectForeachTwo" resultType="com.bjpowernode.entity.Student"> select * from student <if test="list!=null and list.size>0"> where id in <foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="stu"> #{stu.id} </foreach> </if> </select>
@Test public void testSelectForeachTwo() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession(); StudentDao studentDao=session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); List<Student> list=new ArrayList<>(); Student s1=new Student(); s1.setId(1001); Student s2=new Student(); s2.setId(1002); Student s3=new Student(); s3.setId(1003); list.add(s1); list.add(s2); list.add(s3); List<Student> students=studentDao.selectForeachTwo(list); students.forEach( stu-> System.out.println("stu === " + stu)); session.close(); }
根据上面三个代码块,将其中的内容转为等价的 sql 语句如下:👇👇👇
select * from student where id in (1001,1002,1003)
2.4 动态SQL——sql标签
<sql id="..."> sql语句 </sql> <include refid="sql标签的id属性值"></include> <!-- <sql/>标签用于定义 SQL 片断,以便其它 SQL 标签复用。 而其它标签使用该 SQL 片断,需要使用<include/>子标签。 该<sql/>标签可以定义 SQL 语句中的任何部分,所以<include/>子标签可以放在动态 SQL 的任何位置。 -->
package com.bjpowernode.dao; import com.bjpowernode.entity.Student; import java.util.List; /** * */ public interface StudentDao { //代码片段 List<Student> selectSql(List<Student> studentList); }
<!-- 定义代码片段 --> <sql id="selectStudent"> select id,name,age from student </sql> <sql id="studentFieldList"> where id in </sql> <select id="selectSql" resultType="com.bjpowernode.entity.Student"> <include refid="selectStudent"></include> <if test="list!=null and list.size>0"> <include refid="studentFieldList"></include> <foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="student"> #{student.id} </foreach> </if> </select>
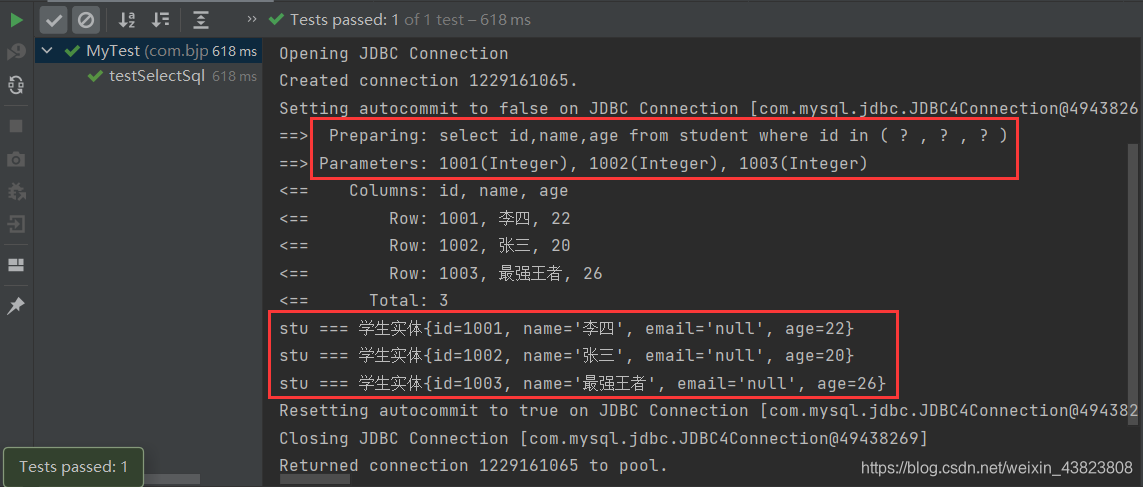
@Test public void testSelectSql() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession(); StudentDao studentDao=session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); List<Student> list=new ArrayList<>(); Student s1=new Student(); s1.setId(1001); Student s2=new Student(); s2.setId(1002); Student s3=new Student(); s3.setId(1003); list.add(s1); list.add(s2); list.add(s3); List<Student> students=studentDao.selectSql(list); students.forEach( stu-> System.out.println("stu === " + stu)); session.close(); }
根据上面三个代码块,将其中的内容转为等价的 sql 语句如下:👇👇👇
select id,name,age from student where id in (1001,1002,1003)