一篇文章带你学会MybatisPlus~(二):https://developer.aliyun.com/article/1424742
自定义分页功能:
第一步:在mapper接口中编写方法:
//@Param Page是MybatisPlus所提供的分页对象,必须位于第一个参数的位置 //通过年龄查询用户信息并分页 Page<User> selectPageVo(@Param("page") Page<User> page,@Param("age") Integer age);
在resources目录下创建对应的映射文件编写sql语句—映射语句中我们并没有书写分页功能
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="selectPageVo" resultType="User"> <!--当前我们编写的sql语句并 --> select * from t_user where age>#{age} </select> </mapper>
测试类:
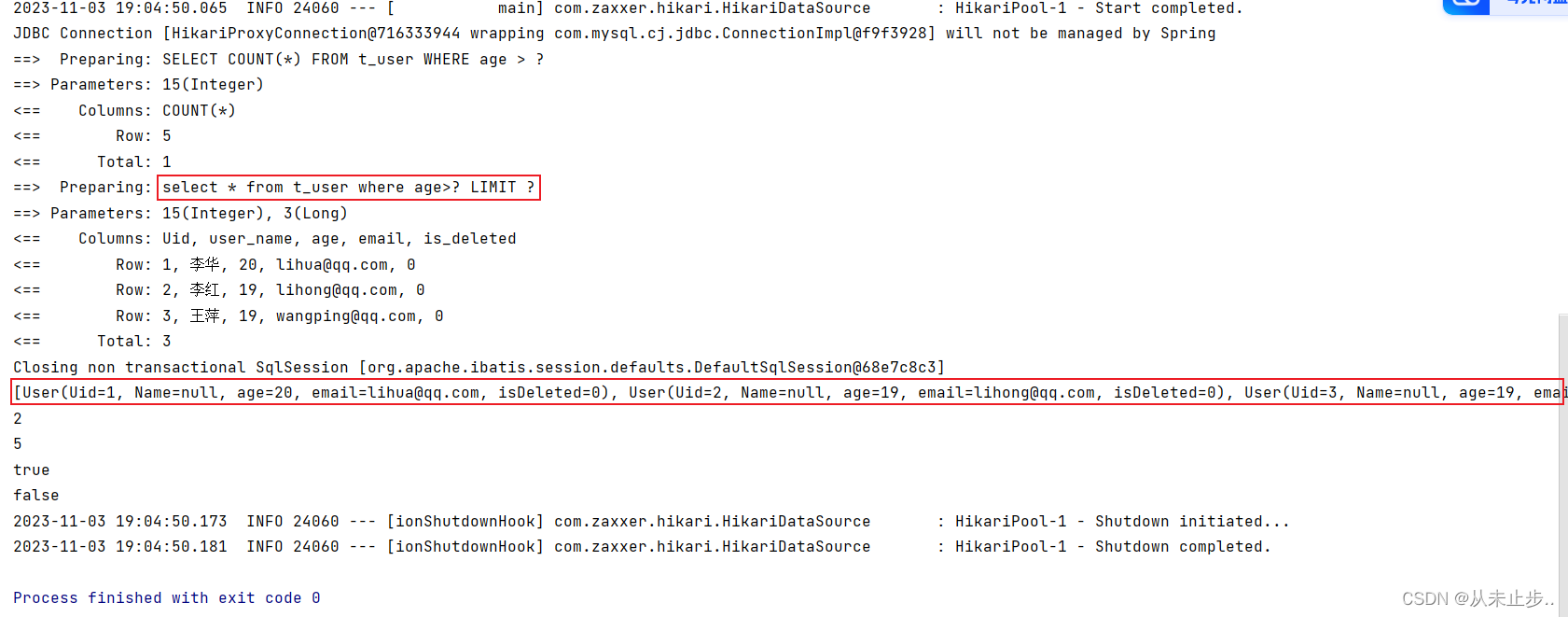
package com.example.mybatisplus.Test; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.pagination.Page; import com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.UserMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest public class MybatisPlusPluginsTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void testPage() { Page<User> userPage = new Page<>(1, 3); userMapper.selectPageVo(userPage,15); //输出的查询到的所有记录数 System.out.println(userPage.getRecords()); //获取总页数 System.out.println(userPage.getPages()); //获取总记录条数 System.out.println(userPage.getTotal()); //判断是否还有下一页 System.out.println(userPage.hasNext()); //判断是否还有上一页 System.out.println(userPage.hasPrevious()); } }
输出如下所示:
乐观锁:
一件商品,成本价是80元,售价是100元。老板先是通知小李,说你去把商品价格增加50元。小李正在玩游戏,耽搁了一个小时。1个小时后,老板觉得商品价格增加到150元,价格太高,可能会影响销量。又通知小王,你把商品价格降低30元。
此时,小李和小王同时操作商品后台系统。小李操作的时候,系统先取出商品价格100元;小王也在操作,取出的商品价格也是100元。小李将价格加了50元,并将100+50=150元存入了数据库;小王将商品减了30元并将100-30=70元存入了数据库。是的,如果没有锁,小李的操作就完全被小王的覆盖了。
现在商品价格是70元,比成本价低10元。几分钟后,这个商品很快出售了1千多件商品,老板亏1万多
上面的故事
如果是乐观锁,小王保存价格前,会检查下价格是否被人修改过了。如果被修改过了,则重新取出的被修改后的价格,150元,这样他会将120元存入数据库。
如果是悲观锁,小李取出数据后,小王只能等小李操作完之后,才能对价格进行操作,也会保证最终的价格是120元。
模拟修改冲突:
创建表:
create table t_product(id bigint(20) not null comment "主键ID", name varchar(30) null default null comment "商品名称", price int(11) default 0 comment "价格", version int(11) default 0 comment "乐观锁版本号", primary key(id));
插入数据:
insert into t_product (id,name,price) values (1,"外星人笔记本",100);
创建实体类:
package com.example.mybatisplus.pojo; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Product { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer price; private Integer version; }
创建对应的接口:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface ProductMapper extends BaseMapper<Product> { }
编写测试类:
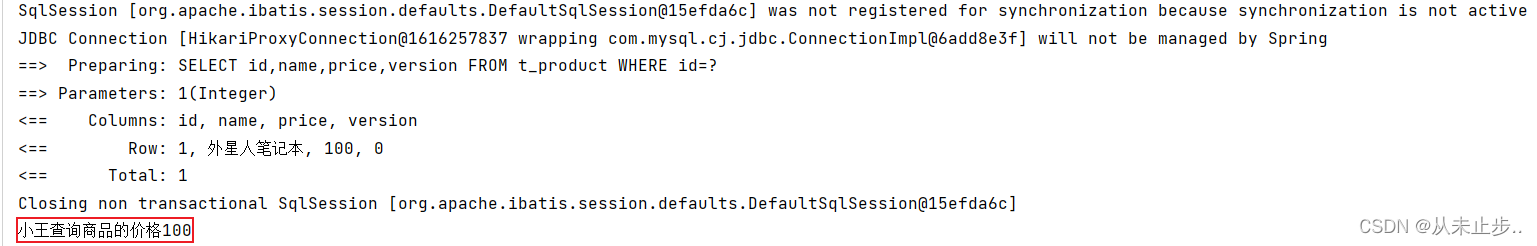
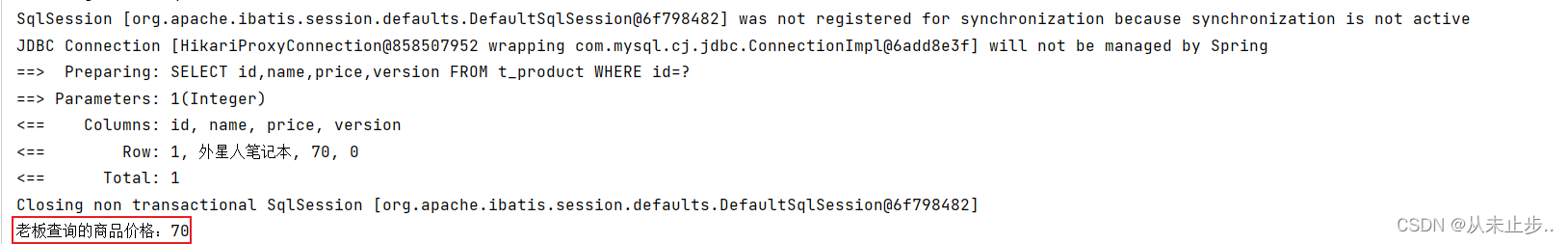
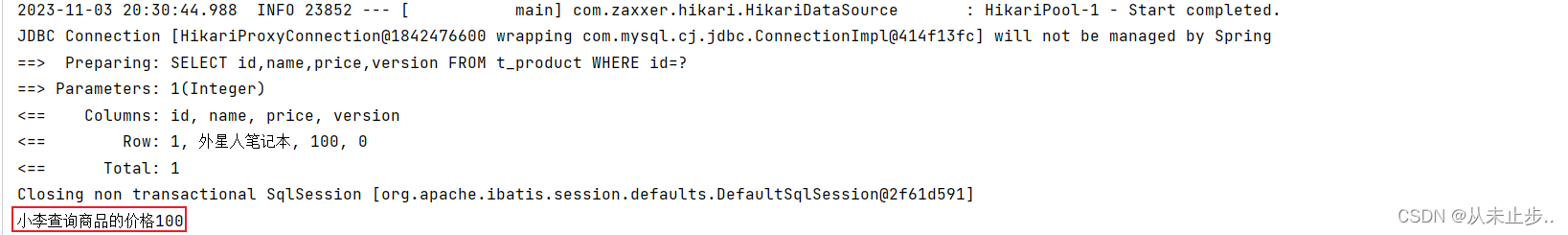
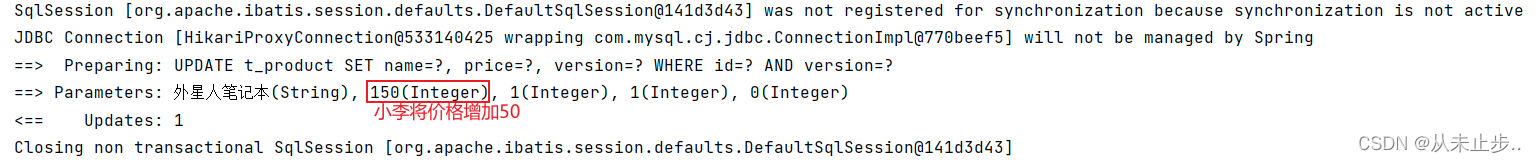
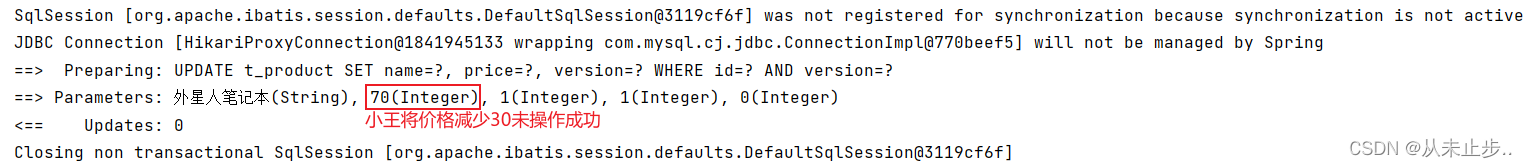
package com.example.mybatisplus.Test; import com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.ProductMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest public class MybatisPlusTest { @Autowired private ProductMapper productMapper; @Test public void test(){ //小李查询商品价格 Product productLi=productMapper.selectById(1); System.out.println("小李查询商品的价格"+productLi.getPrice()); //小王查询商品价格 Product productWang=productMapper.selectById(1); System.out.println("小王查询商品的价格"+productLi.getPrice()); //小李修改商品 productLi.setPrice(productLi.getPrice()+50); productMapper.updateById(productLi); //小王将商品价格-30 productWang.setPrice(productWang.getPrice()-30); productMapper.updateById(productWang); //老板查询的商品价格 Product productboss=productMapper.selectById(1); System.out.println("老板查询的商品价格:"+productboss.getPrice()); } }
输出如下所示:
使用乐观锁插件:
在配置类中添加乐观锁插件:
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
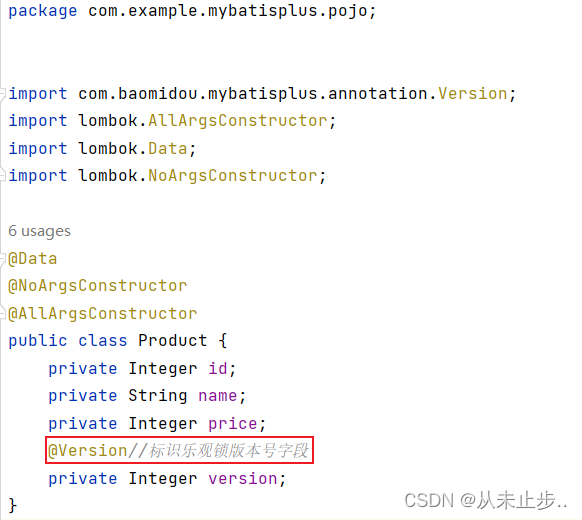
在实体类的对应字段加入表示版本号的注解:
此时重新运行上述的方法,输出如下所示:
//当小王的影响的记录数为0时,那么则出现和上述相同小王修改失败的现象,我们需要先获取最新的价格,再将最新的价格减少30 if(result==0){ Product productNew=productMapper.selectById(1); productNew.setPrice(productNew.getPrice()-30); productMapper.updateById(productNew); }
注意:在进行新的测试之前需要把数据库表中version重新设置为0,price设置成100
输出如下所示:
通用枚举:
表中的有些字段值是固定的,例如性别(男或者女),此时我们可以使用mybatis-plus的通用枚举来实现
创建枚举类用来表示性别:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Enums; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.EnumValue; import lombok.Getter; @Getter public enum SexEnums { MALE(1,"男"), FEMALE(2,"女"); @EnumValue//僵住解锁表示的属性的值直接放入数据库中 private Integer sex; private String sexName; SexEnums(Integer sex, String sexName) { this.sex = sex; this.sexName = sexName; } }
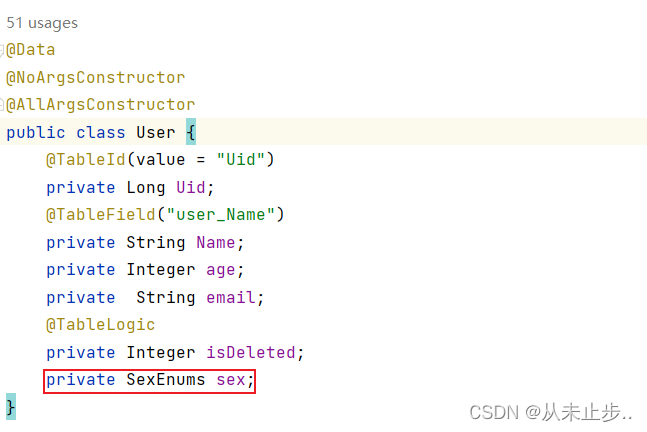
在实体类User中添加枚举类型:
注意:这里枚举类型的属性值必须和数据库表中字段值相同,否则会出现匹配不到对应的列
在application.yaml文件中配置扫描通用枚举的包
mybatis-plus: type-enums-package: com.example.mybatisplus.Enums
编写测试类:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Test; import com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.UserMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.Enums.SexEnums; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest public class MybatisPlusEnumsTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void test1() { User user = new User(); user.setName("蓝月亮"); user.setEmail("lanyueliang@qq.com"); user.setAge(30); user.setSex(SexEnums.FEMALE); int result=userMapper.insert(user); System.out.println(result); } }
输出如下所示:
多数据源:
适用于多种场景:纯粹多库,读写分离,一主多从,混合模式等
下面我们就来模拟纯粹多库的场景
场景说明:
我们创建两个库,分别为mybatisplus与mybatisplus1,将mybatisplus库的product表移动到mybatisplus1库,这样每个库一张表,通过一个测试用例分别获取用户数据与商品数据,如果获取到说明多库模拟成功
导入对应的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.0</version> </dependency>
创建从数据库mybatisplus1:
CREATE DATABASE mybatisplus1; use mybatisplus1 ; CREATE TABLE product( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名称', price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '价格', version INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '乐观锁版本号',PRIMARY KEY (id)); insert into product values(1,"外星人笔记本",100,0);
application.yaml中配置数据源的信息:
spring: # 配置数据源信息 datasource: dynamic: # 设置默认的数据源或者数据源组,黑认值即为master primary: master # 严格匹配数据源,默认false.true未匹配到指定数据源时抛异常,fase使用默认数据源 strict: false datasource: master : url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisplus?characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 你的密码 slave_1: ur]: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisplus1?characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql .cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 你的密码
创建用户service:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.User; public interface UserService extends IService<User> { }
UserService对应的实现类:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Service.impl; import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.UserMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.Service.UserService; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @DS("master")//指定UserServiceImpl操作的数据库为@DS @Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper,User> implements UserService { }
创建产品service:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; public interface ProductService extends IService<Product> { }
创建产品service对应的实现类:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Service.impl; import com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.annotation.DS; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper.ProductMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.Service.ProductService; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @DS("slave_1")//指定UserServiceImpl操作的数据库为slave_1 @Service public class ProductServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ProductMapper, Product> implements ProductService { }
创建User对应的Mapper接口:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { }
创建Product对应的Mapper接口:
package com.example.mybatisplus.Mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.example.mybatisplus.pojo.Product; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface ProductMapper extends BaseMapper<Product> { }
编写测试方法:
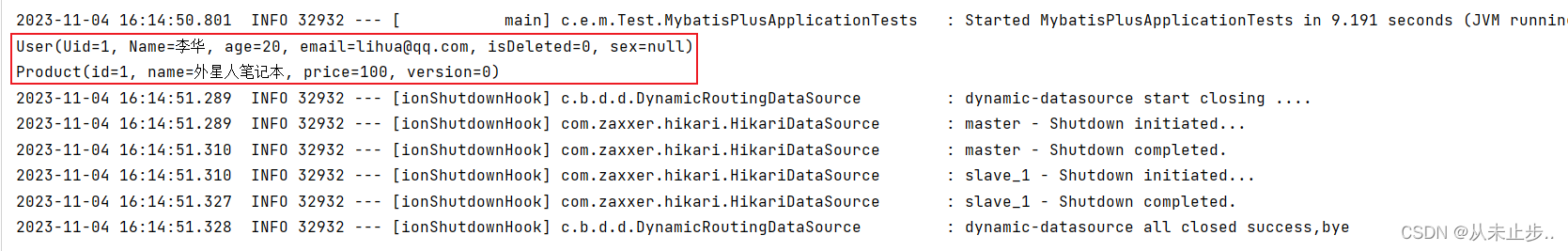
package com.example.mybatisplus.Test; import com.example.mybatisplus.Service.ProductService; import com.example.mybatisplus.Service.UserService; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest class MybatisPlusApplicationTests { @Autowired private UserService userService; @Autowired private ProductService productService; @Test public void test(){ //service对数据库进行操作为了区分mapper对数据进行操作,所有查询操作都是以get开头 System.out.println(userService.getById(1)); System.out.println(productService.getById(1)); } }
输出如下所示: