基于 Spring Framework v5.2.6.RELEASE
概述
前面用 4 篇文章,分析了基于 JDK 的 AOP 代理的回调方法,也就是 JdkDynamicAopProxy 中的invoke方法,是如何获得要执行的拦截器链的。本文开始分析获取到拦截器链之后,是如何执行目标方法和增强逻辑的。
拦截器链的执行
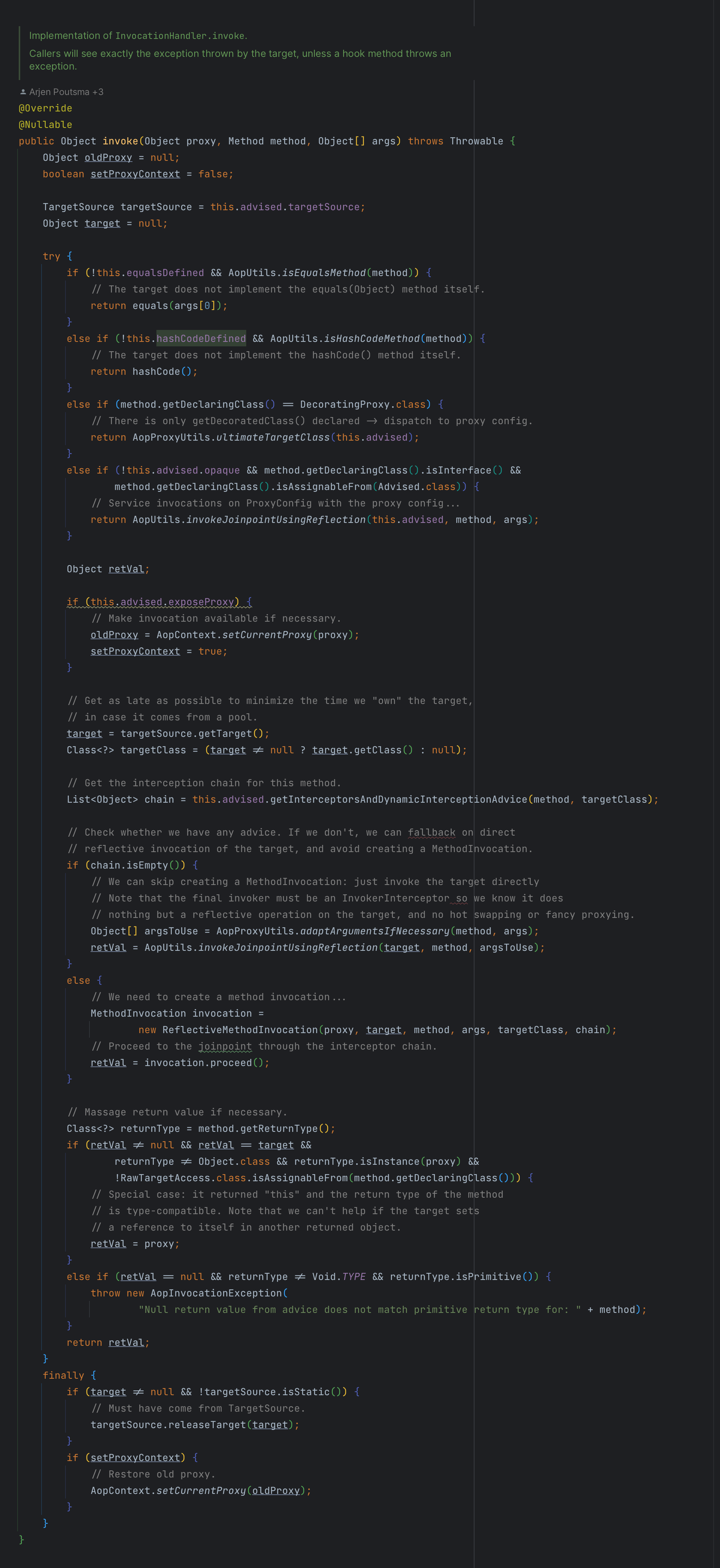
在次回顾一下 JdkDynamicAopProxy 的invoke方法源码。
之前我们分析的获取拦截器链的过程,在下面这行代码中完成。
// Get the interception chain for this method.List<Object>chain=this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
得到的拦截器链是一个 Object 列表,命名为chain。下面进入执行拦截器逻辑的部分。
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse=AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal=AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation...MethodInvocationinvocation=newReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.retVal=invocation.proceed(); }
执行之前,会判断拦截器链是不是为空。如果为空的话,则直接执行目标方法;如果不为空,再处理拦截器链的增强逻辑的执行。我们先看直接执行目标方法的部分。
拦截器链为空时,直接执行目标方法
直接执行目标方法有两个步骤,第一步是通过 AopProxyUtils 的adaptArgumentsIfNecessary方法来得到执行目标方法需要的参数列表。其实在invoke的参数中,已经得到了调用方法的参数值数组args,为什么不直接使用它调用目标方法呢?我们看一下adaptArgumentsIfNecessary方法中具体做了什么。
// org.springframework.aop.framework.AopProxyUtils#adaptArgumentsIfNecessarystaticObject[] adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(Methodmethod, Object[] arguments) { if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(arguments)) { returnnewObject[0]; } if (method.isVarArgs()) { if (method.getParameterCount() ==arguments.length) { Class<?>[] paramTypes=method.getParameterTypes(); intvarargIndex=paramTypes.length-1; Class<?>varargType=paramTypes[varargIndex]; if (varargType.isArray()) { ObjectvarargArray=arguments[varargIndex]; if (varargArrayinstanceofObject[] &&!varargType.isInstance(varargArray)) { Object[] newArguments=newObject[arguments.length]; System.arraycopy(arguments, 0, newArguments, 0, varargIndex); Class<?>targetElementType=varargType.getComponentType(); intvarargLength=Array.getLength(varargArray); ObjectnewVarargArray=Array.newInstance(targetElementType, varargLength); System.arraycopy(varargArray, 0, newVarargArray, 0, varargLength); newArguments[varargIndex] =newVarargArray; returnnewArguments; } } } } returnarguments; }
这个方法只有一条线性的逻辑,主要作用是让给定的参数适配目标方法的参数类型,如果参数列表的最后一个参数类型是一个数组,也就是方法中声明了可变参数,针对给定参数的数组元素类型和目标方法声明的数组元素类型不一致的情况,进行转换,得到新的参数数组。
如果不存在上述的情况,则直接返回原参数数组。
回到invoke方法中,处理完参数之后,下一步就是通过 AopUtils 的invokeJoinpointUsingReflection方法来执行目标方法。
// org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils#invokeJoinpointUsingReflectionpublicstaticObjectinvokeJoinpointUsingReflection(Objecttarget, Methodmethod, Object[] args) throwsThrowable { // Use reflection to invoke the method.try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method); returnmethod.invoke(target, args); } catch (InvocationTargetExceptionex) { // Invoked method threw a checked exception.// We must rethrow it. The client won't see the interceptor.throwex.getTargetException(); } catch (IllegalArgumentExceptionex) { thrownewAopInvocationException("AOP configuration seems to be invalid: tried calling method ["+method+"] on target ["+target+"]", ex); } catch (IllegalAccessExceptionex) { thrownewAopInvocationException("Could not access method ["+method+"]", ex); } }
这里是通过反射的方式执行的,也就是调用目标方法对应的 Method 对象的invoke方法。方法执行的结果,也就是返回值,会被直接返回到invoke方法中,待下一步处理。
接下来我们看拦截器链不为空的情况,是如何执行拦截器链和目标方法的。
拦截器链不为空时的处理方式
// We need to create a method invocation...MethodInvocationinvocation=newReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.retVal=invocation.proceed();
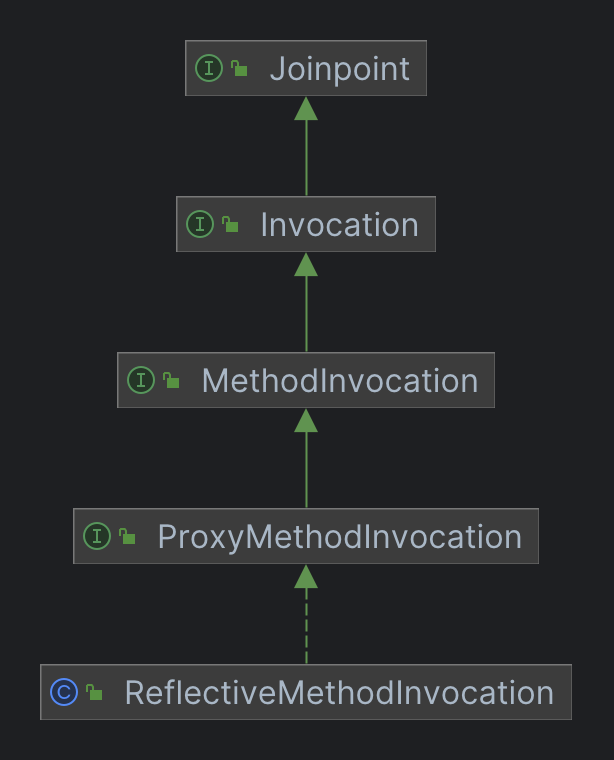
这部分也包含了两个步骤,第一步是创建了一个 MethodInvocation 对象,它的具体类型时 ReflectiveMethodInvocation,创建时,通过构造方法参数传入了代理对象、目标对象、目标方法、方法调用参数、目标对象的类型、拦截器链,可以说把invoke方法的所有参数和之前创建的几乎所有局部变量都包括了。我们先来了解一下这个类。
protectedReflectiveMethodInvocation( Objectproxy, Objecttarget, Methodmethod, Object[] arguments, Class<?>targetClass, List<Object>interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) { this.proxy=proxy; this.target=target; this.targetClass=targetClass; this.method=BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method); this.arguments=AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments); this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers=interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers; }
在构造方法中,没有复杂的逻辑,都是成员变量的初始化,用到的也都是构造方法阐述中传入的内容。
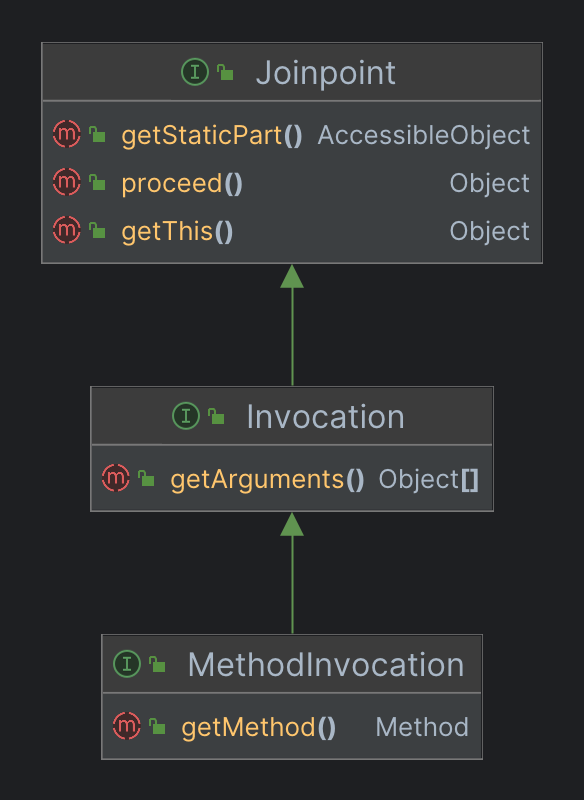
它的继承关系也比较简单,主要就是实现了一些接口,其中包括代码中声明invocation变量的 MethodInvocation。我们再看一下 MethodInvocation 及其继承的接口中都声明了哪些方法。
其中,接下来要被调用的proceed方法,位于 Joinpoint 接口中。
另外,这里还有一个值得关注的点,跟之前的文章中分析内容有关系。
在invoke方法获取拦截器链的步骤中,对于 PointcutAdvisor 类型的增强,也就是我们最常见的增强逻辑,会通过getAdvice方法,获取到对应的 Advice 对象,然后封装成 MethodInterceptor 放到连接器链中。
也就是说,拦截器链中的拦截器都是 MethodInterceptor 的实现类,而 MethodInterceptor 中声明的唯一方法invoke方法的参数就是 MethodInvocation 类型。跟上面声明的invocation对象类型相同,因此这两者之间存在着紧密的关系。
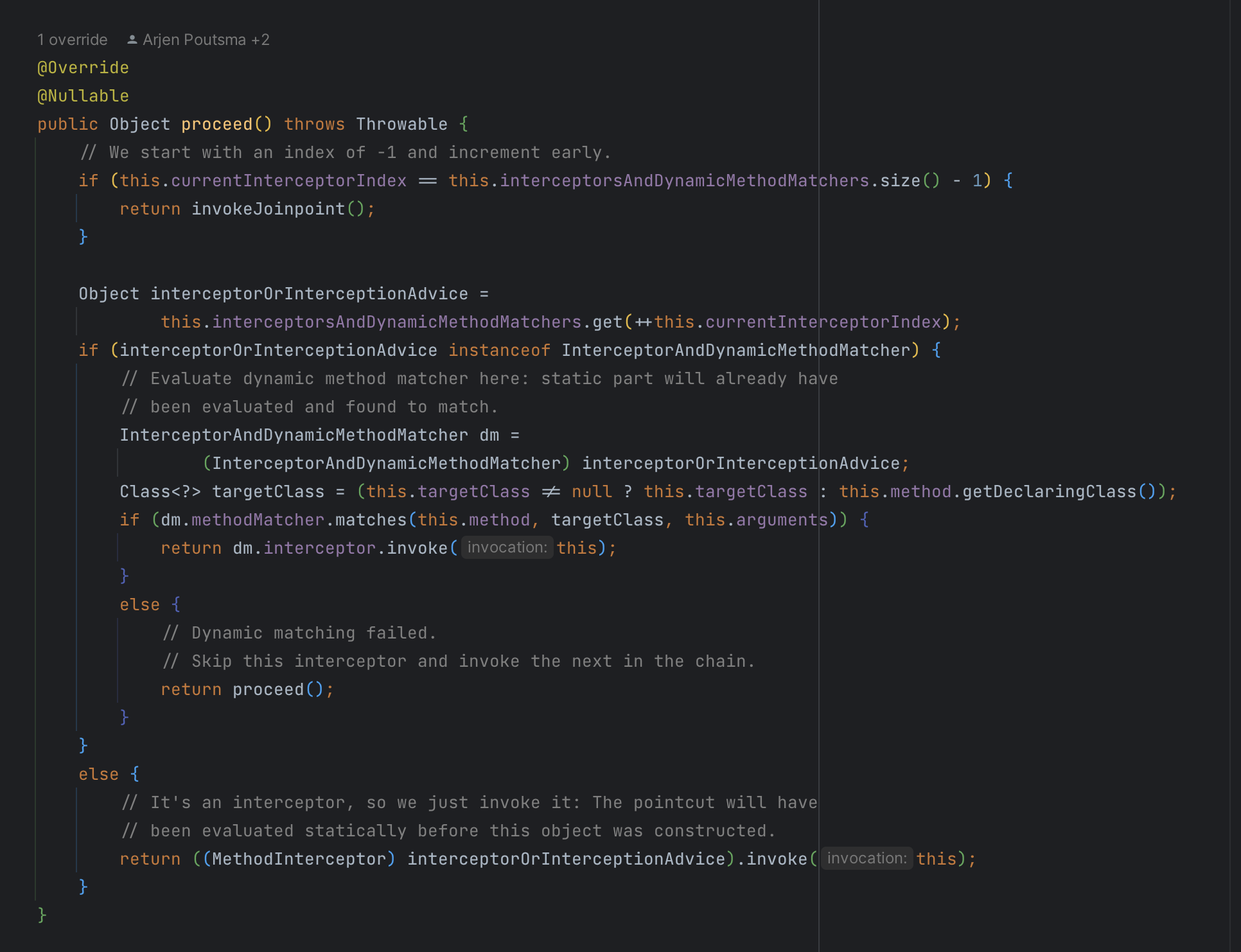
以上对于 MethodInvocation 接口的分析内容,先留个印象,方便对后面的核心流程的理解。接下来,就是执行增强逻辑和目标方法,也就是调用invocation的proceed方法。
这个方法的内容并不长,但其中包含了很多的逻辑,因为拦截器中的增强逻辑包括了在目标方法执行之前和之后的部分,因此,这里其实会存在递归调用,而且每一个拦截器的增强类型不同,对下一层拦截器的调用时机也不同。
这个方法的深入分析,会放到下一篇中。
总结
本文总结了 JdkDynamicAopProxy 的invoke方法在获取到拦截器链之后,是如何开始执行增强逻辑的。对于拦截器链为空的情况,会直接调用目标方法,而存在拦截器的情况下,会将拦截器链和目标方法调用的信息封装成一个 MethodInterceptor 对象,执行其proceed方法,来完成增强逻辑和目标方法的执行。proceed方法的分析,放到下一篇中。