一、vuex介绍
1.vuex概念引入:
当我们修改其中一个头像的时候,我们怎么同步到多个组件当中呢?
这个是平级的非父子关系我们应该怎么传递值进去呢?用vuex来对非父子关系传值
2.为什么要有vuex
- vuex的作用是解决多组件状态共享的问题,在大型的项目中,组件通讯会变得很混乱,使用vuex可以统一管理组件之间的通讯
- vuex是响应式布局: 只要vuex中的数据变化,对应的组件会自动更新(类似于vue数据驱动)
3.Vuex使用场景
不是所有的场景都适用于vuex,只有在必要的时候才使用vuex,如果不必要,尽量别用
1..适合使用vuex场景
- 这个数据需要在很多个地方要写,如果采用组件传值方式,写起来很麻烦,而且多个地方都要写
- 例如:用户信息(姓名,头像),可能会在很多个地方使用(个人页面,评论页面等)
2.不适合使用vuex场景
- 这个数据不需要多个地方使用,如果某个数据仅仅只是在两个组件之间通讯,优先使用props或$emit
3.vuex特点
- 所有组件数据共享
- 响应式: 一旦vuex数据修改,所有使用的地方都会自动更
4.vuex工作流程:
我们先触发了Actions中的异步操作,当异步结果出来之后(如果没有异步操作则直接执行后面的操作),我们触发commit调用mutations去修改我们的state,最后因为我们是具有响应式的特点,因此我们的数据被修改成功。
二、五大核心配置项
1.state
①原生写法
1.概念:
state提供vuex唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到store中的State中存储。
2.声明语法:
state:{ //在此处写共享属性即可 }
3.使用语法:
$store.state.属性名
举个例子:
1.声明:
2.使用:
可以看出我们的存放在state中的数据被我们成功的获取到啦!
②state辅助函数mapSaatate
1.概念:
将vuex中的数据映射到组件的计算属性中,简化书写操作(写在computed中)
2.使用方法:
- 1.导入import { mapState } from 'vuex'
- 2. ...mapState([‘state中属性名’])
3.举个例子
2.getters
①原生写法
1.概念:
state的计算属性
2.声明语法:
getters: { 计算属性名()(state) { return 要返回的值 } }
3.使用语法
$store.getters.getter名
举个例子
1.声明
2.使用
可以看出我们的存放在getters中的数据被我们成功的获取到了,注意步骤是getters下
②getters辅助函数mapGetters
1.概念:
同上是简化我们的写法(写在computed中)
2.使用方法:
- 1.导入import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
- 2. ...mapGetters([‘getters中计算属性’])
3.举个例子
3.mutations
①原生写法
1.概念:
state数据的修改只能通过mutations,并且mutations必须是同步的。Mutations是同步更新state数据的唯一方式!!!
2.声明语法:
mutations:{ mutation名(state , 载荷 ) { },
每一项都是一个函数,可以声明两个形参:
第一个参数是必须的,表示当前的state。
第二个参数是可选的,表示载荷,是可选的。在使用时要传入的数据
专业术语载荷:表示额外的参数
3.使用语法
this.$store.commit('mutation名', 载荷 )
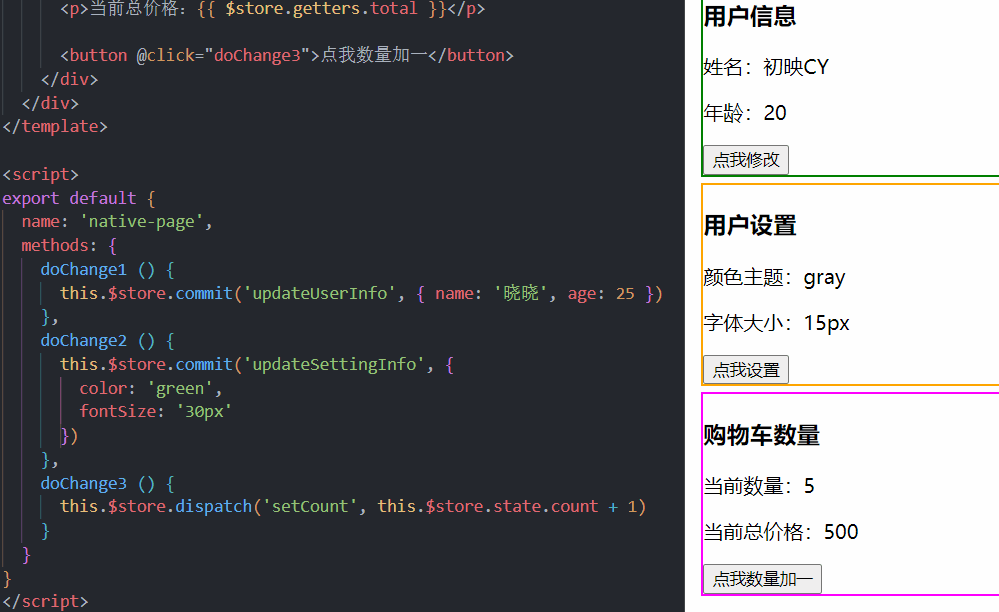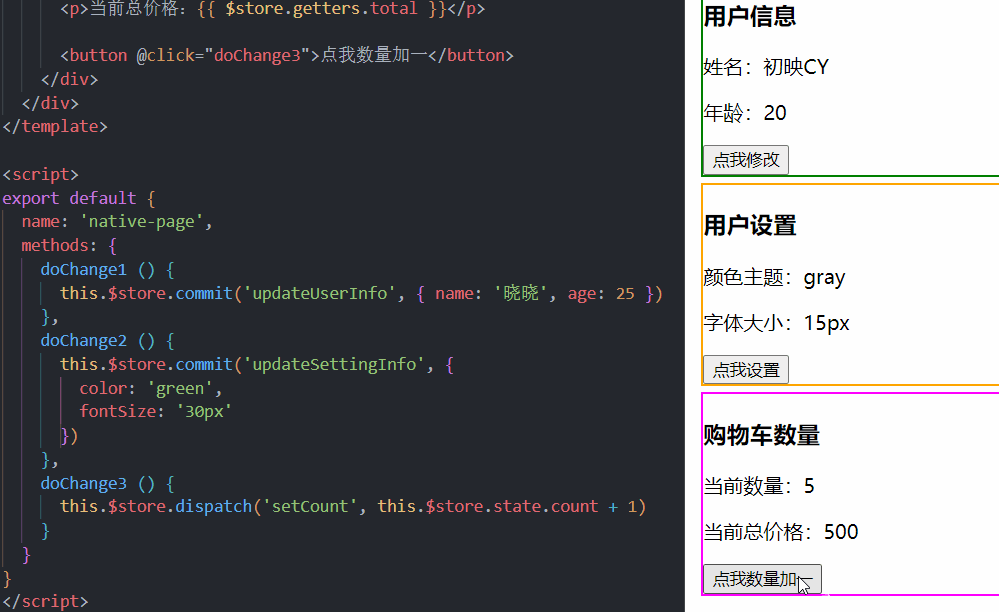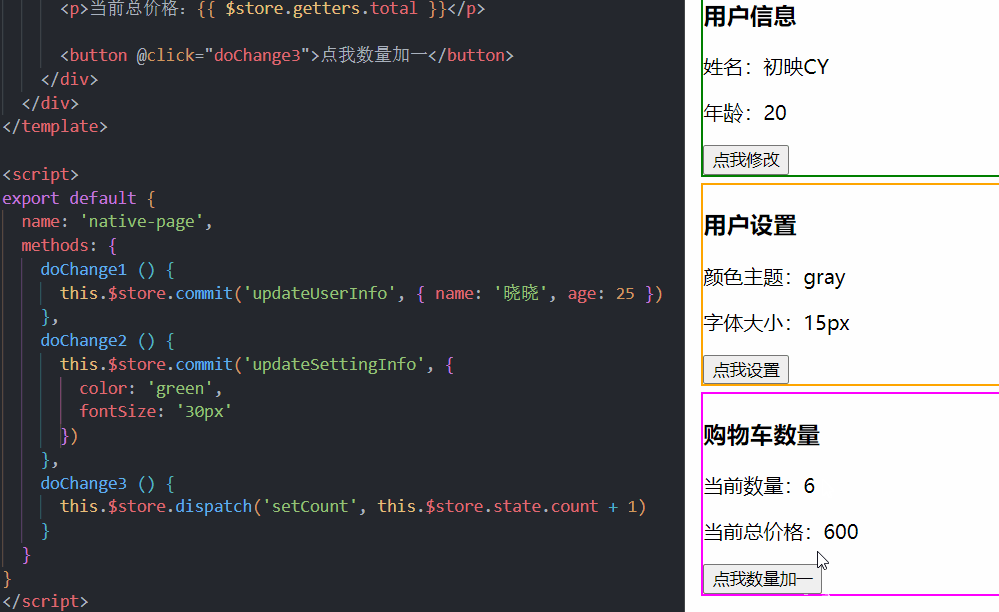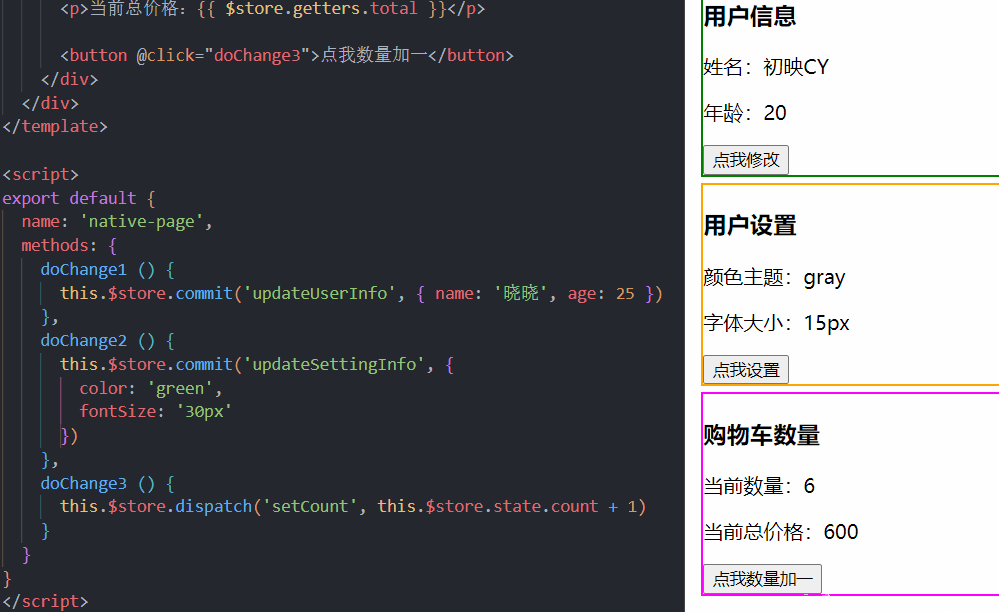
4.举个例子
1.声明
2.使用
当我们点击按钮的时候,我们荷载(payload)中的数据传到了mutation中随后完成我们的值传递,将我们原始的数据改变。
②mutations辅助函数mapMutations
1.概念:
简化书写操作成方法形式(写在methods中)
2.使用方法:
- 1.导入import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
- 2. ...mapMutations([‘mutations名’])
3.举个例子
4.actions
①原生写法
1.概念:
actions: 异步更新我们的数据(例如你的数据来源于ajax)
2.声明语法:
这个地方的载荷一般为ajax接口需要的参数,如果没有就不用传
actions: { // context对象会自动传入,它与store实例具有相同的方法和属性 action的名字: function(context, 载荷) { // 1. 异步操作获取数据 // 2. commit调用mutation来修改数据 // context.commit('mutation名', 载荷) } }
每一项都是一个函数,可以声明两个形参:
第一个参数是必须的,表示当前的state。
第二个参数是可选的,表示载荷,是可选的。在使用时要传入的数据
专业术语载荷:表示额外的参数
3.使用语法
this.$store.dispath ( 'actions的名字',参数 )
4.举个例子
4.1.声明
4.2.使用
②actions辅助函数mapActions
1.概念:
简化书写操作成方法形式(写在methods中)
2.使用方法:
- 1.导入import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
- 2. ...mapmapActions([‘action名’])
3.举个例子
5.modules
①原生写法
1.概念:
模块化处理vuex数据,将我们每个模块的vuex数据分开处理
2.声明语法:
//在我们的store/index.js中书写 modules: { 模块名1: { // namespaced为true,则在使用mutations时,就必须要加上模块名 namespaced: true,
3.使用语法:
//state 全局的: $store.state.数据项名 模块的: $store.state.模块名.数据项名 //getters 全局的: $store.getters.getter名 模块的: $store.getters['模块名/getters名'] //mutations 全局的: $store.commit('mutations名',载荷) 模块的: $store.commit('模块名/mutations名',载荷) //actions 全局的: $store.dispatch('actions名',载荷) 模块的: $store.dispatch('模块名/actions名',载荷)
4.举个例子
4.1声明:
我们先封装模块
在index.js中导入
4.2使用:
注意:模块化语法一定一定需要开启命名空间namespaced:true
②modules封装写法
注意点:我们分了模块,我们的数据要单独的导入进来喔
【vuex辅助函数源素材】
1.先搭建我们的脚手架(务必勾选上以下选项)
2.引入我们的组件
App.vue
<template> <div> <!-- 顶部导航栏 --> <div class="footer_wrap"> <!-- 路由导航 --> <!-- <router-link to="/native">原生写法</router-link> --> <router-link to="/facilitate">辅助函数写法</router-link> </div> <!-- 下面内容 --> <div class="top"> <!-- 路由出口 --> <router-view></router-view> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'facilitate-page', methods: {} } </script> <style scoped> body, html { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .footer_wrap { position: fixed; left: 0; top: 0; display: flex; width: 100%; text-align: center; background-color: #333; color: #ccc; } .footer_wrap a, span { cursor: pointer; flex: 1; text-decoration: none; padding: 15px 0; line-height: 20px; background-color: #333; color: #ccc; border: 1px solid black; } .footer_wrap a:hover, span:hover { background-color: #555; } .top { padding-top: 50px; } .footer_wrap .router-link-active { background-color: #000; } </style>
Facilitate.vue(Views/ Facilitate.vue)
<template> <div> <h2>辅助函数写法</h2> <div class="user"> <h3>用户信息</h3> <p>姓名:{{ userInfo.name }}</p> <p>年龄:{{ userInfo.age }}</p> <button @click="doChange1">点我修改</button> </div> <div class="setting"> <h3>用户设置</h3> <p>颜色主题:{{ settingInfo.color }}</p> <p>字体大小:{{ settingInfo.fontSize }}</p> <button @click="doChange2">点我设置</button> </div> <div class="shopcar"> <h3>购物车数量</h3> <p>当前数量:{{ count }}</p> <p>当前总价格:{{ total }}</p> <button @click="doChange3">点我数量加一</button> </div> </div> </template> <script> // 导入辅助函数 import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { name: 'facilitate-page', computed: { ...mapState('user', ['userInfo']), ...mapState('setting', ['settingInfo']), ...mapState('shopcar', ['count']), ...mapGetters('shopcar', ['total']) }, methods: { ...mapMutations('user', ['updateUserInfo']), ...mapMutations('setting', ['updateSettingInfo']), ...mapActions('shopcar', ['setCount']), // 1.点击修改信息 doChange1 () { // 提交mutations this.updateUserInfo({ name: '结束啦', age: 666 }) }, // 2.点击修改设置 doChange2 () { // 提交mutations this.updateSettingInfo({ color: 'green', fontSize: '20px' }) }, // 3.点击购买按钮 doChange3 () { // 提交actions this.setCount(this.count + 1) } } } </script> <style scoped> .user { border: 2px solid green; margin: 5px; } .setting { border: 2px solid orange; margin: 5px; } .shopcar { border: 2px solid magenta; margin: 5px; } </style>
3.引入路由
index.js (router/index.js)
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' // 1.导入组件 // import native from '@/views/Native.vue' import facilitate from '@/views/Facilitate.vue' Vue.use(VueRouter) // 2.路由规则 const routes = [ // { path: '/', redirect: '/Native' }, // { path: '/native', component: native }, { path: '/facilitate', component: facilitate } ] const router = new VueRouter({ routes }) export default router