spring mvc 一次请求如何映射到对应的controller 如何规避冲突
映射的分析很多了,但是那些看起来冲突的url映射,spring都能正常工作,好奇,故分析一波
看似冲突的URL映射
- /test/hello
- /test/{res}
这两个映射URL,如果输入**/test/hello**,那么两个映射规则应该都是符合的,那么它会走哪一个,是不是随机的?为啥不冲突?
测试代码
创建一个带有spring mvc的简单的spring boot工程,加入下面这个controller文件
package com.example.download; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class MappingTestApi { @GetMapping("/hello") public String sayHello() { return "HELLO."; } @GetMapping("/{res}") public String sayRes(@PathVariable String res) { return res; } }
测试访问
- 访问1:/test/rese
wanglh@dark:~/Desktop$ curl http://localhost:8080/test/rese resewanglh@dark:~/Desktop$
显然,命中的是@GetMapping("/{res}"),意料之中。
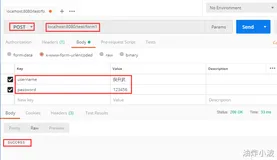
- 访问2:/test/hello
wanglh@dark:~/Desktop$ curl http://localhost:8080/test/hello HELLO.wanglh@dark:~/Desktop$
显然,命中了@GetMapping("/hello"),那么为什么它不会命中@GetMapping("/{res}"),输出hello呢?
源码分析
spring mvc 的请求入口 在org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch,首先在这边打断点,往下走。 这里就省略了。
我们直接上核心获取映射的方法源码:
/** * Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request. * If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected. * @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping * @param request the current request * @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match * @see #handleMatch(Object, String, HttpServletRequest) * @see #handleNoMatch(Set, String, HttpServletRequest) */ @Nullable protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); // 这里获取直接匹配的路径 List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { // 这里获取匹配的路径 addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (matches.size() > 1) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); matches.sort(comparator); bestMatch = matches.get(0); // 省略 } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod()); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod(); } else { return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }
- this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
这个方法获取的是写死的直接路径映射,举个例子"/test/aaaa"就属于,而"/test/{aaaa}“这种包含”{}"路径变量的URL则不算。 - addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
这个方法是当第一步找不到写死直接路径映射的时,将所有注册的映射进行匹配,这个mappingRegistry既包含"/test/aaaa",也包含"/test/{aaaa}“这样的映射,当然还有第三方包注入的路径,我这里比较干净,只有spring mvc额外提供的”/error"。
结论
- 通过DEBUG可以发现,“/test/hello”这样固定的路径,会在第一步this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);中直接找到映射,不会再去匹配下面的全量映射了。
- 如果不符合第一步的映射,第二步匹配时,自然也不会命中第一步中那些直接路径了。
留个问题
我这边没有展示this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);进去的源码,你知道spring mvc是怎么区分固定路径和其他路径的吗?