-
01状态机介绍
游戏中的状态机一般都是有限状态机,简写为FSM(有限状态机),简称状态机,是表示有限个状态以及在这些状态之间的转移和动作等行为的数学模型。
状态机的每一个状态至少需要有以下三个操作:
启动:当从其他状态进入这个状态时,需要进行的初始化操作;
更新:在这个状态运行时进行的更新操作;
清理:当从这个状态退出时,需要进行的清除操作。状态需要的变量: 下一个:表示这个状态退出后要转到的下一个状态;
坚持:在状态间转换时需要传递的数据;
完成:表示这个状态是否结束,状态机会根据这个值来决定转换状态。游戏界面状态机的状态转换图如下,箭头表示可能的状态转换方向:(注意有个转换不太好画出来:超时状态可以转换到Game Over状态。)
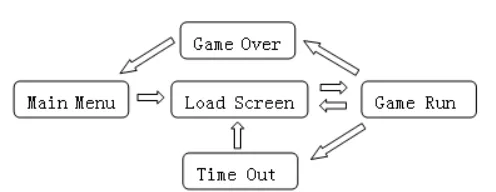
这几个状态的意思比较简单,下面把游戏界面的截图发一下。
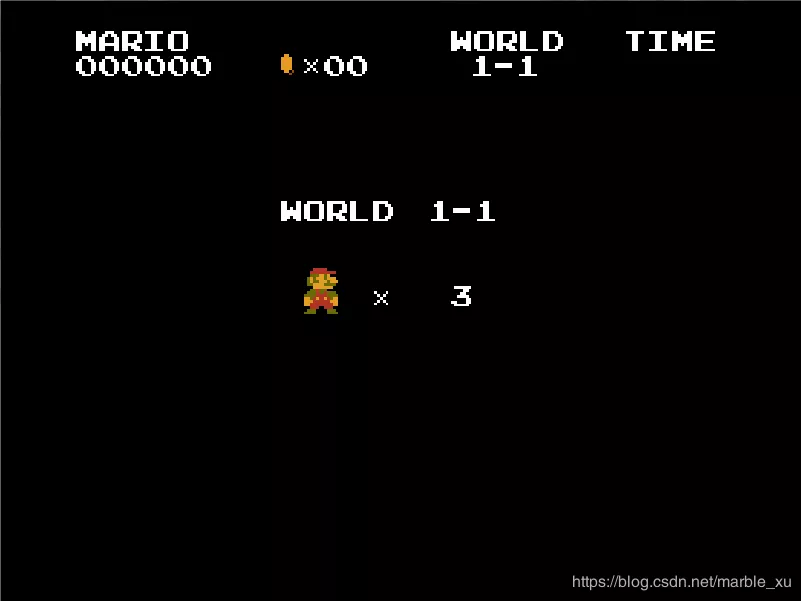
主菜单:主菜单,启动程序就进入这个状态,可以用上和下键选择玩家1或玩家2,按回车键开启游戏。

加载屏幕:游戏开始前的加载界面。
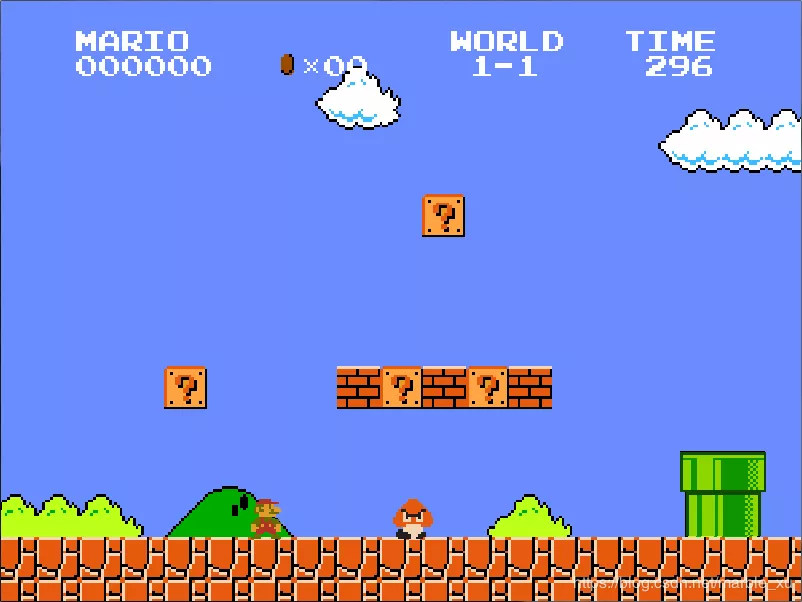
游戏运行:游戏运行时的状态,在代码实现中是Level类。

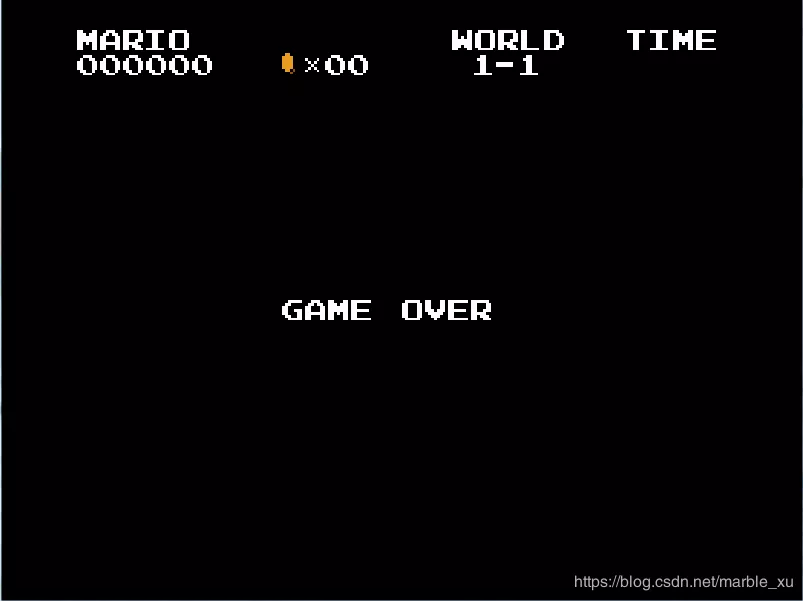
游戏结束:人物死亡且生命数量为0时到这个状态。
超时:在游戏中时间超时会到这个状态,这个和Game Over类似,就不截图了。
02状态机代码实现
因为这篇文章的目的是游戏界面的状态机实现,所以专门写了一个state_demo.py文件,让大家可以更加方便的看代码。
游戏启动代码
开始是pygame的初始化,设置屏幕大小为c.SCREEN_SIZE(800,600)。所有的常量都保存在单独的constants.py中。import os import pygame as pg import constants as c pg.init() pg.event.set_allowed([pg.KEYDOWN, pg.KEYUP, pg.QUIT]) pg.display.set_caption(c.ORIGINAL_CAPTION) SCREEN = pg.display.set_mode(c.SCREEN_SIZE) SCREEN_RECT = SCREEN.get_rect()load_all_gfx函数查找指定目录下所有符合后缀名的图片,使用pg.image.load函数加载,保存在图形set中。
GFX保存在资源/图形目录找到的所有图片,后面获取各种图形时会用到。
def load_all_gfx(directory, colorkey=(255,0,255), accept=('.png', '.jpg', '.bmp', '.gif')): graphics = {} for pic in os.listdir(directory): name, ext = os.path.splitext(pic) if ext.lower() in accept: img = pg.image.load(os.path.join(directory, pic)) if img.get_alpha(): img = img.convert_alpha() else: img = img.convert() img.set_colorkey(colorkey) graphics[name] = img return graphics GFX = load_all_gfx(os.path.join("resources","graphics"))下面是demo的入口函数,先创建了一个保存所有状态的state_dict设置,调用setup_states函数设置启动状态是MAIN_MENU。
if __name__=='__main__': game = Control() state_dict = {c.MAIN_MENU: Menu(), c.LOAD_SCREEN: LoadScreen(), c.LEVEL: Level(), c.GAME_OVER: GameOver(), c.TIME_OUT: TimeOut()} game.setup_states(state_dict, c.MAIN_MENU) game.main()状态类
先定义一个状态基类,按照上面说的状态需要的三个操作分别定义函数(启动,更新,清理)。在init函数中定义了上面说的三个变量(next,persist,```js done),还有start_time和current_time用于记录时间。 class State(): def init(self): self.start_time = 0.0 self.current_time = 0.0 self.done = False self.next = None self.persist = {}@abstractmethod def startup(self, current_time, persist): '''abstract method'''
def cleanup(self): self.done = False return self.persist
@abstractmethod def update(sefl, surface, keys, current_time): '''abstract method'''
看一个状态类LoadScreen的具体实现,这个状态的显示效果如图3。 startup函数保存了预期的persist,设置next为Level状态类,start_time保存进入该状态的开始时间。初始化一个Infoclass,这个就是专门用来显示界面信息的。 update函数根据在这个状态已运行的时间(current_time-self.start_time),决定显示内容和是否结束状态(self.done = True)。 ```js class LoadScreen(State): def __init__(self): State.__init__(self) self.time_list = [2400, 2600, 2635] def startup(self, current_time, persist): self.start_time = current_time self.persist = persist self.game_info = self.persist self.next = self.set_next_state() info_state = self.set_info_state() self.overhead_info = Info(self.game_info, info_state) def set_next_state(self): return c.LEVEL def set_info_state(self): return c.LOAD_SCREEN def update(self, surface, keys, current_time): if (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[0]: surface.fill(c.BLACK) self.overhead_info.update(self.game_info) self.overhead_info.draw(surface) elif (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[1]: surface.fill(c.BLACK) elif (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[2]: surface.fill((106, 150, 252)) else: self.done = True信息类
下面介绍的信息类,界面的显示大部分都是由它来完成,初始化函数中create_info_labels函数创建通用的信息,create_state_labels函数对于不同的状态,会初始化不同的信息。class Info(): def __init__(self, game_info, state): self.coin_total = game_info[c.COIN_TOTAL] self.total_lives = game_info[c.LIVES] self.state = state self.game_info = game_info self.create_font_image_dict() self.create_info_labels() self.create_state_labels() self.flashing_coin = FlashCoin(280, 53)create_font_image_dict函数从之前加载的图片GFX ['text_images']中,截取字母和数字对应的图形,保存在一个设置中,在后面创建文字时会用到。
def create_font_image_dict(self): self.image_dict = {} image_list = [] image_rect_list = [# 0 - 9 (3, 230, 7, 7), (12, 230, 7, 7), (19, 230, 7, 7), (27, 230, 7, 7), (35, 230, 7, 7), (43, 230, 7, 7), (51, 230, 7, 7), (59, 230, 7, 7), (67, 230, 7, 7), (75, 230, 7, 7), # A - Z (83, 230, 7, 7), (91, 230, 7, 7), (99, 230, 7, 7), (107, 230, 7, 7), (115, 230, 7, 7), (123, 230, 7, 7), (3, 238, 7, 7), (11, 238, 7, 7), (20, 238, 7, 7), (27, 238, 7, 7), (35, 238, 7, 7), (44, 238, 7, 7), (51, 238, 7, 7), (59, 238, 7, 7), (67, 238, 7, 7), (75, 238, 7, 7), (83, 238, 7, 7), (91, 238, 7, 7), (99, 238, 7, 7), (108, 238, 7, 7), (115, 238, 7, 7), (123, 238, 7, 7), (3, 246, 7, 7), (11, 246, 7, 7), (20, 246, 7, 7), (27, 246, 7, 7), (48, 246, 7, 7), # -* (68, 249, 6, 2), (75, 247, 6, 6)] character_string = '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ -*' for character, image_rect in zip(character_string, image_rect_list): self.image_dict[character] = get_image(GFX['text_images'], *image_rect, (92, 148, 252), 2.9)get_image函数从一个大的表面工作表中按照面积(x,y,宽度,高度)截取的部分图片放入表面图像对应的起始位置(0,0),并按比例参数调整大小。
pygame的blit函数介绍如下:
pg.Surface.blit(source, dest, area=None, special_flags=0) -> Rect draw one image onto another def get_image(sheet, x, y, width, height, colorkey, scale): image = pg.Surface([width, height]) rect = image.get_rect() image.blit(sheet, (0, 0), (x, y, width, height)) image.set_colorkey(colorkey) image = pg.transform.scale(image, (int(rect.width*scale), int(rect.height*scale))) return image看一下create_info_labels函数中其中一个字符串'MARIO'是如何在界面上显示的。
create_label函数参数(x,y)表示字符串在界面上的起始位置,从self.image_dict中根据字符获取对应的表面对象。 set_label_rects函数会设置字符串中每一个表面对象rect的(x,y)值。
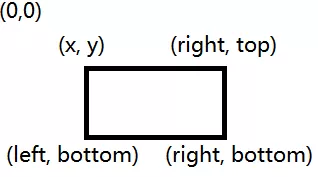
pygame.Rect 对象中常用的成员变量(x,y),表示这个Surface的左上角的位置。 top, bottom: 表示Surface 在y轴上最上边和最下边的值, 所以top和y 值是一样的 left, right: 表示Surface 在x轴上最左边和最右边的值,所以left 和x 值是一样的下面的坐标图可以看到,在左上角是整个屏幕的原点(0,0),图中标识了附件矩形的四个顶点的坐标。
def create_info_labels(self): ... self.mario_label = [] ... self.create_label(self.mario_label, 'MARIO', 75, 30) def create_label(self, label_list, string, x, y): for letter in string: label_list.append(Character(self.image_dict[letter])) self.set_label_rects(label_list, x, y) def set_label_rects(self, label_list, x, y): for i, letter in enumerate(label_list): letter.rect.x = x + ((letter.rect.width + 3) * i) letter.rect.y = y if letter.image == self.image_dict['-']: letter.rect.y += 7 letter.rect.x += 2控制类 Control是状态机类,main函数是游戏的主循环,setup_states函数设置游戏启动时运行的状态。
class Control(): def __init__(self): self.screen = pg.display.get_surface() self.done = False self.clock = pg.time.Clock() self.fps = 60 self.current_time = 0.0 self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed() self.state_dict = {} self.state_name = None self.state = None def setup_states(self, state_dict, start_state): self.state_dict = state_dict self.state_name = start_state self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name] def main(self): while not self.done: self.event_loop() self.update() pg.display.update() self.clock.tick(self.fps)event_loop函数负责监听输入(键盘输入和退出按钮),slef.keys保存键盘输入。
如果检测到当前状态结束,就调用flip_state函数进行旧状态的清理操作,并转换到下一个状态。更新函数会检测状态的完成值,调用状态的更新函数。
def update(self): self.current_time = pg.time.get_ticks() if self.state.done: self.flip_state() self.state.update(self.screen, self.keys, self.current_time) def flip_state(self): previous, self.state_name = self.state_name, self.state.next persist = self.state.cleanup() self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name] self.state.startup(self.current_time, persist) def event_loop(self): for event in pg.event.get(): if event.type == pg.QUIT: self.done = True elif event.type == pg.KEYDOWN: self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed() elif event.type == pg.KEYUP: self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed()03完整代码
有两个文件constants.py和state_demo.py,constants.py保存了所有的字符串定义和常量。 constants.py GAME_TIME_OUT表示游戏的超时时间,这边为了demo演示,设成5秒,实际是300秒。SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600 SCREEN_WIDTH = 800 SCREEN_SIZE = (SCREEN_WIDTH,SCREEN_HEIGHT) ORIGINAL_CAPTION = "Super Mario Bros" GAME_TIME_OUT = 5 ## COLORS ## # R G B BLACK = ( 0, 0, 0) SIZE_MULTIPLIER = 2.5 BRICK_SIZE_MULTIPLIER = 2.69 BACKGROUND_MULTIPLER = 2.679 GROUND_HEIGHT = SCREEN_HEIGHT - 62 #STATES FOR ENTIRE GAME MAIN_MENU = 'main menu' LOAD_SCREEN = 'load screen' TIME_OUT = 'time out' GAME_OVER = 'game over' LEVEL = 'level' #MAIN MENU CURSOR STATES PLAYER1 = '1 PLAYER GAME' PLAYER2 = '2 PLAYER GAME' #GAME INFO DICTIONARY KEYS COIN_TOTAL = 'coin total' SCORE = 'score' TOP_SCORE = 'top score' LIVES = 'lives' CURRENT_TIME = 'current time' LEVEL_NUM = 'level num' PLAYER_NAME = 'player name' PLAYER_MARIO = 'mario' PLAYER_LUIGI = 'luigi' ITEM_SHEET = 'item_objects'state_demo.py
上面讲的状态类,状态机类都放在这里。import os import pygame as pg from abc import ABC, abstractmethod import constants as c class State(): def __init__(self): self.start_time = 0.0 self.current_time = 0.0 self.done = False self.next = None self.persist = {} @abstractmethod def startup(self, current_time, persist): '''abstract method''' def cleanup(self): self.done = False return self.persist @abstractmethod def update(sefl, surface, keys, current_time): '''abstract method''' class Menu(State): def __init__(self): State.__init__(self) persist = {c.COIN_TOTAL: 0, c.SCORE: 0, c.LIVES: 3, c.TOP_SCORE: 0, c.CURRENT_TIME: 0.0, c.LEVEL_NUM: 1, c.PLAYER_NAME: c.PLAYER_MARIO} self.startup(0.0, persist) def startup(self, current_time, persist): self.next = c.LOAD_SCREEN self.persist = persist self.game_info = persist self.overhead_info = Info(self.game_info, c.MAIN_MENU) self.setup_background() self.setup_player() self.setup_cursor() def setup_background(self): self.background = GFX['level_1'] self.background_rect = self.background.get_rect() self.background = pg.transform.scale(self.background, (int(self.background_rect.width*c.BACKGROUND_MULTIPLER), int(self.background_rect.height*c.BACKGROUND_MULTIPLER))) self.viewport = SCREEN.get_rect(bottom=SCREEN_RECT.bottom) self.image_dict = {} image = get_image(GFX['title_screen'], 1, 60, 176, 88, (255, 0, 220), c.SIZE_MULTIPLIER) rect = image.get_rect() rect.x, rect.y = (170, 100) self.image_dict['GAME_NAME_BOX'] = (image, rect) def setup_player(self): self.player_list = [] player_rect_info = [(178, 32, 12, 16), (178, 128, 12, 16)] for rect in player_rect_info: image = get_image(GFX['mario_bros'], *rect, c.BLACK, 2.9) rect = image.get_rect() rect.x, rect.bottom = 110, c.GROUND_HEIGHT self.player_list.append((image, rect)) self.player_index = 0 def setup_cursor(self): self.cursor = pg.sprite.Sprite() self.cursor.image = get_image(GFX[c.ITEM_SHEET], 24, 160, 8, 8, c.BLACK, 3) rect = self.cursor.image.get_rect() rect.x, rect.y = (220, 358) self.cursor.rect = rect self.cursor.state = c.PLAYER1 def update(self, surface, keys, current_time): self.current_time = current_time self.game_info[c.CURRENT_TIME] = self.current_time self.player_image = self.player_list[self.player_index][0] self.player_rect = self.player_list[self.player_index][1] self.update_cursor(keys) self.overhead_info.update(self.game_info) surface.blit(self.background, self.viewport, self.viewport) surface.blit(self.image_dict['GAME_NAME_BOX'][0], self.image_dict['GAME_NAME_BOX'][1]) surface.blit(self.player_image, self.player_rect) surface.blit(self.cursor.image, self.cursor.rect) self.overhead_info.draw(surface) def update_cursor(self, keys): if self.cursor.state == c.PLAYER1: self.cursor.rect.y = 358 if keys[pg.K_DOWN]: self.cursor.state = c.PLAYER2 self.player_index = 1 self.game_info[c.PLAYER_NAME] = c.PLAYER_LUIGI elif self.cursor.state == c.PLAYER2: self.cursor.rect.y = 403 if keys[pg.K_UP]: self.cursor.state = c.PLAYER1 self.player_index = 0 self.game_info[c.PLAYER_NAME] = c.PLAYER_MARIO if keys[pg.K_RETURN]: self.done = True class LoadScreen(State): def __init__(self): State.__init__(self) self.time_list = [2400, 2600, 2635] def startup(self, current_time, persist): self.start_time = current_time self.persist = persist self.game_info = self.persist self.next = self.set_next_state() info_state = self.set_info_state() self.overhead_info = Info(self.game_info, info_state) def set_next_state(self): return c.LEVEL def set_info_state(self): return c.LOAD_SCREEN def update(self, surface, keys, current_time): if (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[0]: surface.fill(c.BLACK) self.overhead_info.update(self.game_info) self.overhead_info.draw(surface) elif (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[1]: surface.fill(c.BLACK) elif (current_time - self.start_time) < self.time_list[2]: surface.fill((106, 150, 252)) else: self.done = True class GameOver(LoadScreen): def __init__(self): LoadScreen.__init__(self) self.time_list = [3000, 3200, 3235] def set_next_state(self): return c.MAIN_MENU def set_info_state(self): return c.GAME_OVER class TimeOut(LoadScreen): def __init__(self): LoadScreen.__init__(self) self.time_list = [2400, 2600, 2635] def set_next_state(self): if self.persist[c.LIVES] == 0: return c.GAME_OVER else: return c.LOAD_SCREEN def set_info_state(self): return c.TIME_OUT class Level(State): def __init__(self): State.__init__(self) def startup(self, current_time, persist): self.game_info = persist self.persist = self.game_info self.player = None self.overhead_info = Info(self.game_info, c.LEVEL) self.setup_background() def setup_background(self): self.background = GFX['level_1'] self.bg_rect = self.background.get_rect() self.background = pg.transform.scale(self.background, (int(self.bg_rect.width*c.BACKGROUND_MULTIPLER), int(self.bg_rect.height*c.BACKGROUND_MULTIPLER))) self.bg_rect = self.background.get_rect() self.level = pg.Surface((self.bg_rect.w, self.bg_rect.h)).convert() self.viewport = SCREEN.get_rect(bottom=self.bg_rect.bottom) def update(self, surface, keys, current_time): self.game_info[c.CURRENT_TIME] = self.current_time = current_time self.overhead_info.update(self.game_info, self.player) if self.overhead_info.time <= 0: self.update_game_info() self.done = True self.draw(surface) def update_game_info(self): self.persist[c.LIVES] -= 1 if self.persist[c.LIVES] == 0: self.next = c.GAME_OVER elif self.overhead_info.time == 0: self.next = c.TIME_OUT else: self.next = c.LOAD_SCREEN def draw(self, surface): self.level.blit(self.background, self.viewport, self.viewport) surface.blit(self.level, (0,0), self.viewport) self.overhead_info.draw(surface) class Character(pg.sprite.Sprite): def __init__(self, image): pg.sprite.Sprite.__init__(self) self.image = image self.rect = self.image.get_rect() class Info(): def __init__(self, game_info, state): self.coin_total = game_info[c.COIN_TOTAL] self.total_lives = game_info[c.LIVES] self.state = state self.game_info = game_info self.create_font_image_dict() self.create_info_labels() self.create_state_labels() self.flashing_coin = FlashCoin(280, 53) def create_font_image_dict(self): self.image_dict = {} image_list = [] image_rect_list = [# 0 - 9 (3, 230, 7, 7), (12, 230, 7, 7), (19, 230, 7, 7), (27, 230, 7, 7), (35, 230, 7, 7), (43, 230, 7, 7), (51, 230, 7, 7), (59, 230, 7, 7), (67, 230, 7, 7), (75, 230, 7, 7), # A - Z (83, 230, 7, 7), (91, 230, 7, 7), (99, 230, 7, 7), (107, 230, 7, 7), (115, 230, 7, 7), (123, 230, 7, 7), (3, 238, 7, 7), (11, 238, 7, 7), (20, 238, 7, 7), (27, 238, 7, 7), (35, 238, 7, 7), (44, 238, 7, 7), (51, 238, 7, 7), (59, 238, 7, 7), (67, 238, 7, 7), (75, 238, 7, 7), (83, 238, 7, 7), (91, 238, 7, 7), (99, 238, 7, 7), (108, 238, 7, 7), (115, 238, 7, 7), (123, 238, 7, 7), (3, 246, 7, 7), (11, 246, 7, 7), (20, 246, 7, 7), (27, 246, 7, 7), (48, 246, 7, 7), # -* (68, 249, 6, 2), (75, 247, 6, 6)] character_string = '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ -*' for character, image_rect in zip(character_string, image_rect_list): self.image_dict[character] = get_image(GFX['text_images'], *image_rect, (92, 148, 252), 2.9) def create_info_labels(self): self.score_text = [] self.coin_count_text = [] self.mario_label = [] self.world_label = [] self.time_label = [] self.stage_label = [] self.create_label(self.score_text, '000000', 75, 55) self.create_label(self.coin_count_text, '*00', 300, 55) self.create_label(self.mario_label, 'MARIO', 75, 30) self.create_label(self.world_label, 'WORLD', 450, 30) self.create_label(self.time_label, 'TIME', 625, 30) self.create_label(self.stage_label, '1-1', 472, 55) self.info_labels = [self.score_text, self.coin_count_text, self.mario_label, self.world_label, self.time_label, self.stage_label] def create_state_labels(self): if self.state == c.MAIN_MENU: self.create_main_menu_labels() elif self.state == c.LOAD_SCREEN: self.create_player_image() self.create_load_screen_labels() elif self.state == c.LEVEL: self.create_level_labels() elif self.state == c.GAME_OVER: self.create_game_over_labels() elif self.state == c.TIME_OUT: self.create_time_out_labels() def create_player_image(self): self.life_times_image = get_image(GFX['text_images'], 75, 247, 6, 6, (92, 148, 252), 2.9) self.life_times_rect = self.life_times_image.get_rect(center=(378, 295)) self.life_total_label = [] self.create_label(self.life_total_label, str(self.total_lives), 450, 285) if self.game_info[c.PLAYER_NAME] == c.PLAYER_MARIO: rect = (178, 32, 12, 16) else: rect = (178, 128, 12, 16) self.player_image = get_image(GFX['mario_bros'], *rect, (92, 148, 252), 2.9) self.player_rect = self.player_image.get_rect(center=(320, 290)) def create_main_menu_labels(self): mario_game = [] luigi_game = [] top = [] top_score = [] self.create_label(mario_game, c.PLAYER1, 272, 360) self.create_label(luigi_game, c.PLAYER2, 272, 405) self.create_label(top, 'TOP - ', 290, 465) self.create_label(top_score, '000000', 400, 465) self.state_labels = [mario_game, luigi_game, top, top_score, *self.info_labels] def create_load_screen_labels(self): world_label = [] self.stage_label2 = [] self.create_label(world_label, 'WORLD', 280, 200) self.create_label(self.stage_label2, '1-1', 430, 200) self.state_labels = [world_label, self.stage_label2, *self.info_labels, self.life_total_label] def create_level_labels(self): self.time = c.GAME_TIME_OUT self.current_time = 0 self.clock_time_label = [] self.create_label(self.clock_time_label, str(self.time), 645, 55) self.state_labels = [*self.info_labels, self.clock_time_label] def create_game_over_labels(self): game_label = [] over_label = [] self.create_label(game_label, 'GAME', 280, 300) self.create_label(over_label, 'OVER', 400, 300) self.state_labels = [game_label, over_label, *self.info_labels] def create_time_out_labels(self): timeout_label = [] self.create_label(timeout_label, 'TIME OUT', 290, 310) self.state_labels = [timeout_label, *self.info_labels] def create_label(self, label_list, string, x, y): for letter in string: label_list.append(Character(self.image_dict[letter])) self.set_label_rects(label_list, x, y) def set_label_rects(self, label_list, x, y): for i, letter in enumerate(label_list): letter.rect.x = x + ((letter.rect.width + 3) * i) letter.rect.y = y if letter.image == self.image_dict['-']: letter.rect.y += 7 letter.rect.x += 2 def update(self, level_info, level=None): self.level = level self.handle_level_state(level_info) def handle_level_state(self, level_info): self.score = level_info[c.SCORE] self.update_text(self.score_text, self.score) self.update_text(self.coin_count_text, level_info[c.COIN_TOTAL]) self.update_text(self.stage_label, level_info[c.LEVEL_NUM]) self.flashing_coin.update(level_info[c.CURRENT_TIME]) if self.state == c.LOAD_SCREEN: self.update_text(self.stage_label2, level_info[c.LEVEL_NUM]) if self.state == c.LEVEL: if (level_info[c.CURRENT_TIME] - self.current_time) > 1000: self.current_time = level_info[c.CURRENT_TIME] self.time -= 1 self.update_text(self.clock_time_label, self.time, True) def update_text(self, text, score, reset=False): if reset and len(text) > len(str(score)): text.remove(text[0]) index = len(text) - 1 for digit in reversed(str(score)): rect = text[index].rect text[index] = Character(self.image_dict[digit]) text[index].rect = rect index -= 1 def draw(self, surface): self.draw_info(surface, self.state_labels) if self.state == c.LOAD_SCREEN: surface.blit(self.player_image, self.player_rect) surface.blit(self.life_times_image, self.life_times_rect) surface.blit(self.flashing_coin.image, self.flashing_coin.rect) def draw_info(self, surface, label_list): for label in label_list: for letter in label: surface.blit(letter.image, letter.rect) class FlashCoin(pg.sprite.Sprite): def __init__(self, x, y): pg.sprite.Sprite.__init__(self) self.frame_index = 0 self.frames = [] self.load_frames() self.image = self.frames[self.frame_index] self.rect = self.image.get_rect() self.rect.x = x self.rect.y = y self.animation_timer = 0 def load_frames(self): sheet = GFX[c.ITEM_SHEET] frame_rect_list = [(1, 160, 5, 8), (9, 160, 5, 8), (17, 160, 5, 8), (9, 160, 5, 8)] for frame_rect in frame_rect_list: self.frames.append(get_image(sheet, *frame_rect, c.BLACK, c.BRICK_SIZE_MULTIPLIER)) def update(self, current_time): time_list = [375, 125, 125, 125] if self.animation_timer == 0: self.animation_timer = current_time elif (current_time - self.animation_timer) > time_list[self.frame_index]: self.frame_index += 1 if self.frame_index == 4: self.frame_index = 0 self.animation_timer = current_time self.image = self.frames[self.frame_index] class Control(): def __init__(self): self.screen = pg.display.get_surface() self.done = False self.clock = pg.time.Clock() self.fps = 60 self.current_time = 0.0 self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed() self.state_dict = {} self.state_name = None self.state = None def setup_states(self, state_dict, start_state): self.state_dict = state_dict self.state_name = start_state self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name] def update(self): self.current_time = pg.time.get_ticks() if self.state.done: self.flip_state() self.state.update(self.screen, self.keys, self.current_time) def flip_state(self): previous, self.state_name = self.state_name, self.state.next persist = self.state.cleanup() self.state = self.state_dict[self.state_name] self.state.startup(self.current_time, persist) def event_loop(self): for event in pg.event.get(): if event.type == pg.QUIT: self.done = True elif event.type == pg.KEYDOWN: self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed() elif event.type == pg.KEYUP: self.keys = pg.key.get_pressed() def main(self): while not self.done: self.event_loop() self.update() pg.display.update() self.clock.tick(self.fps) def get_image(sheet, x, y, width, height, colorkey, scale): image = pg.Surface([width, height]) rect = image.get_rect() image.blit(sheet, (0, 0), (x, y, width, height)) image.set_colorkey(colorkey) image = pg.transform.scale(image, (int(rect.width*scale), int(rect.height*scale))) return image def load_all_gfx(directory, colorkey=(255,0,255), accept=('.png', '.jpg', '.bmp', '.gif')): graphics = {} for pic in os.listdir(directory): name, ext = os.path.splitext(pic) if ext.lower() in accept: img = pg.image.load(os.path.join(directory, pic)) if img.get_alpha(): img = img.convert_alpha() else: img = img.convert() img.set_colorkey(colorkey) graphics[name] = img return graphics # pygame related initial code pg.init() pg.event.set_allowed([pg.KEYDOWN, pg.KEYUP, pg.QUIT]) pg.display.set_caption(c.ORIGINAL_CAPTION) SCREEN = pg.display.set_mode(c.SCREEN_SIZE) SCREEN_RECT = SCREEN.get_rect() GFX = load_all_gfx(os.path.join("resources","graphics")) if __name__=='__main__': game = Control() state_dict = {c.MAIN_MENU: Menu(), c.LOAD_SCREEN: LoadScreen(), c.LEVEL: Level(), c.GAME_OVER: GameOver(), c.TIME_OUT: TimeOut()} game.setup_states(state_dict, c.MAIN_MENU) game.main()用到的图片
图片文件名要保存为对应的,不然代码中会找到,并且保存到state_demo.py所在目录下的resources \ graphics子目录中。如果能上github,可以直接下载resources \ graphics目录中的图片。
1,item_objects.png

2,level_1.png

3,mario_bros.png
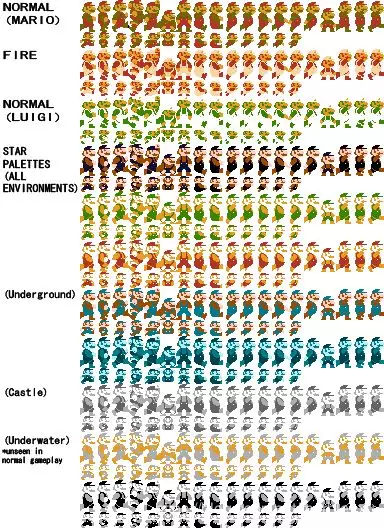
4,text_images.png
5,tile_set.png

6,title_screen.png

编译环境:python3.7 + pygame1.9。
2019-12-25 10:11:52赞同 展开评论 打赏
版权声明:本文内容由阿里云实名注册用户自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,阿里云开发者社区不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。具体规则请查看《阿里云开发者社区用户服务协议》和《阿里云开发者社区知识产权保护指引》。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,填写侵权投诉表单进行举报,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。





