Suppose you have a large number of unit test cases and you don’t want them to be executed all at the same time during Maven build. You can simply achieve it via annotation @Category.
(1) Create empty class FastTests and SlowTests.
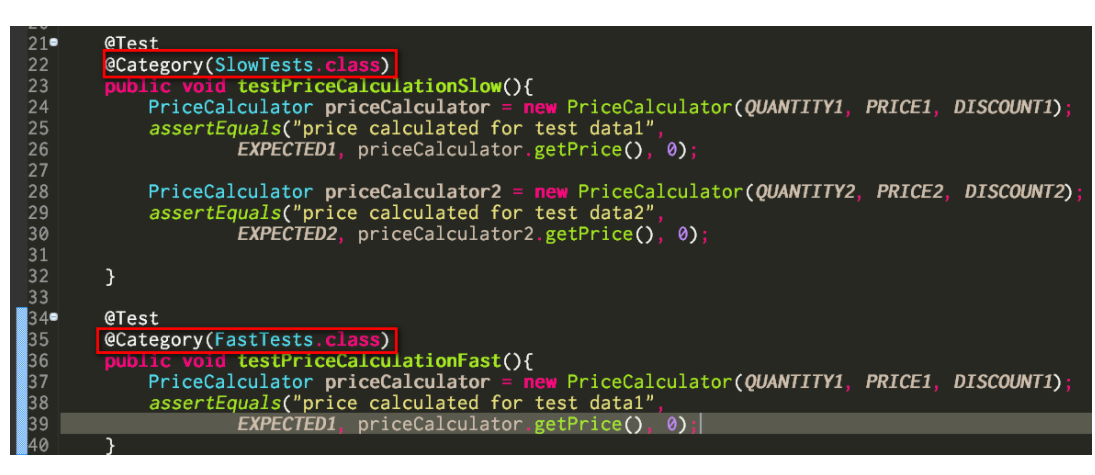
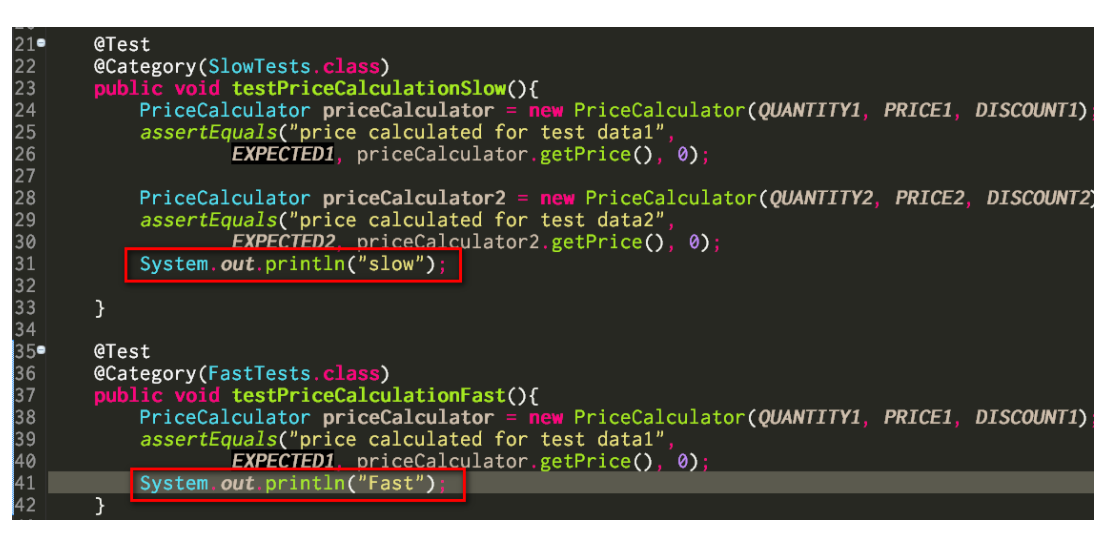
(2) In your test case class, categorize your test method using @Category annotation:
(3) Append the following code to your pom.xml:
<profiles> <profile> <id>SlowTests</id> <properties> <testcase.groups>com.sap.SlowTests</testcase.groups> </properties> </profile> <profile> <id>FastTests</id> <properties> <testcase.groups>com.sap.FastTests</testcase.groups> </properties> </profile> </profiles> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.13</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.maven.surefire</groupId> <artifactId>surefire-junit47</artifactId> <version>2.13</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <configuration> <groups>${testcase.groups}</groups> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
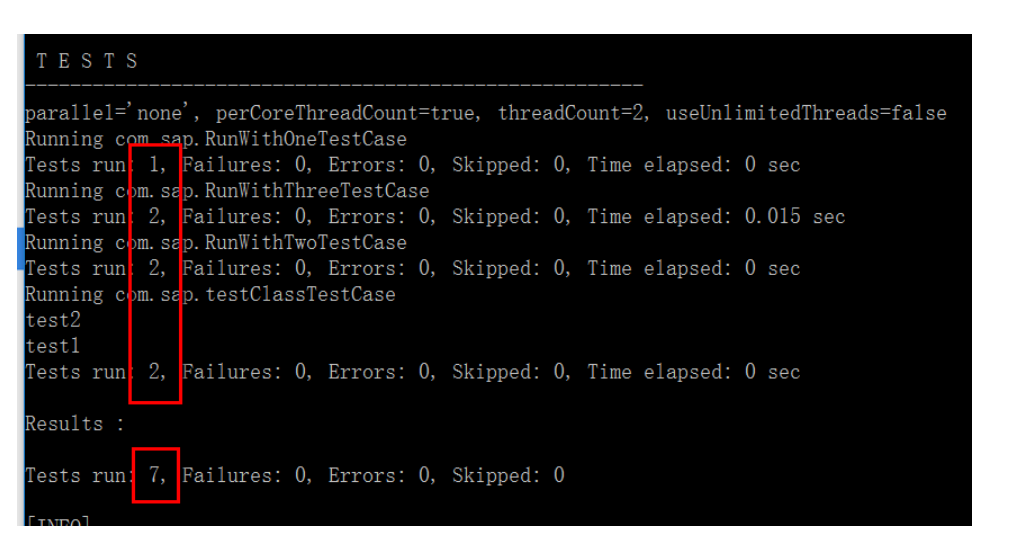
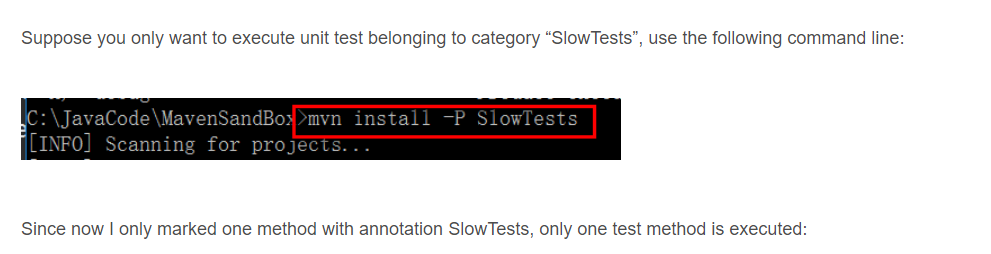
(4) In my project, by default all 7 test methods will be executed during Maven build:If you would like to execute all unit tests EXCEPT @SlowTests, simply add another profile in pom.xml:
<profile> <id>NonSlowTests</id> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <excludedGroups>com.sap.SlowTests</excludedGroups> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </profile>
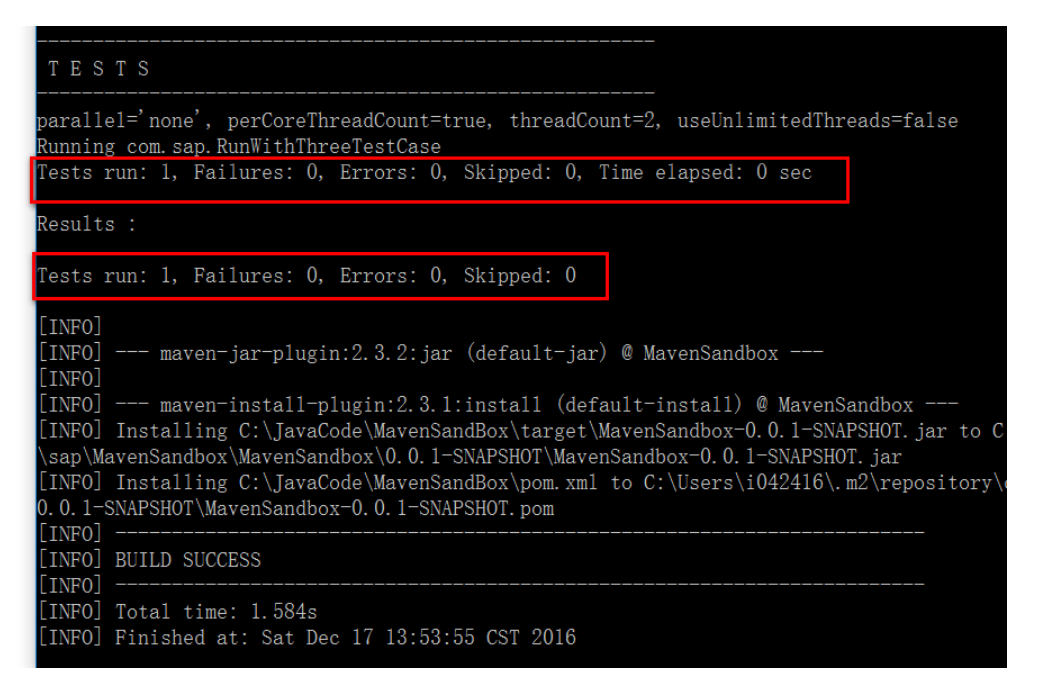
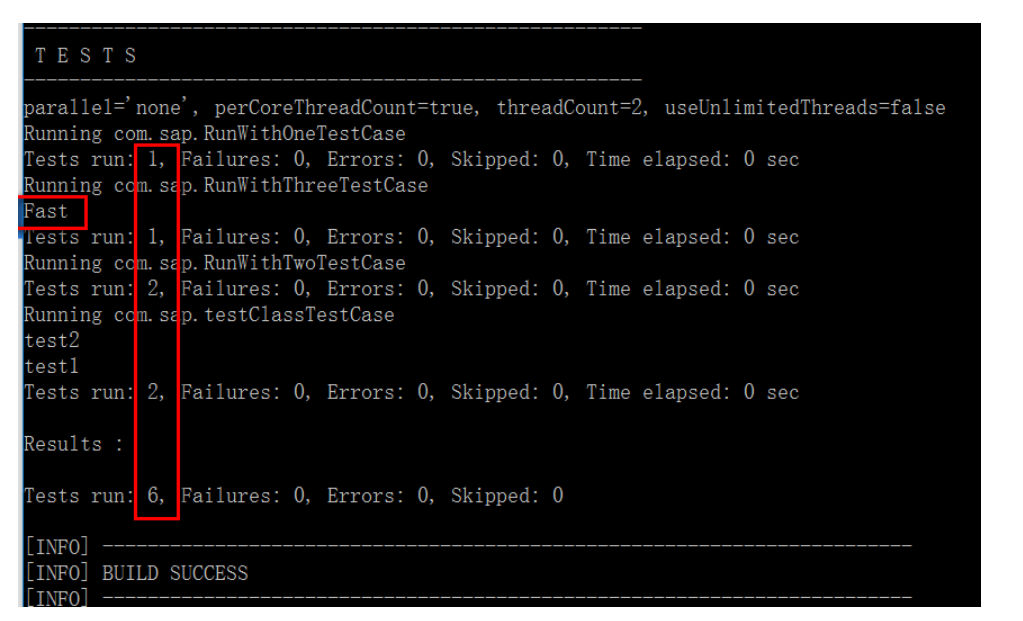
Before test, in order to prove that Slow method is NOT really executed, I add a system.out.println in each method:Use command line: mvn test -P NonSlowTests
From console output, I can ensure that the method with @Category(SlowTests.class) is NOT executed at all.