Java容器类
Java容器类是java提供的工具包,包含了常用的数据结构:集合、链表、队列、栈、数组、映射等。
Java容器主要可以划分为4个部分:List列表、Set集合、Map映射、工具类(Iterator迭代器、Enumeration枚举类、Arrays和Collections)
【文章纯干货 请仔细阅读哦!】
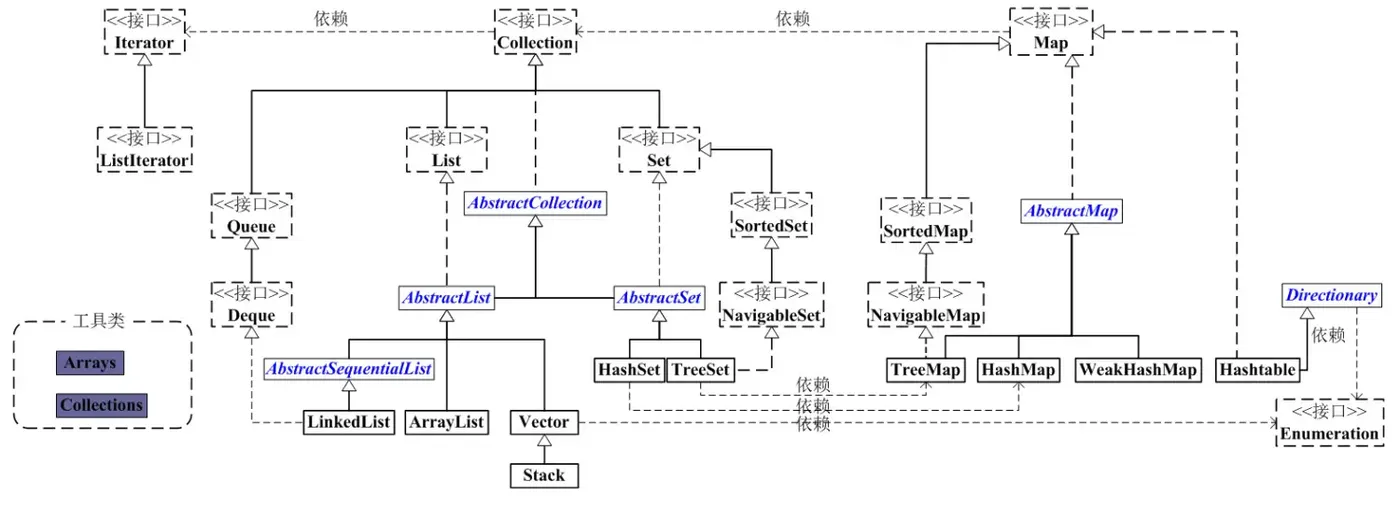
通过上图,可以把握两个基本主体,即Collection和Map。
Colletcion是一个接口,是高度抽象出来的集合,它包含了集合的基本操作和属性。Collection包含了List和Set两大分支。
List是一个有序的队列,每一个元素都有它的索引。第一个元素的索引值是0。List的实现类有LinkedList, ArrayList, Vector, Stack。
Set是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。 Set的实现类有HastSet和TreeSet。HashSet依赖于HashMap,它实际上是通过HashMap实现的;TreeSet依赖于TreeMap,它实际上是通过TreeMap实现的。
Map是一个映射接口,即key-value键值对。Map中的每一个元素包含“一个key”和“key对应的value”。 AbstractMap是一个抽象类,它实现了Map中大部分的API。而HashMap,TreeMap,WeakHashMap都是继承AbstractMap。Hashtable虽然继承Dictionary,但是实现的Map接口。
Iterator是遍历集合的工具,即我们通常通过Iterator迭代器来遍历集合。我们说Collection依赖于Iterator,是因为Collection的实现类都要实现iterator()函数,返回一个Iterator对象。ListIterator是专门为遍历List而存在的。
Arrays和Collections是操作数组、集合的两个工具类。
Collection接口
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {}
它是一个接口,是高度抽象出来的集合,它包含了集合的基本操作:添加、删除、清空、遍历(读取)、是否为空、获取大小、是否保护某元素等等。
在Java中所有实现了Collection接口的类都必须提供两套标准的构造函数,一个是无参,用于创建一个空的Collection,一个是带有Collection参数的有参构造函数,用于创建一个新的Collection,这个新的Collection与传入进来的Collection具备相同的元素。
例如ArrayList:
public ArrayList() {
throw new RuntimeException("Stub!");
}
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stub!");
}
List接口
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {} List是一个继承于Collection的接口,List是集合的一种。List是有序的队列,List中每一个元素都有一个索引;第一个元素索引值是0,往后就依次+1,List中允许有重复的元素。 既然List是继承于Collection接口,它自然就包含了Collection中的全部函数接口;由于List是有序队列,它也额外的有自己的API接口。主要有“添加、删除、获取、修改指定位置的元素”、“获取List中的子队列”等。
// Collection的API
abstract boolean add(E object)
abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection)
abstract void clear()
abstract boolean contains(Object object)
abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection)
abstract boolean equals(Object object)
abstract int hashCode()
abstract boolean isEmpty()
abstract Iterator<E> iterator()
abstract boolean remove(Object object)
abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection)
abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection)
abstract int size()
abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array)
abstract Object[] toArray()
// 相比与Collection,List新增的API:
abstract void add(int location, E object)
abstract boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection)
abstract E get(int location)
abstract int indexOf(Object object)
abstract int lastIndexOf(Object object)
abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location)
abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator()
abstract E remove(int location)
abstract E set(int location, E object)
abstract List<E> subList(int start, int end)
实现List接口的集合主要有:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector、Stack。
ArrayList
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>,
RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable {}
ArrayList 是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组。与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长。它继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
RandmoAccess为List提供快速访问功能。在ArrayList中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象,这就是快速随机访问。
ArrayList中的操作不是线程安全的,所以为了防止意外的非同步访问,最好在创建时声明:List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));
ArrayList有七个字段加一个定义在AbstractList的modCount:
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// Android-note: Also accessed from java.util.Collections
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
protected transient int modCount = 0;
ArrayList的默认容量DEFAULT_CAPACITY为10,EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 和 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是两个常量。
// 默认构造函数
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
// initialCapacity是ArrayList的默认容量大小。当由于增加数据导致容量不足时,容量会添加上一次容量大小的一半。
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
}
}
// 创建一个包含collection的ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
当使用有参构造函数,并且initialCapacity为0或者Colletion中没有元素的时候,返回的就是EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。当使用默认构造函数publicArrayList(),返回DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。 这两个数组都是空的并不会存放值。当第一次往ArrayList添加元素的时候,其实是将元素存放到elementData中,所以真正用来存放元素的是elementData。
add方法:
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); //判断索引位置是否正确
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//将ArrayList容器从index开始的所有元素向右移动到index+numNew的位置,从而腾出numNew长度的空间放c
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
add(E e)将元素直接添加到列表的尾部。另外3种通过System.arraycopy() 将数组进行拷贝。
add(int index, E element)通过将index的位置空出来,进行数组数据的右移,这是非常麻烦和耗时的,所以如果指定的数据集合需要进行大量插入(中间插入)操作,需要考虑性能的消耗。
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)按照指定 collection 的迭代器返回的元素顺序,将该 collection 中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部。
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)从指定的位置开始,将指定 collection 中的所有元素插入到此列表中。
remove方法:
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//向左移的位数,下标从0开始,需要再多减1
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//置空最后一个元素
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
//fastRemove()方法用于移除指定位置的元素,和remove方法类似,区别是void类型
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,numMoved);
// clear to let GC do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
size = newSize;
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
//Checks that the specified object reference is not null
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
//false是移除相同元素,方法retainAll中置为true,是保留相同元素
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++)
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r);
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
扩容
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
? 0: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
ArrayList每次新增元素时都会需要进行容量检测判断,若新增元素后元素的个数会超过ArrayList的容量,就会进行扩容操作来满足新增元素的需求。所以当我们清楚知道业务数据量或者需要插入大量元素前,可以使用ensureCapacity来手动增加ArrayList实例的容量,以减少递增式再分配的数量。
迭代效率
public static void loopOfFor(List<Integer> list){
int value;
int size = list.size();
// 基本的for
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
value = list.get(i);
}
}
/**
* 使用forecah方法遍历数组
* @param list
*/
public static void loopOfForeach(List<Integer> list){
int value;
// foreach
for (Integer integer : list)
{
value = integer;
}
}
/**
* 通过迭代器方式遍历数组
* @param list
*/
public static void loopOfIterator(List<Integer> list){
int value;
// iterator
for (Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();)
{
value = iterator.next();
}
}
在遍历ArrayList中,效率最高的是loopOfFor,loopOfForeach和loopOfIterator之间关系不明确,但在增大运行次数时,loopOfIterator效率高于loopOfForeach。
LinkedList
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>,
Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable {}
LinkedList继承于AbstractSequentialList,实现了List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
AbstractSequentialList继承AbstractList,在功能上,最大限度地减少了实现受“连续访问”数据存储所需的工作。
简单的说是你的列表需要快速的添加删除数据等,用此抽象类,若是需要快速随机的访问数据等用AbstractList抽象类。
通过代价较低在List中间进行插入和移除,提供了优化的顺序访问,但是在随机访问方面相对较慢。
同ArrayList一样,LinkedList中的操作不是线程安全的,所以为了防止意外的非同步访问,最好在创建时声明: List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));
LinkedList实现了一个双向列表,由first字段和last字段指向列表的头部和尾部。列表的每个节点是一个Node对象。

