一.概述:
条件变量是线程同步的一种机制,它是通过一个条件,当条件满足时,唤醒一个线程,但条件不满足时,挂起该线程。由于同步是伴随着互斥的,所以条件变量一般都伴随着互斥锁。
二.相关函数:
(1).cond:pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER
cond是一个全局变量,和mutex一样。
(2).pthread_cond_init函数:int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr)
attr参数:用于初始化cond,NULL表示缺省属性。weiNULL时和声明一个全局的cond一样。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
PS:restrict,C语言中的一种类型限定符(TypeQualifiers),用于告诉编译器,对象已经被指针所引用,不能通过除该指针外所有其他直接或间接的方式修改该对象的内容。
(3).phtread_cond_destroy函数:int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
函数功能:销毁cond。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
(4).pthread_cond_timedwait函数:int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespaec *restrict abstime)
函数功能:将当前线程挂起,直到有信号将其唤醒或出现错误返回。
sbstime参数:等待超时时间,如果到达了abstime所指定的 时刻仍然没有别的线程来唤醒当前线程,就返回ETIMEDOUT。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
(5).pthread_cond_wait函数:int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex)
函数功能:将当前线程挂起,直到有信号将其唤醒或出现错误返回。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
(6).pthread_cond_signal函数:int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond)
函数功能:发出一个信号给用cond等待挂起的线程,使之进入就绪态。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
(7).pthread_cond_broadcastsignal函数:int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond)
函数功能:发出一个信号给所有用cond等待挂起的线程,使它们都进入就绪态。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。
三.相关代码:(生产者与消费者模型)(必须是生产者先生产,消费者再消费的顺序)
在没有加互斥锁和条件变量之前:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<malloc.h>
4 #include<pthread.h>
5
6 static pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
7 static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
8
9 typedef struct node
10 {
11 int _data;
12 struct node* _next;
13 }node_t, *node_p, **node_pp;
14
15 node_p head = NULL;
16 int g_data; //用于表示消费的数据
17
18 node_p buy_node(int data)
19 {
20 node_p tem = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
21 if(tem)
22 {
23 tem->_data = data;
24 tem->_next = NULL;
25 return tem;
26 }
27 return NULL;
28 }
29
30
31 void init_list(node_pp list)
32 {
33 *list = buy_node(0);
34 }
35
36 void head_push(node_p list, int data)
37 {
38 node_p tem = buy_node(data);
39 tem->_next = list->_next;
40 list->_next = tem;
41 }
42
43 int tail_pop(node_p list)
44 {
45 if(list->_next == NULL)
46 {
47 g_data = -1;
48 return -1;
49 }
50
51 node_p tem = list;
52 node_p del = NULL;
53 while(tem->_next != NULL)
54 {
55 del = tem->_next;
56 if(tem->_next->_next == NULL)
57 {
58 tem->_next = NULL;
59 }
60 else
61 {
62 tem = tem->_next;
63 }
64 }
65
66 g_data = del->_data;
67 free(del);
68 return 0;
69 }
70
71 void show_list(node_p list)
72 {
73 node_p tem = list;
74 while(tem != NULL)
75 {
76 printf("%d ",tem->_data);
77 tem = tem->_next;
78 }
79 printf("\n");
80 }
81
82 void* product(void* ptr)
83 {
84 int i = 1;
85 while(1)
86 {
87 head_push(head, i);
88 sleep(1);
89 printf("product data -> %d\n",i);
90 i++;
91 }
92 }
93
94 void* consumer(void* ptr)
95 {
96 while(1)
97 {
98 tail_pop(head);
99 sleep(1);
100 printf("consumer data -> %d\n", g_data);
101 }
102 }
103
104
105
106
107 int main()
108 {
109 init_list(&head);
110
111
112 pthread_t tid1, tid2;
113 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, product, NULL);
114 pthread_create(&tid2,NULL, consumer, NULL);
115 pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
116 pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
117
118 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
119 pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
120
121
122 // int i = 1;
123 // while(i <= 5)
124 // {
125 // head_push(head, i++);
126 // show_list(head);
127 // }
128 // printf("-------------------------------------\n");
129 // while(i >= 1)
130 // {
131 // tail_pop(head);
132 // show_list(head);
133 // i--;
134 // }
135
136 return 0;
137 }
138
139
140
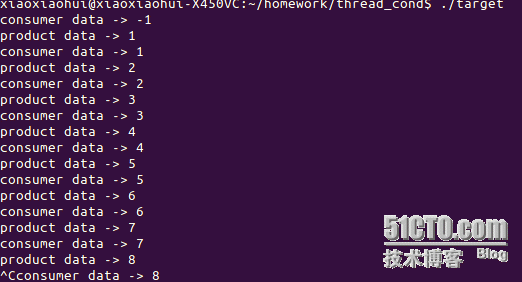
执行结果:
PS:可以看到结果为消费者先消费,而不是生产者先生产。
用互斥锁和条件变量:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<malloc.h>
4 #include<pthread.h>
5
6 static pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
7 static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
8
9 typedef struct node
10 {
11 int _data;
12 struct node* _next;
13 }node_t, *node_p, **node_pp;
14
15 node_p head = NULL; //头指针
16 int g_data; //用于表示消费的数据
17
18 node_p buy_node(int data)
19 {
20 node_p tem = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
21
if(tem)
22 {
23 tem->_data = data;
24 tem->_next = NULL;
25 return tem;
26 }
27 return NULL;
28 }
29
30
31 void init_list(node_pp list)
32 {
33 *list = buy_node(0);
34 }
35
36 void head_push(node_p list, int data)
37 {
38 node_p tem = buy_node(data);
39 tem->_next = list->_next;
40 list->_next = tem;
41 }
42
43 int tail_pop(node_p list)
44 {
45 if(list->_next == NULL)
46
{
47 g_data = -1;
48 return -1;
49 }
50
51 node_p tem = list;
52 node_p del = NULL;
53 while(tem->_next != NULL)
54 {
55 del = tem->_next;
56 if(tem->_next->_next == NULL)
57 {
58 tem->_next = NULL;
59 }
60 else
61 {
62 tem = tem->_next;
63 }
64 }
65
66 g_data = del->_data;
67 free(del);
68 return 0;
69 }
70
71 void show_list(node_p list)
72 {
73 node_p tem = list;
74 while(tem != NULL)
75 {
76 printf("%d ",tem->_data);
77 tem = tem->_next;
78 }
79 printf("\n");
80 }
81
82 void* product(void* ptr)
83 {
84 int i = 1;
85 while(1)
86 {
87 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
88 head_push(head, i);
89 sleep(1);
90 i++;
91 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
92 printf("product data -> %d\n",i);
93 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); //生产一个就可以唤醒消费者了
94 }
95 }
96
97 void* consumer(void* ptr)
98 {
99 while(1)
100 {
101 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
102 while(head->_next == NULL) //注意要用while为不是if 因为可能会出现一个错误信号把
103 { //该线程唤醒,但链表内并没有数据的可能。
104 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &lock);
105 }
106 tail_pop(head);
107 sleep(1);
108 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
109 printf("consumer data -> %d\n", g_data);
110 }
111 }
112
113
114 int main()
115 {
116 init_list(&head);
117
118
119 pthread_t tid1, tid2;
120 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, product, NULL);
121 pthread_create(&tid2,NULL, consumer, NULL);
122 pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
123 pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
124
125 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
126 pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
127
128
129// int i = 1;
130 // while(i <= 5)
131 // {
132 // head_push(head, i++);
133 // show_list(head);
134 // }
135 // printf("-------------------------------------\n");
136 // while(i >= 1)
137 // {
138 // tail_pop(head);
139 // show_list(head);
140 // i--;
141 // }
142
143 return 0;
144 }
145
146
147
147,0-1 底端
129,1 82%
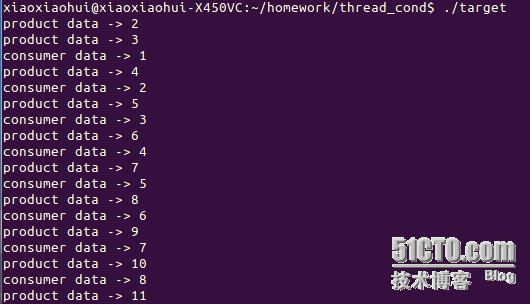
执行结果: