1. 服务注册发现的核心概念
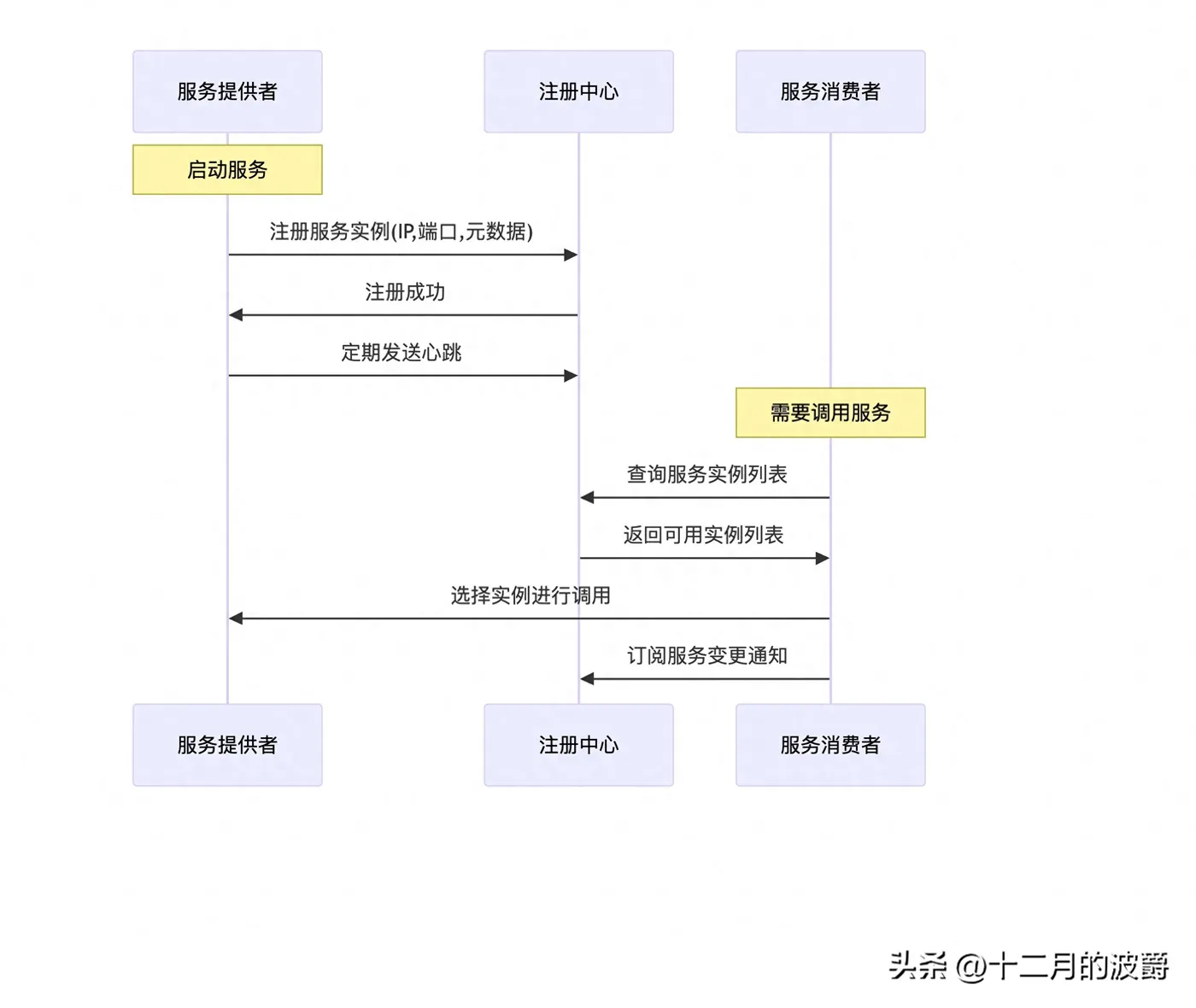
1.1 什么是服务注册与发现?
服务注册与发现是微服务架构中的核心基础设施,它解决了分布式环境中服务如何找到彼此并建立通信的问题。
// 服务注册发现的现实比喻 public class ServiceDiscoveryAnalogy { /** * 电话通讯录 vs 服务注册中心 */ public class PhoneBookComparison { // 保存联系人信息 → 服务注册 // 查找联系人电话 → 服务发现 // 联系人搬家更新 → 健康检查 // 电话簿出版商 → 注册中心 } /** * 没有服务发现的痛苦 */ public class WithoutServiceDiscovery { // 硬编码服务地址 @Value("${order.service.url:http://localhost:8080}") private String orderServiceUrl; // 问题: // 1. 服务地址变更需要重新部署 // 2. 负载均衡需要手动实现 // 3. 服务故障无法自动感知 // 4. 扩容缩容困难 } }
1.2 服务注册发现的基本原理
2. 主流注册中心技术选型
2.1 注册中心对比分析
特性 |
Nacos |
Eureka |
Consul |
Zookeeper |
一致性协议 |
AP/CP 可切换 |
AP |
CP |
CP |
健康检查 |
TCP/HTTP/MYSQL |
心跳 |
TCP/HTTP/gRPC |
心跳 |
负载均衡 |
权重/元数据 |
轮询 |
内置 |
需要客户端实现 |
配置管理 |
支持 |
不支持 |
支持 |
支持 |
雪崩保护 |
有 |
有 |
无 |
无 |
易用性 |
高 |
高 |
中 |
中 |
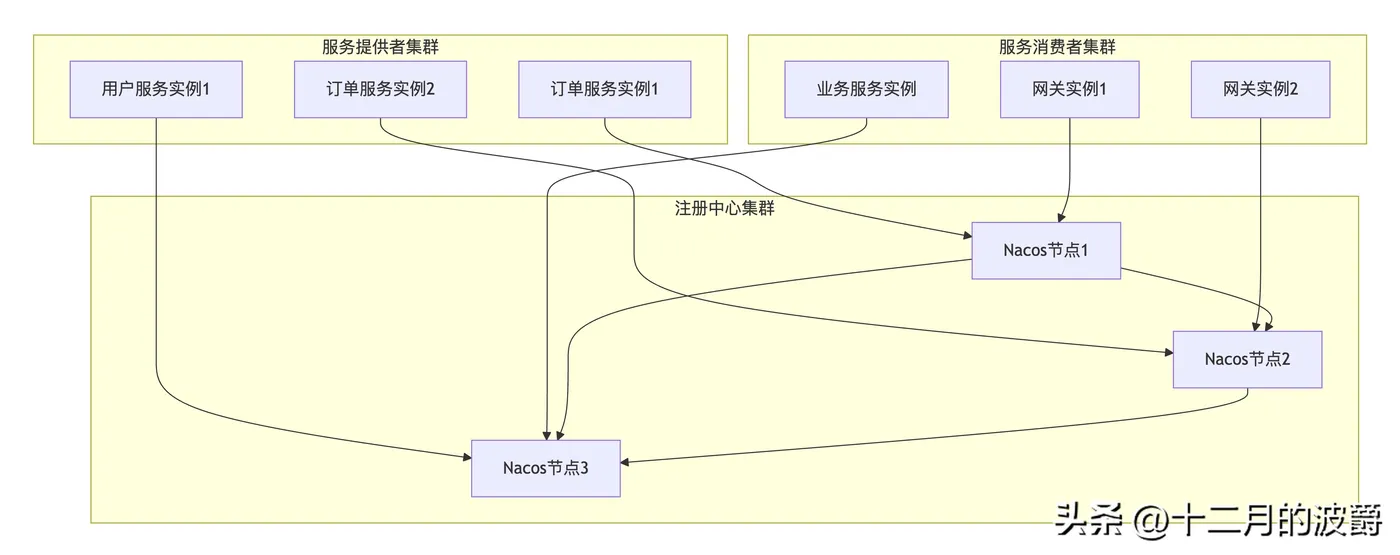
2.2 注册中心部署架构
3. Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos 实战
3.1 环境准备与依赖配置
<!-- pom.xml 依赖配置 --> <dependencies> <!-- Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Discovery --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> <version>2022.0.0.0</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring Cloud LoadBalancer --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Web 支持 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Actuator 健康检查 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
3.2 服务提供者注册实现
// 订单服务 - 服务提供者示例 @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient // 开启服务注册发现 public class OrderServiceApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args); } /** * 配置RestTemplate支持服务发现 */ @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } } // 应用配置文件 // application.yml spring: application: name: order-service # 服务名称 cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: 192.168.1.100:8848 # Nacos服务器地址 namespace: dev-${user.name} # 命名空间隔离 group: DEFAULT_GROUP # 分组 cluster-name: BEIJING # 集群名称 weight: 1.0 # 权重 metadata: version: 1.0.0 environment: production # 心跳配置 heart-beat-interval: 5000 # 心跳间隔(ms) heart-beat-timeout: 15000 # 心跳超时(ms) ip-delete-timeout: 30000 # 实例删除超时(ms) server: port: 8081 servlet: context-path: /order # 健康检查端点配置 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: health,info endpoint: health: show-details: always
// 订单服务业务实现 @RestController @RequestMapping("/orders") @Slf4j public class OrderController { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; /** * 创建订单接口 */ @PostMapping public ResponseEntity<Order> createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request) { log.info("创建订单请求: {}", request); Order order = orderService.createOrder(request); return ResponseEntity.ok(order); } /** * 查询订单接口 */ @GetMapping("/{orderId}") public ResponseEntity<Order> getOrder(@PathVariable String orderId) { log.info("查询订单: {}", orderId); Order order = orderService.getOrder(orderId); return ResponseEntity.ok(order); } /** * 健康检查接口 */ @GetMapping("/health") public ResponseEntity<String> health() { return ResponseEntity.ok("Order Service is healthy"); } } // 订单服务实现 @Service @Slf4j public class OrderService { // 模拟数据存储 private final Map<String, Order> orderStore = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public Order createOrder(OrderRequest request) { String orderId = generateOrderId(); Order order = Order.builder() .id(orderId) .userId(request.getUserId()) .productId(request.getProductId()) .quantity(request.getQuantity()) .amount(request.getAmount()) .status(OrderStatus.CREATED) .createTime(new Date()) .build(); orderStore.put(orderId, order); log.info("订单创建成功: {}", orderId); return order; } public Order getOrder(String orderId) { Order order = orderStore.get(orderId); if (order == null) { throw new OrderNotFoundException("订单不存在: " + orderId); } return order; } private String generateOrderId() { return "ORD" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 9999); } }
3.3 服务消费者发现实现
// API网关服务 - 服务消费者示例 @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class ApiGatewayApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ApiGatewayApplication.class, args); } /** * 配置支持负载均衡的RestTemplate */ @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate loadBalancedRestTemplate() { return new RestTemplateBuilder() .setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5)) .setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10)) .build(); } /** * 自定义负载均衡策略 */ @Bean public ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> randomLoadBalancer( Environment environment, LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory) { String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME); return new RandomLoadBalancer( loadBalancerClientFactory.getLazyProvider(name, ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class), name ); } } // 网关配置文件 // application.yml spring: application: name: api-gateway cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: 192.168.1.100:8848 namespace: dev-${user.name} group: DEFAULT_GROUP server: port: 8080 # 负载均衡配置 spring-cloud: loadbalancer: enabled: true retry: enabled: false # 日志配置 logging: level: com.example.gateway: DEBUG
// 网关路由控制器 @RestController @RequestMapping("/api") @Slf4j public class GatewayController { @Autowired @Qualifier("loadBalancedRestTemplate") private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; /** * 订单服务路由 - 使用服务名进行调用 */ @PostMapping("/orders") public ResponseEntity<?> createOrder(@RequestBody OrderRequest request) { log.info("网关接收创建订单请求: {}", request); try { // 使用服务名而不是具体IP进行调用 String serviceUrl = "http://order-service/order/orders"; ResponseEntity<Order> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( serviceUrl, request, Order.class); return ResponseEntity.status(response.getStatusCode()) .body(response.getBody()); } catch (HttpClientErrorException e) { log.error("调用订单服务失败: {}", e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.status(e.getStatusCode()) .body(Map.of("error", e.getMessage())); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("系统错误: {}", e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) .body(Map.of("error", "系统繁忙,请稍后重试")); } } /** * 查询订单路由 */ @GetMapping("/orders/{orderId}") public ResponseEntity<?> getOrder(@PathVariable String orderId) { log.info("网关接收查询订单请求: {}", orderId); try { String serviceUrl = "http://order-service/order/orders/" + orderId; ResponseEntity<Order> response = restTemplate.getForEntity( serviceUrl, Order.class); return ResponseEntity.status(response.getStatusCode()) .body(response.getBody()); } catch (HttpClientErrorException.NotFound e) { return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) .body(Map.of("error", "订单不存在")); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("查询订单失败: {}", e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) .body(Map.of("error", "系统繁忙,请稍后重试")); } } /** * 手动服务发现示例 */ @GetMapping("/discovery/services") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> listServices() { Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>(); // 获取所有服务名称 List<String> services = discoveryClient.getServices(); result.put("services", services); // 获取每个服务的实例信息 Map<String, List<ServiceInstance>> serviceInstances = new HashMap<>(); for (String service : services) { List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(service); serviceInstances.put(service, instances); } result.put("instances", serviceInstances); return ResponseEntity.ok(result); } /** * 手动负载均衡示例 */ @GetMapping("/discovery/order-instances") public ResponseEntity<List<ServiceInstance>> getOrderServiceInstances() { List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("order-service"); if (instances.isEmpty()) { return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE) .body(Collections.emptyList()); } // 可以在这里实现自定义的负载均衡逻辑 instances.forEach(instance -> { log.info("订单服务实例: {}:{} - {}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), instance.getMetadata()); }); return ResponseEntity.ok(instances); } }
3.4 高级配置与自定义策略
// 自定义服务注册配置 @Configuration public class CustomNacosConfiguration { /** * 自定义服务实例配置 */ @Bean public NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosProperties() { NacosDiscoveryProperties properties = new NacosDiscoveryProperties(); // 设置元数据 Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>(); metadata.put("version", "1.0.0"); metadata.put("environment", getEnvironment()); metadata.put("startup-time", Instant.now().toString()); metadata.put("region", getRegion()); properties.setMetadata(metadata); properties.setWeight(1.0); properties.setClusterName(getClusterName()); properties.setGroup("PRODUCTION_GROUP"); return properties; } /** * 自定义服务注册监听器 */ @Bean public NacosServiceRegistry customServiceRegistry() { return new NacosServiceRegistry(nacosProperties()) { @Override public void register(Registration registration) { log.info("开始注册服务: {}", registration.getServiceId()); super.register(registration); log.info("服务注册完成: {}", registration.getServiceId()); } @Override public void deregister(Registration registration) { log.info("开始注销服务: {}", registration.getServiceId()); super.deregister(registration); log.info("服务注销完成: {}", registration.getServiceId()); } }; } /** * 自定义服务发现配置 */ @Bean public NacosServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery() { return new NacosServiceDiscovery() { @Override public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) throws Exception { List<ServiceInstance> instances = super.getInstances(serviceId); // 过滤健康的实例 List<ServiceInstance> healthyInstances = instances.stream() .filter(instance -> { String healthy = instance.getMetadata().get("nacos.healthy"); return "true".equals(healthy); }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); log.debug("服务 {} 的健康实例数: {}/{}", serviceId, healthyInstances.size(), instances.size()); return healthyInstances; } }; } private String getEnvironment() { // 从环境变量或配置文件中获取环境信息 return System.getenv().getOrDefault("ENV", "dev"); } private String getRegion() { // 从环境变量或配置文件中获取区域信息 return System.getenv().getOrDefault("REGION", "beijing"); } private String getClusterName() { // 从环境变量或配置文件中获取集群信息 return System.getenv().getOrDefault("CLUSTER", "default"); } } // 自定义负载均衡策略 @Component public class CustomLoadBalancerStrategy { @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; /** * 基于权重的负载均衡 */ public ServiceInstance chooseByWeight(String serviceId) { List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId); if (instances.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException("没有可用的服务实例: " + serviceId); } // 计算总权重 double totalWeight = instances.stream() .mapToDouble(instance -> Double.parseDouble( instance.getMetadata().getOrDefault("weight", "1.0"))) .sum(); // 随机选择 double random = Math.random() * totalWeight; double current = 0; for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) { double weight = Double.parseDouble( instance.getMetadata().getOrDefault("weight", "1.0")); current += weight; if (random <= current) { return instance; } } return instances.get(0); } /** * 基于标签的路由 */ public ServiceInstance chooseByTag(String serviceId, String tagKey, String tagValue) { List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId); List<ServiceInstance> filteredInstances = instances.stream() .filter(instance -> tagValue.equals(instance.getMetadata().get(tagKey))) .collect(Collectors.toList()); if (filteredInstances.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException("没有匹配标签的服务实例"); } // 随机选择一个 int index = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(filteredInstances.size()); return filteredInstances.get(index); } }
4. Nacos 控制台操作指南
4.1 服务管理界面操作
# 启动Nacos服务器(单机模式) cd nacos/bin sh startup.sh -m standalone # 访问控制台 # http://localhost:8848/nacos # 用户名/密码:nacos/nacos
4.2 服务注册状态监控
// 服务健康状态监控 @Component @Slf4j public class ServiceHealthMonitor { @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; @Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒检查一次 public void monitorServiceHealth() { List<String> services = discoveryClient.getServices(); for (String service : services) { List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(service); long healthyCount = instances.stream() .filter(this::isHealthy) .count(); if (healthyCount == 0) { log.warn("服务 {} 没有健康实例!", service); // 发送告警 sendAlert(service); } else if (healthyCount < instances.size()) { log.warn("服务 {} 有 {} 个不健康实例", service, instances.size() - healthyCount); } } } private boolean isHealthy(ServiceInstance instance) { try { // 调用健康检查接口 String healthUrl = String.format("http://%s:%s%s/health", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), instance.getMetadata().getOrDefault("context-path", "")); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(healthUrl, String.class); return response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful(); } catch (Exception e) { log.debug("健康检查失败: {}:{}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()); return false; } } private void sendAlert(String serviceName) { // 实现告警逻辑,如发送邮件、短信、钉钉等 log.error("发送服务不可用告警: {}", serviceName); } }
5. 服务注册发现的最佳实践
5.1 服务命名规范
// 服务命名规范示例 public class ServiceNamingConvention { /** * 服务命名规则 */ public class NamingRules { // 格式: {业务领域}-{功能}-service // 示例: public static final String ORDER_CORE_SERVICE = "order-core-service"; public static final String USER_MANAGEMENT_SERVICE = "user-management-service"; public static final String PAYMENT_PROCESSING_SERVICE = "payment-processing-service"; // 禁止的命名: // - 使用IP地址或主机名 // - 包含环境信息(如order-service-dev) // - 过于泛化的名称(如api-service) } /** * 服务元数据规范 */ public class MetadataConvention { public static Map<String, String> buildMetadata(String version, String environment) { Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>(); metadata.put("version", version); metadata.put("environment", environment); metadata.put("startup-time", Instant.now().toString()); metadata.put("weight", "1.0"); metadata.put("region", System.getenv().getOrDefault("REGION", "default")); metadata.put("zone", System.getenv().getOrDefault("ZONE", "default")); return metadata; } } }
5.2 服务注册生命周期管理
// 服务生命周期管理 @Component @Slf4j public class ServiceLifecycleManager { @Autowired private NacosServiceManager nacosServiceManager; /** * 优雅的服务注册 */ @EventListener public void onApplicationReady(ApplicationReadyEvent event) { log.info("应用启动完成,开始服务注册..."); // 等待依赖服务就绪 waitForDependencies(); // 执行健康检查 if (!selfHealthCheck()) { log.error("服务健康检查失败,停止注册"); System.exit(1); } log.info("服务注册准备就绪"); } /** * 优雅的服务下线 */ @EventListener public void onApplicationShutdown(ContextClosedEvent event) { log.info("应用关闭,开始服务下线..."); // 1. 先标记为不接收新流量 markAsDraining(); // 2. 等待正在处理的请求完成 waitForInFlightRequests(); // 3. 从注册中心注销 deregisterFromNacos(); log.info("服务下线完成"); } private void waitForDependencies() { // 等待数据库、缓存等依赖服务就绪 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } private boolean selfHealthCheck() { // 执行自检逻辑 try { // 检查数据库连接 // 检查缓存连接 // 检查磁盘空间 // 检查内存使用 return true; } catch (Exception e) { log.error("健康检查失败", e); return false; } } private void markAsDraining() { // 更新元数据,标记为引流状态 // 让负载均衡器不再将新流量路由到该实例 } private void waitForInFlightRequests() { // 等待正在处理的请求完成 try { Thread.sleep(30000); // 等待30秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } private void deregisterFromNacos() { // 从Nacos注销服务 try { nacosServiceManager.deregister(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("服务注销失败", e); } } }
5.3 多环境配置管理
# application-dev.yml - 开发环境 spring: cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: 192.168.1.100:8848 namespace: dev group: DEV_GROUP metadata: environment: dev version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT # application-test.yml - 测试环境 spring: cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: 192.168.1.101:8848 namespace: test group: TEST_GROUP metadata: environment: test version: 1.0.0-RC1 # application-prod.yml - 生产环境 spring: cloud: nacos: discovery: server-addr: - 192.168.1.102:8848 - 192.168.1.103:8848 - 192.168.1.104:8848 namespace: prod group: PROD_GROUP metadata: environment: production version: 1.0.0
6. 常见问题与解决方案
6.1 服务注册失败排查
// 服务注册故障排查工具 @Component @Slf4j public class RegistrationTroubleshooter { @Autowired private NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosProperties; @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; /** * 诊断服务注册状态 */ public void diagnoseRegistration() { log.info("开始诊断服务注册状态..."); // 1. 检查Nacos服务器连接 checkNacosConnection(); // 2. 检查服务注册信息 checkServiceRegistration(); // 3. 检查实例健康状态 checkInstanceHealth(); log.info("服务注册诊断完成"); } private void checkNacosConnection() { try { String serverAddr = nacosProperties.getServerAddr(); log.info("检查Nacos服务器连接: {}", serverAddr); // 尝试连接Nacos服务器 RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); String healthUrl = "http://" + serverAddr + "/nacos/actuator/health"; ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(healthUrl, String.class); if (response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()) { log.info("Nacos服务器连接正常"); } else { log.error("Nacos服务器连接异常: {}", response.getStatusCode()); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Nacos服务器连接失败: {}", e.getMessage()); } } private void checkServiceRegistration() { String serviceName = nacosProperties.getService(); log.info("检查服务注册: {}", serviceName); List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceName); if (instances.isEmpty()) { log.error("服务 {} 没有注册实例", serviceName); } else { log.info("服务 {} 有 {} 个注册实例", serviceName, instances.size()); instances.forEach(instance -> { log.info("实例: {}:{}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()); }); } } private void checkInstanceHealth() { String serviceName = nacosProperties.getService(); List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceName); for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) { try { String healthUrl = String.format("http://%s:%s/actuator/health", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort()); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<Map> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(healthUrl, Map.class); if (response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()) { Map<String, Object> healthInfo = response.getBody(); String status = (String) healthInfo.get("status"); log.info("实例 {}:{} 健康状态: {}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), status); } else { log.warn("实例 {}:{} 健康检查失败: {}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), response.getStatusCode()); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("实例 {}:{} 健康检查异常: {}", instance.getHost(), instance.getPort(), e.getMessage()); } } } }
6.2 服务发现性能优化
// 服务发现性能优化配置 @Configuration public class DiscoveryPerformanceConfig { /** * 本地服务缓存配置 */ @Bean public ServiceInstanceCache serviceInstanceCache() { return new ServiceInstanceCache(1000, 300); // 缓存1000个服务,5分钟过期 } /** * 优化RestTemplate配置 */ @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate optimizedRestTemplate() { HttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create() .setMaxConnTotal(200) // 最大连接数 .setMaxConnPerRoute(50) // 每个路由最大连接数 .setConnectionTimeToLive(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 连接存活时间 .build(); HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient); factory.setConnectTimeout(3000); // 连接超时3秒 factory.setReadTimeout(10000); // 读取超时10秒 return new RestTemplate(factory); } } // 本地服务缓存实现 @Component @Slf4j public class ServiceInstanceCache { private final Cache<String, List<ServiceInstance>> cache; private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; public ServiceInstanceCache(int maxSize, int expireSeconds) { this.cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() .maximumSize(maxSize) .expireAfterWrite(expireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); this.discoveryClient = null; // 通过构造函数注入 } /** * 获取服务实例(带缓存) */ public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) { return cache.get(serviceId, key -> { log.debug("缓存未命中,从注册中心获取服务实例: {}", serviceId); return discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId); }); } /** * 手动刷新缓存 */ public void refreshCache(String serviceId) { cache.invalidate(serviceId); log.debug("刷新服务缓存: {}", serviceId); } /** * 批量刷新缓存 */ public void refreshAllCache() { cache.invalidateAll(); log.debug("刷新所有服务缓存"); } }
总结
服务注册与发现是微服务架构的基石,它解决了分布式环境中服务动态寻址和负载均衡的核心问题。通过本文的实战指南,我们掌握了:
核心知识点:
- 服务注册:服务实例如何向注册中心注册自己的信息
- 服务发现:消费者如何从注册中心获取服务实例列表
- 健康检查:如何保证服务实例的可用性
- 负载均衡:如何在多个服务实例间分配流量
最佳实践:
- 使用标准化的服务命名规范
- 合理配置健康检查和心跳间隔
- 实现优雅的服务上下线
- 建立多环境隔离策略
- 实施性能优化和故障排查机制
生产建议:
- 注册中心集群化部署保证高可用
- 实施服务分级和熔断保护
- 建立完善的监控告警体系
- 定期进行服务治理演练
服务注册发现虽然看似简单,但在生产环境中需要考虑网络分区、脑裂、雪崩等各种复杂场景。正确的服务注册发现实践能够为微服务架构的稳定运行提供坚实基础。