View 动画
在Android 中的 View 动画框架中,一共提供了 Alpha (透明动画),Rotate(旋转动画),Scale(缩放动画),Translate(平移动画) 四种类型的补间动画。
标签表示 补间动画的集合,对应 AnimationSet 类,所以 set 标签中 可以包含多个补间动画标签,并且还可以包含补间动画中的 集合。
Alpha (透明度 动画)
android:fromAlpha
Float. 设置透明度的初始值,其中0.0是透明,1.0是不透明的。
android:toAlpha
Float. 设置透明度的结束值,其中0.0是透明,1.0是不透明的
duration : 时间
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <!-- 透明动画 --> <alpha android:duration="2000" android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0" /> </set>
调用:
Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.alpha); animation.setFillAfter(true); group.startAnimation(animation);
Scale(缩放动画)
android:fromXScale
Float. 水平方向缩放比例的初始值,其中1.0是没有任何变化。
android:toXScale
Float. 水平方向缩放比例的结束值,其中1.0是没有任何变化。
android:fromYScale
Float. 竖直方向缩放比例的初始值,其中1.0是没有任何变化。
android:toYScale
Float. 竖直方向缩放比例的结束值,其中1.0是没有任何变化。
android:pivotX
Float. 缩放中心点的x坐标
android:pivotY
Float. 缩放中心点的y坐标
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <!--缩放动画--> <scale android:fromXScale="1.0" android:fromYScale="1.0" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:toXScale="0.2" android:toYScale="0.2" /> </set>
使用如上
Translate (平移动画)
android:fromXDelta
Float or percentage. 移动起始点的x坐标. 表示形式有三种:
1 相对于自己的左边界的距离,单位像素值。(例如 "5")
2 相对于自己的左边界的距离与自身宽度的百分比。(例如 "5%")
3 相对于父View的左边界的距离与父View宽度的百分比。(例如 "5%p")
android:toXDelta
Float or percentage. 移动结束点的x坐标. 表现形式同上
android:fromYDelta
Float or percentage. 移动起始点的y坐标. 表示形式有三种:
1 相对于自己的上边界的距离,单位像素值。(例如 "5")
2 相对于自己的上边界的距离与自身高度的百分比。(例如 "5%")
3 相对于父View的上边界的距离与父View高度的百分比。(例如 "5%p")
android:toYDelta
Float or percentage. 移动结束点的y坐标. 表现形式同上
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <translate android:duration="2000" android:fromXDelta="20" android:fromYDelta="20" android:toXDelta="100" android:toYDelta="100" /> </set>
使用如上
Rotate (旋转动画)
android:fromDegrees
Float. 旋转初始的角度。
android:toDegrees
Float. 旋转结束的角度。
android:pivotX
Float or percentage. 旋转中心点x坐标,表示形式有三种:
1 相对于自己的左边界的距离,单位像素值。(例如 "5")
2 相对于自己的左边界的距离与自身宽度的百分比。(例如 "5%")
3 相对于父View的左边界的距离与父View宽度的百分比。(例如 "5%p")
android:pivotY
Float or percentage. 旋转中心点y坐标,表示形式有三种:
1 相对于自己的上边界的距离,单位像素值。(例如 "5")
2 相对于自己的上边界的距离与自身宽度的百分比。(例如 "5%")
3 相对于父View的上边界的距离与父View高度的百分比。(例如 "5%p")
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <rotate android:fromDegrees="0" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000" android:toDegrees="+360" /> </set>
通过补间动画 为 Activity 自动以切换动画
通过调用Activity 类的 overridePendingTransition(int enterAnim, int exitAnim) 方法可以实现自定义Activity 的切换动画,注意这个方方必须在 startActivity 和 finish 之后调用,否则无效
逐帧 动画
逐帧动画 是用来 逐帧 显示预先定义好的 一组图片,类似于电影播放,对应于 AnimationDrawable 类。
动画的资源文件一般放在 Drawable 文件夹下。
通过 xml 定义一个逐帧动画。
<animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:oneshot="true" > <item android:drawable="@drawable/first_pic" android:duration="1000"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/second_pic" android:duration="1000"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/third_pic" android:duration="1000"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/fourth_pic" android:duration="1000"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/fifth_pic" android:duration="1000"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/sixth_pic" android:duration="1000"/> </animation-list>
然后将面定义的AnimationDrawable 作为 View 的背景 并且通过 AnimationDrawable 来播放动画。
image.setImageResource(R.drawable.anim_list); AnimationDrawable animationDrawable = (AnimationDrawable) image.getDrawable(); animationDrawable.start(); //animationDrawable.stop(); //如果oneshot为false,必要时要停止动画
通过代码实现:
//代码定义、创建、执行动画 AnimationDrawable animationDrawable = new AnimationDrawable(); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.first_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.second_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.third_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.fourth_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.fifth_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.addFrame(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.sixth_pic), 1000); animationDrawable.setOneShot(true); image.setImageDrawable(animationDrawable); animationDrawable.start();
属性动画
ViewPropertyAnimator
使用方式:View.animate() 后面根 translationX()等方法
view.animate().translationX(500);
具体可以跟的方法以及方法所对应的 View 中的实际操作的方法如下图所示:
从图中可以看到, View 的每个方法都对应了 ViewPropertyAnimator 的两个方法,其中一个是带有 -By 后缀的,例如,View.setTranslationX() 对应了 ViewPropertyAnimator.translationX() 和 ViewPropertyAnimator.translationXBy() 这两个方法。其中带有 -By() 后缀的是增量版本的方法,例如,translationX(100) 表示用动画把 View 的 translationX 值渐变为 100,而 translationXBy(100) 则表示用动画把 View 的 translationX 值渐变地增加 100。
常用的方法:
ViewPropertyAnimator.withStartAction/EndAction()
这两个方法是 ViewPropertyAnimator 的独有方法。它们和 set/addListener() 中回调的 onAnimationStart() / onAnimationEnd() 相比起来的不同主要有两点:
1,`withStartAction()` / `withEndAction()` 是一次性的,在动画执行结束后就自动弃掉了,就算之后再重用 `ViewPropertyAnimator` 来做别的动画,用它们设置的回调也不会再被调用。而 `set/addListener()` 所设置的 `AnimatorListener` 是持续有效的,当动画重复执行时,回调总会被调用
1
2,withEndAction() 设置的回调只有在动画正常结束时才会被调用,而在动画被取消时不会被执行。这点和 AnimatorListener.onAnimationEnd() 的行为是不一致的。
常用的监听
ViewPropertyAnimator animate = imageView.animate(); //当动画的属性更新时(不严谨的说,即每过 10 毫秒,动画的完成度更新时),这个方法被调用。 animate.setUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { } }); animate.setListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { //当动画被cancel()方法取消时,这个方法会被调用。 //需要说明一下的是,就算动画被取消,onAnimationEnd() 也会被调用。所以当动画被取消时,如果设置了 AnimatorListener,那么 onAnimationCancel() 和 onAnimationEnd() 都会被调用。onAnimationCancel() 会先于 onAnimationEnd() 被调用。 @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationCancel(animation); } //当动画结束时调用 @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationEnd(animation); } //当动画通过 setRepeatMode() / setRepeatCount() 或 repeat() 方法重复执行时,这个方法被调用。 @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationRepeat(animation); } //当动画开始时调用 @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationStart(animation); } });
ObjectAnimator
使用方式 :
1,如果是自定义控件,需要添加 setter/getter 方法;
2,使用 ObjectAnimatior.ofXXX(),创建 ObjectAnimator 对象,
3,使用start 方法执行动画
与属性动画相比,View 动画存在一个缺陷,View 动画只是改变 View 的显示,并没有改变 View 的响应区域,并且View 动画只能对View 做四种类型的补间动画。因此 在 3.0 以后 添加了 属性动画框架
实现View 的四种动画
//利用 ObjectAnimator 实现透明动画。group 代表的是 视图 ObjectAnimator .ofFloat(group, "alpha", 1, 0, 1) .setDuration(2000) .start(); //利用AnimatorSet 和 ObjectAnimation 实现缩放动画 final AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet(); group.setPivotX(group.getWidth()/2); group.setPivotY(group.getHeight()/2); animatorSet.playTogether( ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(group,"scaleX",1,0.2f).setDuration(5000), ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(group,"scaleY",1,0.2f).setDuration(5000) ); animatorSet.start(); //使用AnimatorSet 和 ObjectAnimation 实现平移动画 AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet(); animatorSet.playTogether( ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(group,"translationX",20,100).setDuration(2000), ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(group,"translationY",20,100).setDuration(2000) ); animatorSet.start(); //利用ObjectAnimation 实现旋转动画 group.setPivotX(group.getWidth() / 2); group.setPivotY(group.getHeight() / 2); ObjectAnimator .ofFloat(group, "rotation", 0, 180) .setDuration(2000) .start();
上面是通过代码形式实现的 属性动画,对用通过xml 定义升序工会的方式不是很常用,因为属性的起始值 和 结束值 大多是程序运行时候动态获取的。[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5GFWpp1v-1594189542250)(C:\Users\Lv_345\Desktop\ObjectAnimator.gif)]
给自定义的View 设置属性动画
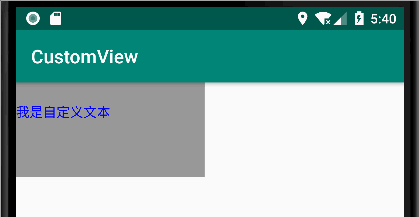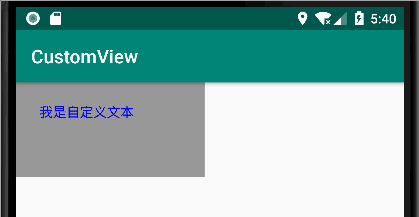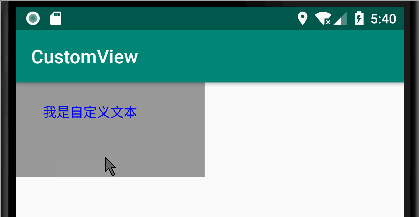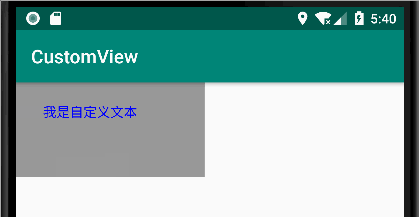
public class Text extends View { int TextX = 0; public int getTextX() { return TextX; } public void setTextX(int textX) { TextX = textX; invalidate(); } public Text(Context context) { super(context); } public Text(Context context,AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override public void draw(Canvas canvas) { super.draw(canvas); Paint paint = new Paint(); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//描边 paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.BUTT); //线帽:默认 paint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.BEVEL); //直线 paint.setTextSize(50); paint.setTypeface(Typeface.defaultFromStyle(Typeface.NORMAL));//字体类型 //对齐方式 paint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.LEFT); //文本 Paint.FontMetrics fontMetrics = paint.getFontMetrics(); //获取基线 的坐标 float TextY = getHeight()/2 +((fontMetrics.top - fontMetrics.bottom)/2 - fontMetrics.bottom); canvas.drawText("我是自定义文本",TextX,TextY,paint); } }
以上是自定义的 文本。只不过 给他的 起始位置 的 x 值添加了一个 get/set 方法。默认是0
<com.admin.view_core.viewGroup.Text android:id="@+id/text" android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#999999" />
下面给 其实位置的 x 设置属性动画
Text text = findViewById(R.id.text); ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(text,"TextX",0,100); animator.start()
效果如下:
属性动画常用的方法和监听:
1, 设置动画时长
ObjectAnimator .ofFloat(group, "alpha", 1, 0, 1) .setDuration(2000) .start();
2,设置 速度控制器
Text text = findViewById(R.id.text); ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(text,"TextX",0,900); //速度设置器。设置不同的 Interpolator ,动画就会以不同的速度来执行 // animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());//匀速 // animator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());//先加速,在减速,这个是默认的 // animator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());//持续加速 // animator.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());//持续 减速直到0 // 先回拉一下在进行正常的 动画轨迹,如果是 放大,就先缩小一下在放大,其他同理 // animator.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator()); //动画会超过目标值一些,然后 弹回来 // animator.setInterpolator(new OvershootInterpolator()); //上面两个的结合,开始前会拉,最后 超过一些在回弹 // animator.setInterpolator(new AnticipateOvershootInterpolator()); //在目标出处弹跳 // animator.setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator()); //这是一个 正弦./余弦曲线。他可以自定义 曲线的生命周期,所以动画可以不到终点就结束 // 也可以 到达终点后 反弹,回弹的次数由 曲线的周期确定,曲线的周期由 CycleInterpolator 构造方法的参数决定 // animator.setInterpolator(new CycleInterpolator(0.5f)); animator.start();
3,常用的监听
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(text,"TextX",50,200); animator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationCancel(animation); } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationEnd(animation); } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationRepeat(animation); } @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationStart(animation); } //由于ObjectAnimation 支持使用 onPause 暂停, // 所以增加了下面两个 监听 @Override public void onAnimationPause(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationPause(animation); } @Override public void onAnimationResume(Animator animation) { super.onAnimationResume(animation); } }); animator.start();
效果和 ViewPropertyAnimator 的监听一样。
渐变 ArgbEvaluator
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(view, "color", 0xffff0000, 0xff00ff00); // 在这里使用 ObjectAnimator.setEvaluator() 来设置 ArgbEvaluator,修复闪烁问题 animator.setEvaluator(new ArgbEvaluator()); animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()); animator.setDuration(2000); animator.start();
在同一个动画中改变多个属性值
// 使用 PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat() 来创建不同属性的动画值方案 PropertyValuesHolder holder1 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleX", 0,1); PropertyValuesHolder holder2 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleY", 0,1); PropertyValuesHolder holder3 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("alpha", 0,1); // 然后,用 ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder() 把三个属性合并,创建 Animator 然后执行 ObjectAnimator .ofPropertyValuesHolder(view, holder1, holder2, holder3) .start();
AnimatorSet 多个动画配合执行
说白了,就是按照指定的顺序执行
view.setTranslationX(-200f); ObjectAnimator animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "alpha", 0, 1); animator1.setDuration(1000); ObjectAnimator animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "translationX", -200, 200); ObjectAnimator animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "rotation", 0, 1080); animator3.setDuration(1000); AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet(); // 用 AnimatorSet 的方法来让三个动画协作执行 // 要求 1: animator1 先执行,animator2 在 animator1 完成后立即开始 // 要求 2: animator2 和 animator3 同时开始 //先执行 1,在执行2 animatorSet.playSequentially(animator1,animator2); //2 和 3 一起执行 animatorSet.playTogether(animator2,animator3); animatorSet.start();
PropertyValuesHolders.ofKeyframe() 把同一个属性拆分
除了合并 多个属性和调配多个动画,你还可以在 PropertyValueHodler 的基础上更进一步,例如,你可以让一个进度增加到 100% 后在 反弹回来。
// 使用 Keyframe.ofFloat() 来为 view 的 progress 属性创建关键帧 // 初始帧:progress 为 0 Keyframe keyframe1 = Keyframe.ofFloat(0,0); // 时间进行到一半:progress 为 100 Keyframe keyframe2 = Keyframe.ofFloat(0.5f,100); // 结束帧:progress 回落到 80 Keyframe keyframe3 = Keyframe.ofFloat(1,80); // 使用 PropertyValuesHolder.ofKeyframe() 来把关键帧拼接成一个完整的属性动画方案 PropertyValuesHolder holder = PropertyValuesHolder .ofKeyframe("progress",keyframe1,keyframe2,keyframe3); // 使用 ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder() 来创建动画 ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(view,holder); animator.setDuration(1000); animator.start();