MaxCompute 的 UDF 包括:UDF,UDAF 和 UDTF 三种函数,本文将重点介绍如何通过 Java 实现这三种函数。
参数与返回值类型
MaxCompute2.0 版本升级后,Java UDF 支持的数据类型从原来的 Bigint,String,Double,Boolean 扩展了更多基本的数据类型,同时还扩展支持了 ARRAY,MAP,STRUCT 等复杂类型。
Java UDF 使用新基本类型的方法,如下所示:
UDTF 通过 @Resolve 注解来获取 signature,如:@Resolve("smallint->varchar(10)")。
UDF 通过反射分析 evaluate 来获取 signature,此时 MaxCompute 内置类型与 Java 类型符合一一映射关系。
UDAF暂时还不支持新数据类型。
JAVA UDF 使用复杂类型的方法,如下所示:
UDTF 通过 @Resolve annotation 来指定 sinature,在 MaxCompute2.0 上线后,您即可在 Resolve annotation 中。如:@Resolve("array<string>,struct<a1:bigint,b1:string>,string->map<string,bigint>,struct<b1:bigint>")。
UDF 通过 evaluate 方法的 signature 来映射 UDF 的输入输出类型,此时参考MaxCompute 类型与 Java 类型的映射关系。其中 array 对应 java.util.List,map 对应java.util.Map,struct 对应 com.aliyun.odps.data.Struct。
UDAF暂时还不支持。
注意:
com.aliyun.odps.data.Struct 从反射看不出 field name 和 field type,所以需要用@Resolve annotation 来辅助。即如果需要在 UDF 中使用 struct,要求在 UDF class 上也标注上@Resolve 注解,这个注解只会影响参数或返回值中包含 com.aliyun.odps.data.Struct 的重载。
目前 class 上只能提供一个 @Resolve annotation,因此一个 UDF 中带有 struct 参数或返回值的重载只能有一个。
MaxCompute 数据类型与 Java 类型的对应关系,如下所示:
注意:
- Java 中对应的数据类型以及返回值数据类型是对象,首字母请务必大写。
- SQL 中的 NULL 值通过 Java 中的 NULL 引用表示,因此 Java primitive type 是不允许使用的,因为无法表示 SQL 中的 NULL 值。
- 此处 Array 类型对应的 Java 类型是 List,而不是数组。
UDF
实现UDF 需要继承 com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF 类,并实现 evaluate 方法。evaluate 方法必须是非static 的 public 方法 。Evaluate 方法的参数和返回值类型将作为 SQL 中 UDF 的函数签名。这意味着您可以在 UDF中实现多个 evaluate 方法,在调用 UDF 时,框架会依据 UDF 调用的参数类型匹配正确的 evaluate 方法 。
UDF 的示例如下:
- package org.alidata.odps.udf.examples;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF;
- public final class Lower extends UDF {
- public String evaluate(String s) {
- if (s == null) { return null; }
- return s.toLowerCase();
- }
- }
可以通过实现void setup(ExecutionContext ctx)和void close()来分别实现 UDF 的初始化和结束代码。
UDF 的使用方式与 MaxCompute SQL 中普通的内建函数相同,详情请参见
内建函数。
UDAF
实现 Java UDAF 类需要继承 com.aliyun.odps.udf.Aggregator,并实现如下几个接口:
- public abstract class Aggregator implements ContextFunction {
- @Override
- public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException {
- }
- @Override
- public void close() throws UDFException {
- }
- /**
- * 创建聚合Buffer
- * @return Writable 聚合buffer
- */
- abstract public Writable newBuffer();
- /**
- * @param buffer 聚合buffer
- * @param args SQL中调用UDAF时指定的参数
- * @throws UDFException
- */
- abstract public void iterate(Writable buffer, Writable[] args) throws UDFException;
- /**
- * 生成最终结果
- * @param buffer
- * @return Object UDAF的最终结果
- * @throws UDFException
- */
- abstract public Writable terminate(Writable buffer) throws UDFException;
- abstract public void merge(Writable buffer, Writable partial) throws UDFException;
- }
其中最重要的是 iterate,merge 和 terminate 三个接口,UDAF 的主要逻辑依赖于这三个接口的实现。此外,还需要您实现自定义的 Writable buffer。
以实现求平均值 avg 为例,下图简要说明了在 MaxCompute UDAF 中这一函数的实现逻辑及计算流程:
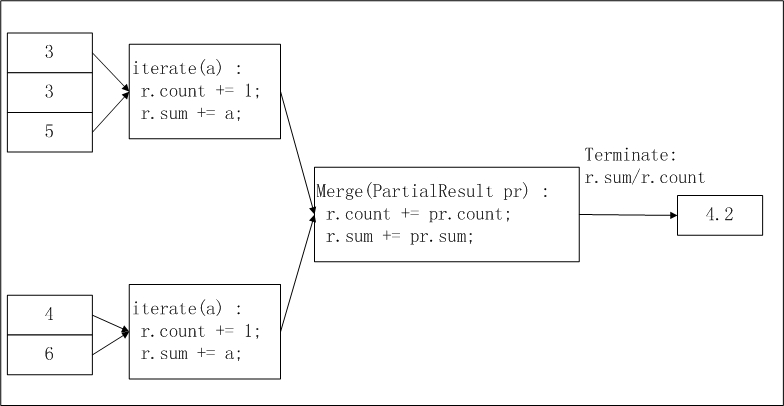
在上图中,输入数据被按照一定的大小进行分片(有关分片的描述请参见
MapReduce),每片的大小适合一个 worker 在适当的时间内完成。这个分片大小的设置需要您手动配置完成。
UDAF 的计算过程分为两个阶段:
第一阶段:每个 worker 统计分片内数据的个数及汇总值,您可以将每个分片内的数据个数及汇总值视为一个中间结果。
第二阶段:worker 汇总上一个阶段中每个分片内的信息。在最终输出时,r.sum / r.count 即是所有输入数据的平均值。
计算平均值的 UDAF 的代码示例,如下所示:
- import java.io.DataInput;
- import java.io.DataOutput;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import com.aliyun.odps.io.DoubleWritable;
- import com.aliyun.odps.io.Writable;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.Aggregator;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
- @Resolve({"double->double"})
- public class AggrAvg extends Aggregator {
- private static class AvgBuffer implements Writable {
- private double sum = 0;
- private long count = 0;
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- out.writeDouble(sum);
- out.writeLong(count);
- }
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- sum = in.readDouble();
- count = in.readLong();
- }
- }
- private DoubleWritable ret = new DoubleWritable();
- @Override
- public Writable newBuffer() {
- return new AvgBuffer();
- }
- @Override
- public void iterate(Writable buffer, Writable[] args) throws UDFException {
- DoubleWritable arg = (DoubleWritable) args[0];
- AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
- if (arg != null) {
- buf.count += 1;
- buf.sum += arg.get();
- }
- }
- @Override
- public Writable terminate(Writable buffer) throws UDFException {
- AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
- if (buf.count == 0) {
- ret.set(0);
- } else {
- ret.set(buf.sum / buf.count);
- }
- return ret;
- }
- @Override
- public void merge(Writable buffer, Writable partial) throws UDFException {
- AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
- AvgBuffer p = (AvgBuffer) partial;
- buf.sum += p.sum;
- buf.count += p.count;
- }
- }
注意:
- UDAF 在 SQL 中的使用语法与普通的内建聚合函数相同,详情请参见 聚合函数。
- 关于如何运行 UDTF 的方法与 UDF 类似,详情请参见 运行 UDF。
UDTF
Java UDTF 需要继承 com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF 类。这个类需要实现 4 个接口,如下表所示:
UDTF 的程序示例,如下所示:
- package org.alidata.odps.udtf.examples;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTFCollector;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
- // TODO define input and output types, e.g., "string,string->string,bigint".
- @Resolve({"string,bigint->string,bigint"})
- public class MyUDTF extends UDTF {
- @Override
- public void process(Object[] args) throws UDFException {
- String a = (String) args[0];
- Long b = (Long) args[1];
- for (String t: a.split("\\s+")) {
- forward(t, b);
- }
- }
- }
注意:
以上只是程序示例,关于如何在 MaxCompute 中运行 UDTF 的方法与 UDF 类似,详情请参见:
运行 UDF。
在 SQL 中可以这样使用这个 UDTF,假设在 MaxCompute 上创建 UDTF 时注册函数名为 user_udtf:
- select user_udtf(col0, col1) as (c0, c1) from my_table;
假设 my_table 的 col0,col1 的值如下所示:
- +------+------+
- | col0 | col1 |
- +------+------+
- | A B | 1 |
- | C D | 2 |
- +------+------+
则 select 出的结果,如下所示:
- +----+----+
- | c0 | c1 |
- +----+----+
- | A | 1 |
- | B | 1 |
- | C | 2 |
- | D | 2 |
- +----+----+
使用说明
UDTF 在 SQL 中的常用方式如下:
- select user_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from my_table;
- select user_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from
- (select * from my_table distribute by key sort by key) t;
- select reduce_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from
- (select col0, col1, col2 from
- (select map_udtf(a0, a1, a2, a3) as (col0, col1, col2) from my_table) t1
- distribute by col0 sort by col0, col1) t2;
但使用 UDTF 有如下使用限制:
同一个 SELECT 子句中不允许有其他表达式。
-
select value, user_udtf(key) as mycol ...
UDTF 不能嵌套使用。
-
select user_udtf1(user_udtf2(key)) as mycol...
不支持在同一个 select 子句中与 group by / distribute by / sort by 联用。
-
select user_udtf(key) as mycol ... group by mycol
其他 UDTF 示例
在 UDTF 中,您可以读取 MaxCompute 的
资源。利用 UDTF 读取 MaxCompute 资源的示例,如下所示:
编写 UDTF 程序,编译成功后导出 jar 包(udtfexample1.jar)。 package com.aliyun.odps.examples.udf;- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.io.InputStreamReader;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.ExecutionContext;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF;
- import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
- /**
- * project: example_project
- * table: wc_in2
- * partitions: p2=1,p1=2
- * columns: colc,colb
- */
- @Resolve({ "string,string->string,bigint,string" })
- public class UDTFResource extends UDTF {
- ExecutionContext ctx;
- long fileResourceLineCount;
- long tableResource1RecordCount;
- long tableResource2RecordCount;
- @Override
- public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException {
- this.ctx = ctx;
- try {
- InputStream in = ctx.readResourceFileAsStream("file_resource.txt");
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
- String line;
- fileResourceLineCount = 0;
- while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
- fileResourceLineCount++;
- }
- br.close();
- Iterator<Object[]> iterator = ctx.readResourceTable("table_resource1").iterator();
- tableResource1RecordCount = 0;
- while (iterator.hasNext()) {
- tableResource1RecordCount++;
- iterator.next();
- }
- iterator = ctx.readResourceTable("table_resource2").iterator();
- tableResource2RecordCount = 0;
- while (iterator.hasNext()) {
- tableResource2RecordCount++;
- iterator.next();
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new UDFException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void process(Object[] args) throws UDFException {
- String a = (String) args[0];
- long b = args[1] == null ? 0 : ((String) args[1]).length();
- forward(a, b, "fileResourceLineCount=" + fileResourceLineCount + "|tableResource1RecordCount="
- + tableResource1RecordCount + "|tableResource2RecordCount=" + tableResource2RecordCount);
- }
- }
添加资源到 MaxCompute。
- Add file file_resource.txt;
- Add jar udtfexample1.jar;
- Add table table_resource1 as table_resource1;
- Add table table_resource2 as table_resource2;
在 MaxCompute 中创建 UDTF 函数(my_udtf)。
- create function mp_udtf as com.aliyun.odps.examples.udf.UDTFResource using 'udtfexample1.jar, file_resource.txt, table_resource1, table_resource2';
在 MaxCompute 创建资源表 table_resource1、table_resource2 和物理表 tmp1,并插入相应的数据。
运行该 UDTF。
- select mp_udtf("10","20") as (a, b, fileResourceLineCount) from table_resource1;
- 返回:
- +-------+------------+-------+
- | a | b | fileResourceLineCount |
- +-------+------------+-------+
- | 10 | 2 | fileResourceLineCount=3|tableResource1RecordCount=0|tableResource2RecordCount=0 |
- | 10 | 2 | fileResourceLineCount=3|tableResource1RecordCount=0|tableResource2RecordCount=0 |
- +-------+------------+-------+
复杂数据类型示例
如以下代码,定义了一个有三个overloads 的 UDF,其中第一个用了 array 作为参数,第二个用了 map 作为参数,第三个用了 struct。由于第三个overloads 用了 struct 作为参数或者返回值,因此要求必须要对 UDF class 打上 @Resolveannotation,来指定 struct 的具体类型。
- @Resolve("struct<a:bigint>,string->string")
- public class UdfArray extends UDF {
- public String evaluate(List<String> vals, Long len) {
- return vals.get(len.intValue());
- }
- public String evaluate(Map<String,String> map, String key) {
- return map.get(key);
- }
- public String evaluate(Struct struct, String key) {
- return struct.getFieldValue("a") + key;
- }
- }
您可以直接将复杂类型传入 UDF 中,如下所示:
- create function my_index as 'UdfArray' using 'myjar.jar';
- select id, my_index(array('red', 'yellow', 'green'), colorOrdinal) as color_name from colors;

