前言
在之前的文章中,我们已经讲了如何利用 Spring Boot 来集成 Swagger2,详情可戳:Spring Boot 集成 Swagger2,构建强大的 API 文档。但其实 Swagger2 中主流的 2.9.2 自 2018 年发布后就已经好久没更新了,而在时隔两年之后的 2020 年,Swagger3 终于发布了。
相比于之前的 Swagger2,Swagger3 无疑新添了更多的特点,而相对集中地,主要集中在如下几点。
- 支持 OpenApi 3.0.3
- 兼容 Swagger2 的注释,而且进一步丰富了 open API 3.0 的规范
- 支持 Webflux
既然 Swagger3 有了这么多的改变,那用法是不是还和 Swagger2 一样呢?答案是:不一样。
不过虽然两者的使用方式不一样,但是总体流程还是差不多了,只不过有些步骤有所小变动而已,只要你掌握了 Swagger2 的使用方法,那使用 Swagger3 起来就是需要注意小改动就行了。那接下来,我们就来看看,如何利用 Spring Boot 来集成 Swagger3,对我们的 Swagger2 进行一次升级!
Spring Boot 集成 Swagger
创建 Spring Boot 项目
同样的,开始之前,我们需要创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目,这里不展开讲了,如果你对此还有所疑惑,可以先去熟悉下,这里建议参考我之前写过的一篇文章:创建 Spring Boot 项目的 3 种方式。
项目创建成功之后,总体结构如下:
这里的 config、controller、entity 模块是我后续加入的,所以不用理会,也就是说你创建好之后的项目是不包含这三个部分的,关于他们的用途,文章后续内容我会讲到。
引入依赖
创建项目后,在 pom.xml 文件中引入 Swagger3 的相关依赖。回忆一下,我们集成 Swagger2 时,引入的依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
而在 Swagger3 中,我们不需要再引入两个不同的依赖了,我们只需要引入一个依赖就足够,具体引入的依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
而这部分,Swagger2 和 Swagger3 就有所不同了,Swagger2 需要添加两项不同依赖,而 Swagger3 只用添加一项依赖就可以了。
构建 Swagger 配置类
为了统一管理 Swagger,这里还是推荐给 Swagger3 添加一个配置类。当然这里也可以根据自己的需求,可要可不要,但总体来说还是建议配置。
另外,在之前集成 Swagger2 的文章中,忘记了给大家说一点。平常在工作中,Swagger 的使用仅限于在开发环境,而在生产环境中,我们是要将其移除的。这里为了灵活管理,推荐大家在项目配置文件 application.yml 中添加关于 Swagger 开关的配置,比如这里我添加的配置如下,true 则代表开启 Swagger,false 则表示关闭 Swagger。
swagger:
enabled: true
配置完成之后,我们就需要在 Swagger 配置类中获取 Swagger 开关的值了,关于具体用法就可以看下边配置代码。
packagecom.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.config;
importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
importspringfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
importspringfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
importspringfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
importspringfox.documentation.oas.annotations.EnableOpenApi;
importspringfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
importspringfox.documentation.service.Contact;
importspringfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
importspringfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
importjava.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : 村雨遥
* @version : 1.0
* @project : springboot-swagger3-demo
* @package : com.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.config
* @className : SwaggerConfig
* @createTime : 2022/1/6 14:19
* @email : 747731461@qq.com
* @微信 : cunyu1024
* @公众号 : 村雨遥
* @网站 : https://cunyu1943.github.io
* @description :
*/
@Configuration
@EnableOpenApi
publicclassSwaggerConfig {
/**
* 用于读取配置文件 application.properties 中 swagger 属性是否开启
*/
@Value("${swagger.enabled}")
BooleanswaggerEnabled;
@Bean
publicDocketdocket() {
returnnewDocket(DocumentationType.OAS_30)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
// 是否开启swagger
.enable(swaggerEnabled)
.select()
// 过滤条件,扫描指定路径下的文件
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.controller"))
// 指定路径处理,PathSelectors.any()代表不过滤任何路径
//.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
privateApiInfoapiInfo() {
/*作者信息*/
Contactcontact=newContact("村雨遥", "https://cunyu1943.github.io", "747731461@qq.com");
returnnewApiInfo(
"Spring Boot 集成 Swagger3 测试",
"Spring Boot 集成 Swagger3 测试接口文档",
"v1.0",
"https://cunyu1943.github.io",
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
newArrayList()
);
}
}
这里的配置和 Swagger2 大同小异,这里最大的区别在于加入了从配置文件中获取 Swagger 开关的属性。这里也可以选择添加到 Swagger2 的配置类中,同样通过配置文件来控制是否开启 Swagger2。此外,还有就是 DocumentationType 属性的不同了,Swagger2 中我们使用的是 SWAGGER_2,而在 Swagger3 中,我们使用的则是 OAS_30。其实点进去 DocumentationType 的源码我们就可以发现,Swagger 已经是给我们定义好的,你用的是哪一个版本的 Swagger,那我们使用的属性值应该选择对应版本。三个版本的属性值对应如下:
publicstaticfinalDocumentationTypeSWAGGER_12=newDocumentationType("swagger", "1.2");
publicstaticfinalDocumentationTypeSWAGGER_2=newDocumentationType("swagger", "2.0");
publicstaticfinalDocumentationTypeOAS_30=newDocumentationType("openApi", "3.0");
编写实体类
完成上面的步骤之后,我们的 Swagger 就配置好了,接下来我们就添加一个接口来看看 Swagger3 和 Swagger2 的不同。
- 新建实体类
这里我以一个用户类为实例,带有 name、age 两个属性,也就是本文一开始项目结构截图中 entity 包下的内容。
packagecom.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.entity;
importio.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
importio.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
importlombok.AllArgsConstructor;
importlombok.Data;
importlombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : 村雨遥
* @version : 1.0
* @project : springboot-swagger3-demo
* @package : com.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2022/1/6 11:17
* @email : 747731461@qq.com
* @微信 : cunyu1024
* @公众号 : 村雨遥
* @网站 : https://cunyu1943.github.io
* @description :
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
publicclassUser {
@ApiModelProperty(value="姓名", required=true, example="村雨遥")
privateStringname;
@ApiModelProperty(value="年龄", required=true, example="20")
privateIntegerage;
}
- 新建接口
这里写了两个接口,一个是直接传参,另一种是通过利用创建的 User 实体类来传输,也就是项目结构中 controller 包中的内容。
packagecom.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.controller;
importcom.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.entity.User;
importio.swagger.annotations.Api;
importio.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
importio.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : 村雨遥
* @version : 1.0
* @project : springboot-swagger3-demo
* @package : com.cunyu.springbootswagger3demo.controller
* @className : UserController
* @createTime : 2022/1/6 11:02
* @email : 747731461@qq.com
* @微信 : cunyu1024
* @公众号 : 村雨遥
* @网站 : https://cunyu1943.github.io
* @description :
*/
@Api(tags="测试")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
publicclassUserController {
@ApiOperation("测试接口1")
@PostMapping("/show1")
publicStringshow1(@ApiParam(value="姓名", required=true, example="村雨遥") @RequestBodyStringname) {
return"hello,"+name+",welcome to springboot swagger3!";
}
@ApiOperation("测试接口2")
@PostMapping("/show2")
publicStringshow2(@ApiParam(value="用户对象", required=true) @RequestBodyUseruser) {
return"hello,"+user.getName() +",welcome to springboot swagger3!";
}
}
查看并测试接口
启动我们的项目,然后在浏览器中访问如下地址,就可以访问项目的接口文档了。
访问上面的地址后,如果出现下面的界面,则说明集成 Swagger3 就成功了。
这里也要注意一点,Swagger2 中的接口访问地址是:
这里 Swagger2 和 Swagger3 是不同的,这里大家一定要注意,否则可能你继续拿着 Swagger2 接口访问地址来放到 Swagger3 项目中不适用。
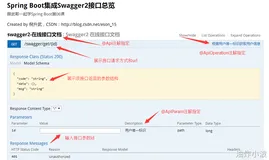
点开具体接口,我们以直接传参的接口来对比 Swagger3 和 Swagger2 的区别。第一张图是在 Swagger3 中,第二张图是在 Swagger2 中。这里可以发现,我们都是传的一个 name 属性,Swagger2 中会把我们接口中参数部分 Parameters 直接标识出来,而 Swagger3 中则不会,这里需要注意。
- Swagger2 中接口代码
@ApiOperation(value="有参接口")
@PostMapping("demo")
publicStringdemo(@ApiParam(value="姓名", required=true, example="村雨遥") @RequestBodyStringname) {
return"hello,"+name;
}
- Swagger3 中接口代码
@ApiOperation("测试接口1")
@PostMapping("/show1")
publicStringshow1(@ApiParam(value="姓名", required=true, example="村雨遥") @RequestBodyStringname) {
return"hello,"+name+",welcome to springboot swagger3!";
}
此外,我们来看 Swagger3 中的另一个接口,这里我们传递的是一个用户对象,接口中它将我们设置的默认值给传了过来。下图中第一张图为 Swagger3 中的截图,第二张图为 Swagger2 中的截图。同样的,Swagger2 中的参数会在 Parameters 模块标识出来,而 Swagger3 则不会标识。
还有一点值得注意的是,Swagger 中如果传递的部分是对象,那么 Swagger2 会在 Models 部分进行标识,而 Swagger3 中则是变成了 Schemas 部分,这也算是一个小变动吧。
最后,我们同样来进行测试,测试方法同 Swagger2,点击接口右上方的 Try it out,然后编辑参数的值,编辑完成后点击下方的 Execute 即可查看接口调用结果。
Swagger2 VS Swagger3
经过上面的步骤,我们就完成了 Spring Boot 集成 Swagger3 的实例测试了,而经过对比,也总结出了 Swagger2 和 Swagger3 的区别主要体现在如下几个方面:
- 所需依赖不同,Swagger2 需要添加两个依赖,而 Swagger3 则只需要添加一个依赖;
- 启用 Swagger 的注解不同,不知道大家有没有发现,无论是 Swagger2 还是 Swagger3 中的配置类,其实都是有一个注解用来启用 Swagger 的,不同之处在于 Swagger2 中用的是
@EnableSwagger2,而 Swagger3 中则用的是@EnableOpenApi; - 文档摘要信息(Docket)文件类型不同,可以发现在 Swagger 的配置类中,Swagger2 用的是
SWAGGER_2,而 Swagger3 中则用的是OAS_3; - Swagger UI 访问地址不同,在 Swagger2 中,如果我们要访问文档地址,需要访问
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html,而在 Swagger3 中,则是访问http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html;
总结
以上就是本文的所有内容了,主要介绍了如何使用 Spring Boot 集成 Swagger3,并在此过程中对比了 Swagger2 和 Swagger3 的一些区别。总体来讲,Swagger2 向 Swagger3 的升级还是比较平滑的。如果你已经掌握熟练使用 Swagger2,那么向 Swagger3 过度也很简单,只需要注意上一部分中的一些主要区别就可以了。其他的用于描述接口的注解,还是可以按照 Swagger2 的方式使用,毕竟 Swagger3 向下兼容了 Swagger2。
代码示例
最后,关于本文示例的代码,我已经上传至 Github,需要的小伙伴可以自取:
如果您觉得本文不错,欢迎 Star 支持,您的关注就是我坚持不断更新的动力!