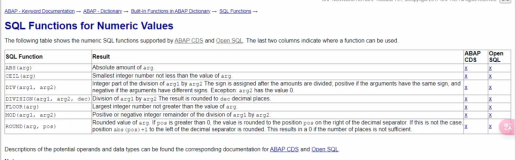
Recently I learned a new approach to access database table content without having to transport the column data into ABAP program using locator. There is a sample program provided in SAP help.
I make modifications on this sample. The modified one:
REPORT demo_db_locator.
DATA: otr_text_locator TYPE REF TO cl_abap_db_c_locator,
length TYPE i.
DATA: pattern TYPE string VALUE 'ABAP',
lv_index TYPE int4 VALUE 1.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>start_timer( ).
TRY.
SELECT text FROM sotr_textu WHERE langu = @sy-langu INTO @otr_text_locator.
length = length + otr_text_locator->get_length( ).
IF otr_text_locator->find( start_offset = 0
pattern = pattern ) <> -1.
lv_index = lv_index + 1.
ENDIF.
otr_text_locator->close( ).
ENDSELECT.
CATCH cx_lob_sql_error.
WRITE 'Exception in locator' COLOR = 6.
RETURN.
ENDTRY.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>stop_timer( ).
WRITE: / 'total length:', length, ' matched for ABAP:', lv_index.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).
CLEAR: otr_text_locator.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>gc( ).
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).So this report just calculates the total number of records in table sotr_textu in which the data of column “text” ( type String in ABAP dictionary ) has a substring of “ABAP”, and meantime calculate the total length of text fields from all table records.
For example if the table contains these three table rows below,
the total length should be 5 * 3 = 15 and number of records whose Text fields has pattern “ABAP” is 2.
The find method provided by locator is implemented in kernel:According to SAP help, the benefit for us to use locators is the data transfer from database to ABAP program could be avoided, at the cost of high resource ( I guess mainly from memory usage point of view ) consumption. I cannot not help wondering that using this approach, what kinds of runtime behavior could we get? Shorter execution time?
For comparison I write another program which uses the traditional way to get the same result:
According to SAP help, the benefit for us to use locators is the data transfer from database to ABAP program could be avoided, at the cost of high resource ( I guess mainly from memory usage point of view ) consumption. I cannot not help wondering that using this approach, what kinds of runtime behavior could we get? Shorter execution time?
For comparison I write another program which uses the traditional way to get the same result:
REPORT demo_db_locator.
DATA: lv_text TYPE string,
length TYPE i.
DATA: pattern TYPE string VALUE 'ABAP',
lv_index TYPE int4 VALUE 1.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>start_timer( ).
SELECT text FROM sotr_textu WHERE langu = @sy-langu INTO @lv_text.
length = length + strlen( lv_text ).
IF find( val = lv_text sub = pattern ) <> -1.
lv_index = lv_index + 1.
ENDIF.
ENDSELECT.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>stop_timer( ).
WRITE: / 'total length:', length, ' matched for ABAP:', lv_index.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).
CLEAR: lv_text.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>gc( ).
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).In the traditional way I use an ABAP variable lv_text to hold the text content from database, and perform the find operation in ABAP layer.
I compare the performance and memory consumption of both. The result shows traditional approach is 10 times faster and has less memory consumption than locator approach. So why do we need it at all?
Since the total length calculated is only 883309 bytes which is not a big number. So I make further testing. I copy several Z table from SOTR_TEXTU with post fix 1 ~ 9.
And I copy content from original table to these 9 tables with following report:DATA: lt_new_table TYPE TABLE OF zsotr_textu1,
lt_old_table TYPE TABLE OF sotr_textu.
SELECT * INTO TABLE lt_old_table FROM sotr_textu.
MOVE-CORRESPONDING lt_old_table TO lt_new_table.
LOOP AT lt_new_table ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<new>).
DO 1 TIMES.
<new>-text = <new>-text && <new>-text.
ENDDO.
ENDLOOP.
INSERT zsotr_textu1 FROM TABLE lt_new_table.During copy, the text content of new Z table is assigned within the DO N TIMES loop.
The table ZSOTR_TEXTU will have its text field assigned with content with DO N TIMES. This means for example ZSOTR_TEXTU1 will have its every record with text content two times longer than original table, and length of text column in ZSOTR_TEXTU will be two to the power of n times long than original table.
I make a new series of test against these tables:
The comparison result clearly shows that the power of locator approach can only be released till a set of records which contain REALLY long String content as table column. If the content in String column is not long enough, it is not necessary to use locator approach. In real case it might take some effort to find this boundary value.
By the way, for traditional approach, there is one variant that instead of reading each record using SELECT inside a LOOP, an alternative could be read out all text using SELECT text INTO TABLE, and do calculation using LOOP on the result internal table.
REPORT demo_db_locator.
DATA: lt_text TYPE string_table,
length TYPE i.
DATA: pattern TYPE string VALUE 'ABAP',
lv_index TYPE int4 VALUE 1.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>start_timer( ).
SELECT text FROM zsotr_textu1 WHERE langu = @sy-langu INTO TABLE @lt_text.
LOOP AT lt_text ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<text>).
length = length + strlen( <text> ).
IF find( val = <text> sub = pattern ) <> -1.
lv_index = lv_index + 1.
ENDIF.
ENDLOOP.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>stop_timer( ).
WRITE: / 'total length:', length, ' matched for ABAP:', lv_index.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).
CLEAR: lt_text.
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>gc( ).
zcl_abap_benchmark_tool=>print_used_memory( ).Comparison result between traditional approach and its variantAlthough the variant seems quite promising at a first glance, it could hardly be applied to productive usage – the huge memory consumption which is used to hold all result data in a single internal table should never be neglected.
In real case at least in CRM this approach is never used in productive application – instead the pattern OPEN CURSOR and FETCH CURSOR is used to avoid out of memory exception.