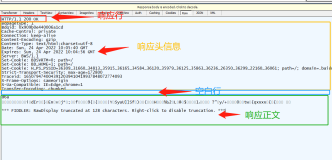
这个是很久以前的笔记,最近遇到一个编码问题,重新把它翻出来了。
这个只和java servlet有关,现在通常都用各种框架,很少会直接用到Servlet了。
查看servlet源代码的方法
查看servlet源代码的方法。因为servlet只是一些接口,并不是真正的实现,所以,如果想看真正的代码。
要去下对应的服务器的实现的源代码。比如Tomcat的代码在这里:
http://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-6/v6.0.33/src/
Servlet里的PrintWriter和ServletOutputStream
在servlet里有两种方法可以输出:
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();其中PrintWriter只提供了一系列的println函数,不能写二进制内容。其实这个是很合理的,下面会解释原因。
ServletOutputStream则有println系列函数和wirte系列函数。
当使用ServletOutputStream来输出中文字符,则会出现设置了CharacterEncoding,而无效的情况。
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //这句话并不能解决编码问题
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
outputStream.println("中文");真正的罪人是ServletOutputStream,它根本没有实现编码转换。我们可以看下它是怎样实现的:
public void print(String s) throws IOException {
if (s==null) s="null";
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = s.charAt (i);
//
// XXX NOTE: This is clearly incorrect for many strings,
// but is the only consistent approach within the current
// servlet framework. It must suffice until servlet output
// streams properly encode their output.
//
if ((c & 0xff00) != 0) { // high order byte must be zero
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("err.not_iso8859_1");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = new Character(c);
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
throw new CharConversionException(errMsg);
}
write (c);
}
}很明显,它根本没有进行编码转换:XXX NOTE: This is clearly incorrect for many strings。。
我们再用PrintWriter来输出:
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("中文");我们可以在浏览器上查看,页面编码是utf-8,则显示是正确的中文字符。
我们再看看PrintWriter是怎样工作的:
在Tomcat中PrintWriter实际上是org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteWriter类,
public void print(String s) {
if (s == null) {
s = "null";
}
write(s);
}
public void write(String s, int off, int len) {
if (error)
return;
try {
ob.write(s, off, len);
} catch (IOException e) {
error = true;
}
}
public void write(String s) {
write(s, 0, s.length());
}
public void write(String s, int off, int len) {
if (error)
return;
try {
ob.write(s, off, len); //ob是org.apache.catalina.connector.OutputBuffer类
} catch (IOException e) {
error = true;
}
}org.apache.catalina.connector.OutputBuffer类中的write函数:
public void write(String s, int off, int len)
throws IOException {
if (suspended)
return;
charsWritten += len;
if (s == null)
s = "null";
//这里进行编码转换,conv的声明:protected C2BConverter conv;
//在调试过程中可以看到C2BConverter中的存放的正是utf-8编码。
conv.convert(s, off, len);
conv.flushBuffer();
}至此,我们终于找到了真相。PrintWriter会在底层把字符串的编码转换为对应的CharacterEncoding的编码。
这也就是为什么PrintWriter没有提供wirte系列函数的原因。
BTW:怎样用ServletOutputStream来输出我们想要的编码字符串?
在刚才的代码中,我们可以看到ServletOutputStream的pirnt系列函数实际上什么转换工作都没有做。所以我们可以先把字符串转换成想要的编码,再写到ServletOutputStream中。
如:
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
printStream.write("中文".getBytes("utf-8"));tomcat里一劳永逸解决乱码问题
要想在tomcat中一劳永逸解决乱码问题,可以这样做:
1.设置tomcat,conf/server.xml文件中,useBodyEncodingForURI="true":
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" useBodyEncodingForURI="true"/>public class CodeFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
} <filter>
<filter-name>CodeFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.leg.filter.CodeFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CodeFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>