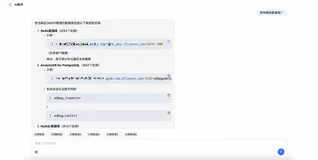
一. MyBatis 框架的搭建
本篇所用sql 表:
drop table if exists userinfo; create table userinfo( id int primary key auto_increment, username varchar(100) not null, password varchar(32) not null, photo varchar(500) default '', createtime timestamp default current_timestamp, updatetime timestamp default current_timestamp, `state` int default 1 ) default charset 'utf8mb4';
添加 MyBatis 框架
设置 MyBatis 配置
(i) 设置数据库的连接信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/blog?characterEncoding=utf8 spring.datasource.name=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
(ii) 设置MyBatis配置信息
# 设置 MyBatis XML 存放路径和命名规则 mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/*Mapper.xml #设置 MyBatis 执行时打印 SQL(可选配置项) mybatis.configuration.log_impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #上述MyBatis 打印设置默认是debug级别,因此需要在demo路径下的日志级别设置为debug,否则上述配置是没用的 logging.level.com.example.demo=debugout.StdOutImpl
二. 根据 MyBatis 完成数据库的操作
1. 定义接口
@Mapper public interface UserMapper { List<Userinfo> getAll(); }
2. 生成数据库表对应的类对象
@Data public class Userinfo { private int id; private String username; private String password; private String photo; private LocalDateTime createtime; private LocalDateTime updatetime; private int state; }
类中的属性和数据库表中的字段名不一致时,那么查询结果为null, 解决方案:
• 将类中的属性和表中的字段名保持一致
• 在 SQL 语句中使用 as 将字段名进行重命名
<!--假设我的数据库中的字段名为username,类中的属性名为name--> select username as name from userinfo where id=#{id}
定义一个 resultMap ,将属性名和字段名进行手动映射。
<!-- type: 要映射的实体类--> <resultMap id="MyMap" type="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> <!-- id标签中写的是主键的字段,column 对应的是数据库中的字段, property 对应的是类中的属性名--> <id column="id" property="id"></id> <!-- result 标签中是普通的字段与属性--> <result column="username" property="name"></result> <result column="password" property="password"></result> </resultMap> <!-- <select id="getUsrByID" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo">--> <select id="getUsrByID" resultMap="com.example.demo.dao.UserMapper.MyMap"> select * from userinfo where id=#{id} </select>
• MyBatis Plus : @TableField("数据库字段名")
3. 使用xml 实现接口
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.example.demo.dao.UserMapper"> <!-- id 为方法名,resultType是返回类型,resultType使用全路径--> <select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo; </select> </mapper>
4. 生成测试类验证
//告诉当前测试程序,目前项目时运行在Spring Boot 容器中的 @SpringBootTest class UserMapperTest { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test void getAll() { List<Userinfo> list=userMapper.getAll(); System.out.println(list); } }
三. 增删查改操作
3.1 查询操作
//参数名以注解中的为准 Userinfo getUsrByID(@Param("id")Integer uid); <select id="getUsrByID" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> <!--select * from userinfo where id=${id}--> select * from userinfo where id=#{id} </select>
3.2 SQL注入
//SQL注入 Userinfo getUser(@Param("username") String name,@Param("password")String password); <select id="getUser" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo where username='${username}' and password='${password}' </select> @Test void getUser() { String username="admin"; String password="'or 1='1"; Userinfo user=userMapper.getUser(username,password); System.out.println(user); } //替换后语句: //select * from userinfo where username='admin' and password=''or 1='1'
#{} 和 ${} 的区别:
• ${} 是直接替换; #{} 是预执行.
• ${} 是不安全的,存在SQL注入;而#{} 是安全的,不存在SQL注入
• 如果是非数值类型,${} 替换需要手动添加 '' ,而#{}不需要
从上述的事例可以看出${}可以实现的功能 #{}都能实现,并且${}还有SQL的问题,那${}存在的意义是什么?
//使用${}排序 List<Userinfo> getByOrder(@Param("myorder")String myorder); <select id="getByOrder" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> <!-- select * from userinfo order by id #{myorder}--> select * from userinfo order by id ${myorder} </select> @Test void getByOrder() { List<Userinfo> list=userMapper.getByOrder("desc"); System.out.println(list); }
• ${} 适用场景: 当业务需要传递 SQL 命令时, 只能使用 ${}, 不能使用 #{}。(例如需要排序时)
• ${} 注意事项:如果要使用${},那么传递的参数一定要能够被穷举,否则是不能使用的。(引起 SQL 注入问题)
3.3 删除操作
//删除操作 int delete(@Param("id")Integer id); <delete id="delete"> delete from userinfo where id=#{id} </delete> //操作不影响数据库 @Transactional @Test void delete() { int row=userMapper.delete(1); System.out.println("受影响的行数: "+row); }
3.4 修改操作
//更行操作 int update(Userinfo userinfo); <update id="update"> update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id} </update> @Test void update() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); userinfo.setId(2); userinfo.setUsername("lisi"); int n=userMapper.update(userinfo); }
3.5 插入操作
//插入操作 int add(Userinfo userinfo); <insert id="add"> insert into userinfo(username,password) values(#{username},#{password}) </insert> @Test void add() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); userinfo.setUsername("王五"); userinfo.setPassword("23456"); int num=userMapper.add(userinfo); System.out.println("受影响的行数: "+num); }
3.6 特殊的添加: 返回自增的 id
默认情况下返回的是受影响的行号,如果想要返回自增id,具体实现如下
//返回自增id int insert (Userinfo userinfo); <insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id"> insert into userinfo(username,password) values(#{username},#{password}) </insert> @Test void insert() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); userinfo.setUsername("zhangsan"); userinfo.setPassword("23456"); int num=userMapper.insert(userinfo); System.out.println("受影响的行数: "+num +" | ID: "+userinfo.getId()); }
• useGeneratedKeys:使MyBatis 使用JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键
• keyColumn:数据库自增主键字段名
• keyProperty:数据库自增的id 在类对象中对应的属性名,会将数据库中的自增主键的值赋值给该属性
3.7 like 查询
List<Userinfo> selectLike(@Param("username")String username); <select id="selectLike" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{username},'%') </select> @Test void selectLike() { String usename="san"; List<Userinfo> userinfo=userMapper.selectLike(usename); System.out.println(userinfo); }
这里不使用${}的原因是因为传入的参数不能穷举。除了使用concat函数,还可以将参数拼接后在进行传入。例如:传入的是"san",可以在业务层先拼接为"%san%",再进行传参。
3.8 多表查询
3.8.1 一对一
@Data public class Articleinfo { int id; String title; String content; LocalDateTime createtime; LocalDateTime updatetime; int uid; int rcount; int state; //用户表关联字段 private String username; }
//使用注解替代xml来实现SQL @Select("select a.*, u.username from articleinfo a left join userinfo u on u.id=a.uid") List<Articleinfo> select(); @Autowired ArticleMapper articleMapper; @Test void select() { List<Articleinfo> list=articleMapper.select(); System.out.println(list); }
3.8.2 一对多
@Select("select * from userinfo where id=#{id}") Userinfo getUserById(@Param("id") Integer id); @Select("select * from Articleinfo where uid=#{uid}") List<Articleinfo> selectByUid(@Param("uid")Integer id); @Test void selectMuch() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ThreadPoolExecutor pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 2, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque(), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); Callable<Userinfo> callable=new Callable<Userinfo>() { @Override public Userinfo call(){ return userMapper.getUserById(4); } }; Callable<List<Articleinfo>> callable1=new Callable<List<Articleinfo>>() { @Override public List<Articleinfo> call() throws Exception { return articleMapper.selectByUid(4); } }; FutureTask<Userinfo> futureTask= (FutureTask<Userinfo>) pool.submit(callable); FutureTask<List<Articleinfo>> futureTask1= (FutureTask<List<Articleinfo>>) pool.submit(callable1); // while (pool.getTaskCount()!= pool.getCompletedTaskCount()); Userinfo userinfo=futureTask.get(); List<Articleinfo> list=futureTask1.get(); userinfo.setList(list); System.out.println(userinfo); }
四. 复杂情况: 动态SQL使用
在某些场景,如再添加用户的时候不确定某些字段是否会传递,为了不使数据库中对应的值为null,就需要用到下面的标签.
4.1 <if> 标签
int add2(Userinfo userinfo); <insert id="add2"> insert into userinfo(username,password <if test="photo!=null"> ,photo </if> )values(#{username},#{password} <if test="photo!=null"> ,#{photo} </if> ) </insert> @Test void add2() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); userinfo.setUsername("张三"); userinfo.setPassword("123"); // userinfo.setPhoto(""); int result=userMapper.add2(userinfo); System.out.println("成功操作: "+result); }
4.2 <trim> 标签
<if>标签,只适用于一个非必填的字段,如果所有要插入的属性都是非必填的属性,就考虑使用<trim>标签结合<if> 标签,对多个字段都采取动态生成的方式.
<trim>标签的属性:
• prefix: 表示整个语句块,以prefix 的值作为前缀
• suffix: 表示整个语句块,以suffix 的值作为后缀
• prefixOverrides: 表示整个语句块要去掉的前缀
• suffixOverrides: 表示整个语句块要去掉的后缀
<insert id="add3"> insert into userinfo <trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="username!=null"> username, </if> <if test="password!=null"> password, </if> <if test="photo!=null"> photo, </if> </trim> values <trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="username!=null"> #{username}, </if> <if test="password!=null"> #{password}, </if> <if test="photo!=null"> #{photo}, </if> </trim> </insert>
4.3 <where> 标签
<where>标签会动态的生成where
List<Userinfo> selectByWhere(Userinfo userinfo); <select id="selectByWhere" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo <where> <if test="id>0"> id=#{id} </if> <if test="username!=null"> and username=#{username} </if> <if test="password!=null"> and password=#{password} </if> <if test="photo!=null"> and photo=#{photo} </if> </where> </select> @Test void selectByWhere() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); // userinfo.setId(2); userinfo.setUsername("lisi"); // userinfo.setPassword("234567"); // userinfo.setPhoto("cat.png"); List<Userinfo> list=userMapper.selectByWhere(userinfo); System.out.println(list); }
4.4 <set> 标签
int updateByID(Userinfo userinfo); <update id="updateByID"> update userinfo <set> <if test="username!=null"> username=#{username}, </if> <if test="password!=null"> password=#{password}, </if> <if test="photo!=null"> photo=#{photo} </if> </set> where id=#{id} </update> @Test void updateByID() { Userinfo userinfo=new Userinfo(); userinfo.setId(12); userinfo.setUsername("张三"); userinfo.setPassword("123"); userinfo.setPhoto("cat.png"); int result=userMapper.updateByID(userinfo); System.out.println("成功操作: "+result); }
4.5 <foreach> 标签
<foreach>标签属性:
• collection: 绑定方法参数中的集合,如List,Set,Map或数组对象(值和传入的参数名相同)
• item: 遍历时的每一个对象
• open: 语句块开头的字符串
• close: 语句块结束的字符串
• separator: 每次遍历之间间隔的字符串
List<Userinfo> selectByIds(List<Integer> IDs); <select id="selectByIds" resultType="com.example.demo.model.Userinfo"> select * from userinfo where id in <foreach collection="IDs" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </select> @Test void selectByIds() { List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>() {{ add(2); add(12); }}; List<Userinfo> list1=userMapper.selectByIds(list); System.out.println(list1); }