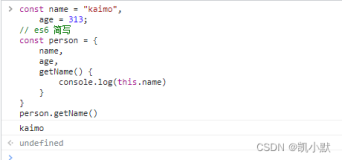
解构
解构是一种从对象和数组中获取值的快速方法。例如,您可以使用一行代码提取值并将它们分配给变量。
以下是如何对对象使用解构的示例:
const person = { name: 'John Doe', age: 32, location: 'San Francisco' }; const { name, age, location } = person; console.log(name, age, location); // John Doe 32 San Francisco
这是一个数组示例:
const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']; const [first, second, third] = colors; console.log(first, second, third); // red green blue
解构使得从对象和数组中提取值并将它们分配给变量变得简单。
块作用域
您可以使用块作用域来声明仅在特定代码块内可用的变量。在 JavaScript 中有两种声明变量的方法:var和let。
var 关键字声明一个全局或函数范围的变量,这意味着它可以从同一函数内的任何地方访问。另一方面,let 关键字声明了一个块作用域的变量,这意味着它只能在同一代码块内访问。
下面是一个基于 let 的块作用域的例子:
if (true) { let message = 'Hello, world!'; console.log(message); // Hello, world! } console.log(message); // Uncaught ReferenceError: message is not defined
消息变量仅在 if 语句定义的代码块中可用。
传播运算符
使用展开运算符可以将数组或对象的值展开到新的数组或对象中。这是组合数组或对象或将类似数组的对象转换为适当数组的快速方法。
下面是如何使用扩展运算符组合两个数组的示例:
const first = [1, 2, 3]; const second = [4, 5, 6]; const combined = [...first, ...second]; console.log(combined); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
下面是一个如何使用扩展运算符将类数组对象转换为实际数组的示例:
const arrayLike = { 0: 'one', 1: 'two', 2: 'three' }; const realArray = [...arrayLike]; console.log(realArray); // ['one', 'two', 'three']
展开运算符是简化和提高代码可读性的强大工具。
模板文字
允许在字符串中嵌入表达式的字符串文字称为模板文字。它们不是引号(' 或 "),而是使用反引号 (`) 字符定义的。
这是一个实际使用的模板文字示例:
const name = 'John Doe'; const age = 32; const message = Hello, my name is ${name} and I am ${age} years old.; console.log(message); // Hello, my name is John Doe and I am 32 years old.
模板字面量使在字符串中嵌入表达式变得简单,并允许您在不使用字符串连接的情况下编写多行字符串。
箭头函数
在 JavaScript 中,箭头函数是编写匿名函数的简写语法。它们使您能够编写更短、更简洁、更易读的代码。
下面是如何使用箭头函数的示例:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const square = number => number * number; const squares = numbers.map(square); console.log(squares); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
箭头函数使编写匿名函数变得简单,并且语法比常规函数更短。