openGauss向量化引擎--hash join
传统的行执行器采用一次一个元组的执行模式,执行过程中CPU大部分时间没有用了处理数据,都用在了遍历执行树等操作,导致CPU的有效利用率较低。面向OLAP场景大量函数调用次数,需要巨大开销,为解决次问题,openGauss中开发了向量化引擎。采用一次一批元组的执行模式,可大幅减少遍历执行节点及调用函数的开销。
本文主要介绍hash join如何进行向量化的。
算子之间数据传递结构
算子之间数据组织及传递结构是VectorBatch:
class VectorBatch : public BaseObject { public: // number of rows in the batch. int m_rows; // number of columns in the batch. int m_cols; // Shall we check the selection vector. bool m_checkSel; // Selection vector; bool* m_sel; // ScalarVector ScalarVector* m_arr; // SysColumns SysColContainer* m_sysColumns; // Compress buffer StringInfo m_pCompressBuf; ... }
主要由3个数组在表示:m_vals为列值数组,m_flag为对应列的行值是否为NULL,m_sel为该行是否满足过滤条件。
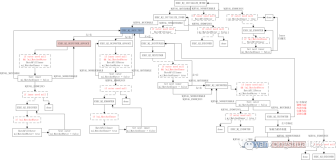
VecHashJoin
向量化hash join的算子是VecHashJoin。其执行函数是ExecVecHashJoin,分为2个阶段:HASH_BUILD和HASH_PROBE。
VectorBatch* ExecVecHashJoin(VecHashJoinState* node) { int64 rows = 0; for (;;) { switch (node->joinState) { case HASH_BUILD: { if (node->hashTbl == NULL) node->hashTbl = New(CurrentMemoryContext) HashJoinTbl(node); ((HashJoinTbl*)(node->hashTbl))->Build();//构建hash表 rows = ((HashJoinTbl*)(node->hashTbl))->getRows(); } break; case HASH_PROBE: { result = ((HashJoinTbl*)(node->hashTbl))->Probe();//进行hash探测并构建join结果 return result; } default: break; } } }
HASH_BUILD
其中build的阶段又分为2个小阶段:1)获取内表的batch,然后通过m_funBuild:申请hashCell *cell_arr连续内存,每个节点是一个hashCell,大小是m_cellSize,共有batch中记录的行数个。然后将其接入m_cache链表。然后将batch中列值依次存入cell_arr中。2)通过PrepareProbe函数构建Hash表,并将cell_arr中值放到hash表中。
void HashJoinTbl::Build() { for (;;) { batch = VectorEngine(inner_node);//获取内表batch if (unlikely(BatchIsNull(batch))) break; RuntimeBinding(m_funBuild, m_strategy)(batch); } PushDownFilterIfNeed(); PrepareProbe(); ... }
第1阶段:
第2阶段:
第2阶段,通过m_keyIdx数组得到哪一列是join key,将cell_arr中该列值拿出来通过m_innerHashFuncs函数计算hash值,将其保存到m_cacheLoc[]数组中,作为m_data数组下标,通过这种方式将内表列值放到hash表中。
HASH_PROBE
通过probeHashTable进行探测,并join。也分为2个小阶段:1)外表hash阶段:首先获取外表的batch,通过m_outerHashFuncshash函数将外表的join key列hash出的值放到m_cacheLoc数组中,作为hash表数组的下标:m_hashTbl->m_data[m_cacheLoc[i]]。2)join阶段:定位到的m_hashTbl->m_data[m_cacheLoc[i]]中列值和外表中列值是否相同,若相等则通过m_keyMatch[]数组标记。最后将m_keyMatch[]数组标记为1的列值构建成向量batch,并返回。
VectorBatch* HashJoinTbl::probeHashTable(hashSource* probSource) { VectorBatch* res_batch = NULL; while (true) { switch (m_probeStatus) { case PROBE_FETCH: //获取外表batch m_outRawBatch = probSource->getBatch(); if (BatchIsNull(m_outRawBatch)) { } else { int row = m_outRawBatch->m_rows; int mask = m_hashTbl->m_size - 1; hashBatch(m_outRawBatch, m_outKeyIdx, m_cacheLoc, m_outerHashFuncs); for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { m_cacheLoc[i] = m_outRawBatch->m_arr[icol].m_vals[i] & mask; m_cellCache[i] = m_hashTbl->m_data[m_cacheLoc[i]]; m_match[i] = false; /* flag all the row no match */ m_keyMatch[i] = true; } ... } break; case PROBE_DATA: res_batch = (this->*m_joinFun)(m_outRawBatch); if (!BatchIsNull(res_batch)) return res_batch; break; case PROBE_FINAL: return endJoin(); default: break; } } } // VectorBatch* HashJoinTbl::innerJoinT(VectorBatch* batch)//外部batch { while (m_doProbeData) { last_build_idx = 0; RuntimeBinding(m_matchKeyFunction, i)(&batch->m_arr[m_outKeyIdx[i]], row, m_keyIdx[i], i); for (row_idx = last_build_idx; row_idx < row; row_idx++) { if (m_keyMatch[row_idx]) { val = m_cellCache[row_idx]->m_val; for (i = 0; i < m_innerBatch->m_cols; i++) { p_vector = &m_innerBatch->m_arr[i]; p_vector->m_vals[result_row] = val[i].val; p_vector->m_flag[result_row] = val[i].flag; } for (i = 0; i < m_outerBatch->m_cols; i++) { p_vector = &m_outerBatch->m_arr[i]; p_vector->m_vals[result_row] = batch->m_arr[i].m_vals[row_idx]; p_vector->m_flag[result_row] = batch->m_arr[i].m_flag[row_idx]; } result_row++; } } } return buildResult(m_innerBatch, m_outerBatch, true); }