The code in Data book (5th Edition) from the 83 page to 86 page
Update completed
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct linknode {
ElemType data;//Data domain
struct linknode *next;//Pointer domain
} LinkStNode;
//Initialize the stack
void InitStack(LinkStNode *&s) {
s=(LinkStNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
s->next=NULL;
}
//Create linked stack
void CreateLinkStack(LinkStackNode *&L, ElemType a[], int n) {
LinkStackNode *s, *r;
L = (LinkStackNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStackNode)); //Create head node
r = L; //r point to tail node
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //Loop create data node
s = (LinkStackNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStackNode));
s->data = a[i]; //Create node s
r->next = s; //Insert node s to end of node r
r = s;
}
r->next = NULL; //Set tail node is NULL
}
//Destroy linked stack
void DestroyStack(LinkStNode *&s) {
LinkStNode *p=s, *q=s->next;
while (q!=NULL) {
free(p);
p=q;
q=p->next;
}
free(p); //Free up its space
}
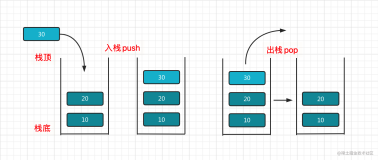
//Into stack
void Push(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType e) {
LinkStNode *p;
p=(LinkStNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
p->data=e; //Create node p of elements e
p->next=s->next;
s->next=p;
}
//Out stack
bool Pop(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType &e) {
LinkStNode *p;
if (s->next==NULL) //When stack is NULL
return false;
p=s->next; //p point to start node
e=p->data;
s->next=p->next;
free(p); //Release p
return true;
}
//Top element of the stack
bool GetTop(LinkStNode *s,ElemType &e) {
if (s->next==NULL) //When stack is NULL
return false;
e=s->next->data;
return true;
}
//Output linked stack
void ShowLinkStack(LinkStackNode* L) {
LinkStackNode* p = L->next; //p point to head node
while (p != NULL) { //When p no NULL, output data of node p
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next; //Move p to next node
}
printf("\n");
}
如有侵权,请联系作者删除