作者:Melisha Dsouza
文章来源:微信公众号 数据派THU
翻译:吴金笛
校对:国相洁
本文约3000字,建议阅读10+分钟。
本文是创建聊天机器人实现网络运营的简单教程。
在本教程中,我们将了解如何利用聊天机器人来协助网络运营。随着我们向智能化运营迈进,另一个需要关注的领域是移动性。用一个脚本来进行配置,修复甚至故障检修是很好的,但它仍然需要有人在场来监督,启动甚至执行这些程序或脚本。
Nokia’s MIKA 是一个很好的聊天机器人例子,操作人员可以用它来进行网络故障排除和修复。根据 Nokia’s blog,MIKA会根据此单个网络的实际情况给出一个警报优先级信息,并将当前的情况与该网络和其他网络过去事件的整个服务历史进行比较,以确定当前问题的最佳解决方案。
Nokia’s MIKA
https://networks.nokia.com/services/digital-assistant-as-a-service
Nokia’s blog
让我们创建一个聊天机器人来协助网络运营。对于这个用例,我们将使用一个被广泛使用的聊天应用程序Slack。参考Splunk的智能数据分析能力,我们将看到一些用户与聊天机器人的互动,从而对环境有一些了解。
本教程摘自AbhishekRatan撰写的名为《Practical Network Automation – SecondEdition》的书。 这本书将向您介绍网络自动化的基本概念,并帮助您提高你的数据中心的稳健性和安全性。
可以在GitHub中找到本教程的代码:
Github链接:
https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Practical-Network-Automation-Second-Edition/tree/master/Chapter0
在我们部署web框架时,我们将利用相同的框架与Slack聊天机器人进行交互,后者又将与Splunk进行交互。它还可以直接与网络设备交互,所以我们可以发起一些复杂的聊天,例如在需要时从Slack重启路由器。这最终为工程师提供了移动性,工程师可以在任何地方(甚至是手机)处理任务,而不必被固定在某个地点或办公室。
要创建聊天机器人,以下是基本步骤:
- 在Slack上创建一个工作区(或帐户):
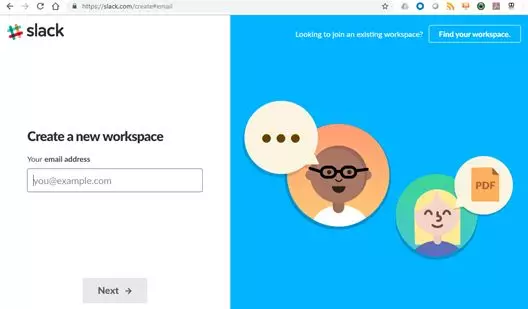
- 在你的工作区创建一个应用程序(在我们的例子中,我们创建了一个叫做mybot的应用程序):
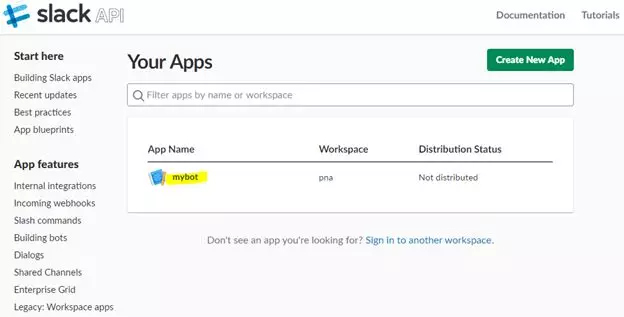
- 以下是关于该应用程序的基本信息(App ID 和Client ID可以与唯一标识此应用程序的其他信息一起使用):
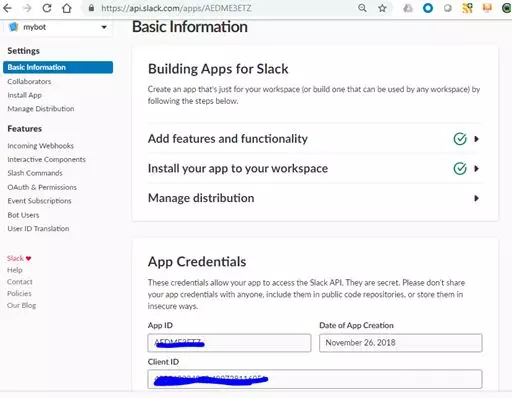
- 为此应用程序添加bot功能:
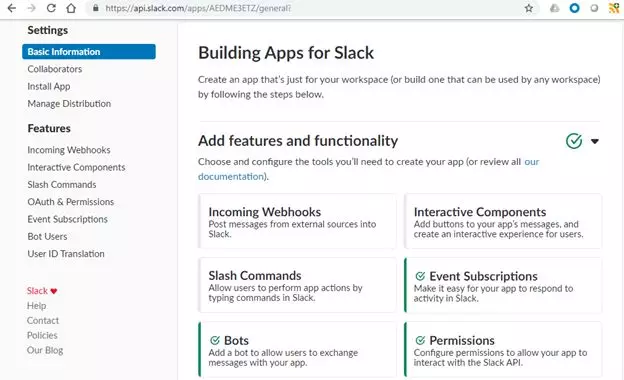
- 添加事件订阅并映射到将要发布消息的外部API。
事件订阅是指某人在聊天中键入对聊天机器人的引用,然后使用该聊天机器人与聊天中被输入的数据调用这个API:
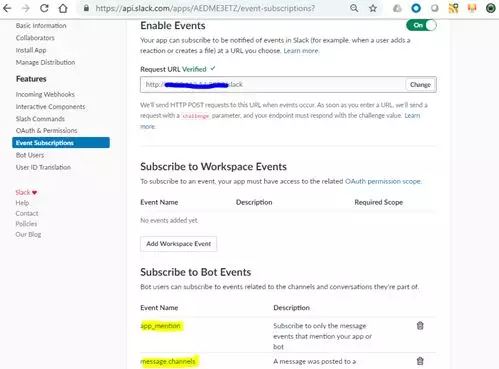
这里,一个关键的步骤是,一旦我们输入了接受聊天消息的URL,就需要从Slack验证这个特定的URL。验证就是API端点以字符串或JSON的格式返回,与从Slack发送的响应相同的响应。如果我们收到相同的响应,Slack确认该端点是可信的并将其标记为已验证。这是一个一次性的过程,并且API URL中的任何更改都将导致此步骤的重复。
以下是Ops API框架中响应特定查询的Python代码:
1. import falcon
2. import json
3. def on_get(self,req,resp):
4. # Handles GET request
5. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200 # Default status
6. resp.body=json.dumps({"Server is Up!"})
7. def on_post(self,req,resp):
8. # Handles POST Request
9. print("In post")
10. data=req.bounded_stream.read()
11. try:
12. # Authenticating end point to Slack
13. data=json.loads(data)["challenge"]
14. # Default status
15. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200
16. # Send challenge string back as response
17. resp.body=data
18. except:
19. # URL already verified
20. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200
21. resp.body=""
这将验证,如果从Slack发出一个”challenge”,它将返回相同的”challenge”,这个值确认该端点是Slack频道发送聊天数据的正确端点。
- 安装此应用程序(或聊天机器人)到任何频道(这类似于在群聊中添加用户):
响应特定聊天信息的核心API框架代码执行以下操作:
- 确认任何发送到Slack的信息在三秒内响应200次。如果没有这样,Slack报告:endpoint not reachable.
- 确保任何从聊天机器人(不是来自任何真实用户)发出的信息不作为回复信息再次被发回。这可能会造成循环,因为从聊天机器人发送的消息将被视为Slack聊天中的新消息,然后它将被再次发送到URL。这最终会使聊天无法使用,从而导致聊天中出现重复的消息。
- 使用将被发送回Slack的令牌对响应进行身份验证,以确保来自Slack的响应来自经过身份验证的源。
代码如下:
1. import falcon
2. import json
3. import requests
4. import base64
5. from splunkquery import run
6. from splunk_alexa import alexa
7. from channel import channel_connect,set_data
8. class Bot_BECJ82A3V():
9. def on_get(self,req,resp):
10. # Handles GET request
11. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200 # Default status
12. resp.body=json.dumps({"Server is Up!"})
13. def on_post(self,req,resp):
14. # Handles POST Request
15. print("In post")
16. data=req.bounded_stream.read()
17. try:
18. bot_id=json.loads(data)["event"]["bot_id"]
19. if bot_id=="BECJ82A3V":
20. print("Ignore message from same bot")
21. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200
22. resp.body=""
23. return
24. except:
25. print("Life goes on. . .")
26. try:
27. # Authenticating end point to Slack
28. data=json.loads(data)["challenge"]
29. # Default status
30. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200
31. # Send challenge string back as response
32. resp.body=data
33. except:
34. # URL already verified
35. resp.status=falcon.HTTP_200
36. resp.body=""
37. print(data)
38. data=json.loads(data)
39. #Get the channel and data information
40. channel=data["event"]["channel"]
41. text=data["event"]["text"]
42. # Authenticate Agent to access Slack endpoint
43. token="xoxp-xxxxxx"
44. # Set parameters
45. print(type(data))
46. print(text)
47. set_data(channel,token,resp)
48. # Process request and connect to slack channel
49. channel_connect(text)
50. return
51.# falcon.API instance , callable from gunicorn
52.app= falcon.API()
53.# instantiate helloWorld class
54.Bot3V=Bot_BECJ82A3V()
55.# map URL to helloWorld class
56.app.add_route("/slack",Bot3V) - 执行频道交互响应
此代码解释聊天频道中使用chat-bot执行的特定聊天。此外,这将使用对特定用户或频道ID的响应,以及对Slack API 的身份验证令牌进行响应。
Slack API:
这保证Slack聊天的消息或回复显示在其起源的特定频道上。作为示例,我们将使用聊天对特定值进行加密或解密。
例如,如果我们写入encrypt username[:]password,它将返回一个利用base64值加密的字符串。
类似地,如果我们写入decrypt, 聊天机器人会返回一个加密字符串解密后的字符串。
代码如下:
1. import json
2. import requests
3. import base64
4. from splunk_alexa import alexa
5. channl=""
6. token=""
7. resp=""
8. def set_data(Channel,Token,Response):
9. global channl,token,resp
10. channl=Channel
11. token=Token
12. resp=Response
13.def send_data(text):
14.global channl,token,res
15.print(channl)
16.resp = requests.post("https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage",data='{"channel":"'+channl+'","text":"'+text+'"}',headers={"Content-type": "application/json","Authorization": "Bearer "+token},verify=False)
17.
18.def channel_connect(text):
19.global channl,token,resp
20.try:
21.print(text)
22.arg=text.split(' ')
23.print(str(arg))
24.path=arg[0].lower()
25.print(path in ["decode","encode"])
26.if path in ["decode","encode"]:
27.print("deecode api")
28.else:
29.result=alexa(arg,resp)
30.text=""
31.try:
32.for i in result:
33.print(i)
34.print(str(i.values()))
35.for j in i.values():
36.print(j)
37.text=text+' '+j
38.#print(j)
39.if text=="" or text==None:
40.text="None"
41.send_data(text)
42.return
43.except:
44.text="None"
45.send_data(text)
46.return
47.decode=arg[1]
48.except:
49.print("Please enter a string to decode")
50.text=" argument cannot be empty"
51.send_data(text)
52.return
53.deencode(arg,text)
54.
55.def deencode(arg,text):
56.global channl,token,resp
57.decode=arg[1]
58.if arg[1]=='--help':
59.#print("Sinput")
60.text="encode/decode "
61.send_data(text)
62.return
63.if arg[0].lower()=="encode":
64.encoded=base64.b64encode(str.encode(decode))
65.if '[:]' in decode:
66.text="Encoded string: "+encoded.decode('utf-8')
67.send_data(text)
68.return
69.else:
70.text="sample string format username[:]password"
71.send_data(text)
72.return
73.try:
74.creds=base64.b64decode(decode)
75.creds=creds.decode("utf-8")
76.except:
77.print("problem while decoding String")
78.text="Error decoding the string. Check your encoded string."
79.send_data(text)
80.return
81.if '[:]' in str(creds):
82.print("[:] substring exists in the decoded base64 credentials")
83.# split based on the first match of "[:]"
84.credentials = str(creds).split('[:]',1)
85.username = str(credentials[0])
86.password = str(credentials[1])
87.status = 'success'
88.else:
89.text="encoded string is not in standard format, use username[:]password"
90.send_data(text)
91.print("the encoded base64 is not in standard format username[:]password")
92.username = "Invalid"
93.password = "Invalid"
94.status = 'failed'
95.temp_dict = {}
96.temp_dict['output'] = {'username':username,'password':password}
97.temp_dict['status'] = status
98.temp_dict['identifier'] = ""
99.temp_dict['type'] = ""
100.#result.append(temp_dict)
101.print(temp_dict)
102.text=" "+username+" "+password
103.send_data(text)
104.print(resp.text)
105.print(resp.status_code)
106.return
此代码查询Splunk实例以查找与聊天机器人的特定聊天。聊天会请求当前关闭的任何一个管理接口(Loopback45)。 此外,在聊天中,用户可以查询所有具有up管理接口的路由器。 此英语响应将被转换为Splunk查询,并根据Splunk的响应将状态返回到Slack聊天。
让我们看看对Slack聊天执行操作来响应结果的代码:
1. from splunkquery import run
2. def alexa(data,resp):
3. try:
4. string=data.split(' ')
5. except:
6. string=data
7. search=' '.join(string[0:-1])
8. param=string[-1]
9. print("param"+param)
10. match_dict={0:"routers management interface",1:"routers management loopback"}
11. for no in range(2):
12. print(match_dict[no].split(' '))
13. print(search.split(' '))
14. test=list(map(lambda x:x in search.split(' '),match_dict[no].split(' ')))
15. print(test)
16. print(no)
17. if False in test:
18. pass
19. else:
20. if no in [0,1]:
21. if param.lower()=="up":
22. query="search%20index%3D%22main%22%20earliest%3D0%20%7C%20dedup%20interface_name%2Crouter_name%20%7C%20where%20interface_name%3D%22Loopback45%22%20%20and%20interface_status%3D%22up%22%20%7C%20table%20router_name"
23. elif param.lower()=="down":
24. query="search%20index%3D%22main%22%20earliest%3D0%20%7C%20dedup%20interface_name%2Crouter_name%20%7C%20where%20interface_name%3D%22Loopback45%22%20%20and%20interface_status%21%3D%22up%22%20%7C%20table%20router_name"
25. else:
26. return "None"
27. result=run(query,resp)
28. return result 下面的Splunk查询来获取状态:
- 对于UP接口——“查询”如下:
index="main"earliest=0 | dedup interface_name,router_name | whereinterface_name="Loopback45" and interface_status="up" |table router_name- 对于DOWN接口(除此以外的任何状态)——“查询”如下:
index="main"earliest=0 | dedup interface_name,router_name | whereinterface_name="Loopback45" and interface_status!="up" |table router_name
让我们看看与聊天机器人聊天的最后结果以及根据聊天记录发回的响应。
编码/解码示例如下:
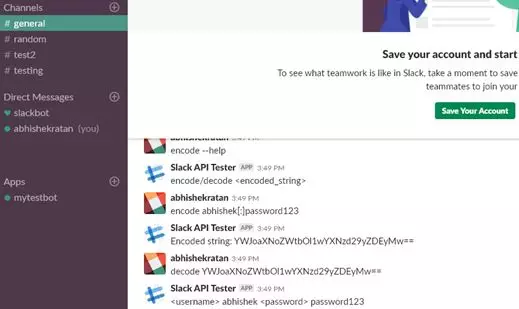
正如我们所见,我们发送了一个带有encode abhishek[:]password123 信息的聊天。此聊天作为POST请求发送到API,后者又将其加密到base64并添加到Encoded string: 之后被返回。在下一个聊天中,我们使用decode选项传入相同的字符串。这将通过解码来自API函数的信息进行响应,并且用用户名abhishek和密码password123来响应Slack聊天。
让我们看一看Splunk查询聊天的示例:
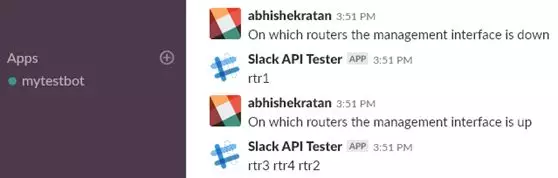
在此查询中,我们关闭了rtr1上的Loopback45接口。通过Python脚本,在我们对这些接口预定的发现过程中,数据位于Splunk中。当查询到哪个管理接口(Loopback45)关闭时,它将用rtr1响应。Slack聊天将“On which routers the management interface is down”传递给API,在收到有效载荷时,后者将运行Splunk查询以获取统计信息。返回值(在本例中为rtr1)将作为聊天中的响应信息被返回。
类似地,“On which routers the management interface is down”的反向查询将查询Splunk并最终共享rtr2, rtr3, 和rtr4的响应(因为所有这些路由器上的接口都是UP)。
此聊天用例可以被扩展,以确保使用简单聊天来进行完整的端到端故障排除。使用各种后端功能可以构建从问题的基本识别到复杂任务的大量案例,例如基于已识别情况的修复。
总结
在本教程中,我们实现了一些真实的用例,并研究了使用chatbot执行故障排除的技术。这些用例使我们深入了解了执行智能修复以及进行大规模审查,这是当前环境中的关键挑战。
要学习如何利用Python的强大功能,毫无困难地自动化你的网络,请查看我们的书:《Practical Network Automation – Second Edition》。
原文标题:
Creating a chatbot to assist in network operations [Tutorial]
原文链接:
https://hub.packtpub.com/creating-a-chatbot-to-assist-in-network-operations-tutorial/
译者简介

吴金笛,雪城大学计算机科学硕士一年级在读。迎难而上是我最舒服的状态,动心忍性,曾益我所不能。我的目标是做个早睡早起的Cool Girl。
翻译组招募信息
工作内容:需要一颗细致的心,将选取好的外文文章翻译成流畅的中文。如果你是数据科学/统计学/计算机类的留学生,或在海外从事相关工作,或对自己外语水平有信心的朋友欢迎加入翻译小组。
你能得到:定期的翻译培训提高志愿者的翻译水平,提高对于数据科学前沿的认知,海外的朋友可以和国内技术应用发展保持联系,THU数据派产学研的背景为志愿者带来好的发展机遇。
其他福利:来自于名企的数据科学工作者,北大清华以及海外等名校学生他们都将成为你在翻译小组的伙伴。



